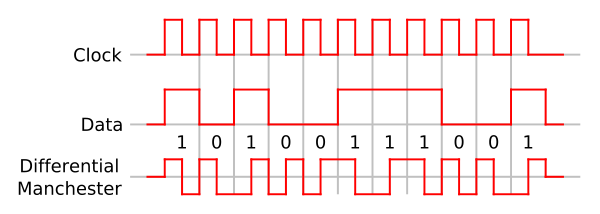
- Differential Manchester encoding
-
Differential Manchester encoding, also called biphase mark code (BMC) or FM1, is a line code in which data and clock signals are combined to form a single 2-level self-synchronizing data stream. It is a differential encoding, using the presence or absence of transitions to indicate logical value. It has the following advantages over some other line codes:
- A transition is guaranteed at least once every bit, allowing the receiving device to perform clock recovery.
- Detecting transitions is often less error-prone than comparing against a threshold in a noisy environment.
- Unlike with Manchester encoding, only the presence of a transition is important, not the polarity. Differential coding schemes will work exactly the same if the signal is inverted (wires swapped). (Other line codes with this property include NRZI, bipolar encoding, coded mark inversion, and MLT-3 encoding).
- If the high and low signal levels have the same voltage with opposite polarity, coded signals have zero average DC voltage, thus reducing the necessary transmitting power and minimizing the amount of electromagnetic noise produced by the transmission line.
The symbol rate is twice the bitrate of the original signal. Each bit period is divided into two half-periods: clock and data. The clock half-period always begins with a transition from low to high or from high to low. The data half-period makes a transition for one value and no transition for the other value. One version of the code makes a transition for 0 and no transition for 1 in the data half-period; the other makes a transition for 1 and no transition for 0. Thus, if a "1" is represented by one transition, then a "0" is represented by two transitions and vice versa, making Differential Manchester a form of frequency shift keying. Either code can be interpreted with the clock half-period either before or after the data half-period.
Differential Manchester is self-synchronizing since there is a change in the signal at least every two bits. It is not necessary to know the polarity of the sent signal since the information is not kept in the actual values of the voltage but in their change: in other words it does not matter whether a logical 1 or 0 is received, but only whether the polarity is the same or is different from the previous value; this makes synchronization even easier. Finally, if the high and low states have the same voltage with opposite polarity, coded signals have zero average DC voltage, thus reducing the necessary transmitting power and minimizing the amount of electromagnetic noise produced by the transmission line. All these positive aspects are achieved at the expense of doubling clock frequency.
Differential Manchester is specified in the IEEE 802.5 standard for token ring LANs, and is used for many other applications, including magnetic and optical storage. BMC is used as the encoding method in AES3 and S/PDIF. Many magnetic stripe cards also use BMC encoding, often called F2F (frequency/double frequency) or Aiken Biphase. That standard is described in ISO/IEC 7811. SMPTE time code also uses BMC. BMC is also the original "frequency modulation" used on single-density floppy disks, before being replaced by "double-density" modified frequency modulation.
References
 This article incorporates public domain material from the General Services Administration document "Federal Standard 1037C".
This article incorporates public domain material from the General Services Administration document "Federal Standard 1037C".- Watkinson, J. (1994) The Art of Digital Audio, 2nd edition. Oxford: Focal Press. ISBN 0-240-51320-7
- Introduction to magnetic stripe technology
See also
- Biphase space encoding (FM0 encoding)
- Manchester code
- McASP
Line coding (digital baseband transmission) Main articles 
Basic line codes Return to zero (RZ) · Non-return-to-zero, level (NRZ/NRZ-L) · Non-return-to-zero, inverted (NRZ-I) · Non-Return-to-Zero, space (NRZ-S) · Manchester · Differential Manchester/Biphase (Bi-φ)Extended line codes Optical line codes Carrier-Suppressed Return-to-Zero · Alternate-Phase Return-to-ZeroSee also: Baseband · Baud · Bit rate · Digital signal · Digital transmission · Ethernet physical layer · Pulse modulation methods · Pulse-amplitude modulation (PAM) · Pulse code modulation (PCM) · Serial communication · Category:Line codesCategories:- Line codes
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.