- Loom
-
 An early nineteenth century Japanese loom with several heddles, which the weaver controls with her foot
An early nineteenth century Japanese loom with several heddles, which the weaver controls with her foot
A loom is a device used to weave cloth. The basic purpose of any loom is to hold the warp threads under tension to facilitate the interweaving of the weft threads. The precise shape of the loom and its mechanics may vary, but the basic function is the same.
Contents
Etymology
The word "loom" comes from the Old English "geloma" formed from ge-(perfective prefix) and loma, a root of unknown origin; this meant utensil or tool of any kind. In 1404 it was used to mean a machine to enable weaving thread into cloth. [1] By 1838 it had gained the meaning of a machine for interlacing thread as in weaving, knitting or lacemaking. [2]
Weaving
Weaving is done by intersecting the longitudinal threads, the warp, i.e. "that which is thrown across", with the transverse threads, the weft, i.e. "that which is woven".
The major components of the loom are the warp beam, heddles, harnesses, shuttle, reed and takeup roll. In the loom, yarn processing includes shedding, picking, battening and taking-up operations.
- Shedding. Shedding is the raising of part of the warp yarn to form a shed (the vertical space between the raised and unraised warp yarns), through which the filling yarn, carried by the shuttle, can be inserted. On the modern loom, simple and intricate shedding operations are performed automatically by the heddle or heald frame, also known as a harness. This is a rectangular frame to which a series of wires, called heddles or healds, are attached. The yarns are passed through the eye holes of the heddles, which hang vertically from the harnesses. The weave pattern determines which harness controls which warp yarns, and the number of harnesses used depends on the complexity of the weave. Two common methods of controlling the heddles are dobbies and a Jacquard Head.
- Picking. As the harnesses raise the heddles or healds, which raise the warp yarns, the shed is created. The filling yarn in inserted through the shed by a small carrier device called a shuttle. The shuttle is normally pointed at each end to allow passage through the shed. In a traditional shuttle loom, the filling yarn is wound onto a quill, which in turn is mounted in the shuttle. The filling yarn emerges through a hole in the shuttle as it moves across the loom. A single crossing of the shuttle from one side of the loom to the other is known as a pick. As the shuttle moves back and forth across the shed, it weaves an edge, or selvage, on each side of the fabric to prevent the fabric from raveling.
- Battening. As the shuttle moves across the loom laying down the fill yarn, it also passes through openings in another frame called a reed (which resembles a comb). With each picking operation, the reed presses or battens each filling yarn against the portion of the fabric that has already been formed. The point where the fabric is formed is called the fell. Conventional shuttle looms can operate at speeds of about 150 to 160 picks per minute.[3]
With each weaving operation, the newly constructed fabric must be wound on a cloth beam. This process is called taking up. At the same time, the warp yarns must be let off or released from the warp beams. To become fully automatic, a loom needs a filling stop motion which will brake the loom, if the weft thread breaks.[3] An automatic loom requires 0.125 hp to 0.5 hp to operate.
Types of looms
Back strap loom
A simple loom which has its roots in ancient civilizations comprising two sticks or bars between which the warps are stretched. One bar is attached to a fixed object and the other to the weaver usually by means of a strap around the back. On traditional looms, the two main sheds are operated by means of a shed roll over which one set of warps pass, and continuous string heddles which encase each of the warps in the other set. The weaver leans back and uses her body weight to tension the loom. To open the shed controlled by the string heddles, the weaver relaxes tension on the warps and raises the heddles. The other shed is usually opened by simply drawing the shed roll toward the weaver. Both simple and complex textiles can be woven on this loom. Width is limited to how far the weaver can reach from side to side to pass the shuttle. Warp faced textiles, often decorated with intricate pick-up patterns woven in complementary and supplementary warp techniques are woven by indigenous peoples today around the world. They produce such things as belts, ponchos, bags, hatbands and carrying cloths. Supplementary weft patterning and brocading is practiced in many regions. Balanced weaves are also possible on the backstrap loom. Today, commercially produced backstrap loom kits often include a rigid heddle.
Warp weighted loom
Main article: Warp-weighted loomThe warp-weighted loom is a vertical loom that may have originated in the Neolithic period. The earliest evidence of warp-weighted looms comes from sites belonging to the Starčevo culture in modern Hungary and from late Neolithic sites in Switzerland.[4] This loom was used in Ancient Greece, and spread north and west throughout Europe thereafter.[5] Its defining characteristic is hanging weights (loom weights) which keep bundles of the warp threads taut. Frequently, extra warp thread is wound around the weights. When a weaver has reached the bottom of the available warp, the completed section can be rolled around the top beam, and additional lengths of warp threads can be unwound from the weights to continue. This frees the weaver from vertical size constraints.
Drawloom
A drawloom is a hand-loom for weaving figured cloth. In a drawloom, a "figure harness" is used to control each warp thread separately.[6] A drawloom requires two operators, the weaver and an assistant called a "drawboy" to manage the figure harness.
Handloom
Elements of a foot-treadle floor loom 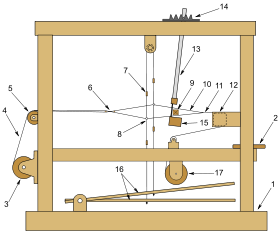
A handloom is a simple machine used for weaving in which no power is used. In a wooden vertical-shaft looms the heddles were fixed in place in the shaft. The warp threads pass alternately through a heddle and through a space between the heddles (the shed), so that raising the shaft raises half the threads (those passing through the heddles), and lowering the shaft lowers the same threads—the threads passing through the spaces between the heddles remain in place.
Flying Shuttle
Hand weavers could only weave a cloth as wide as their armspan. If cloth needed to be wider, two people would do the task (often this would be an adult with a child). John Kay(1704–1779) patented the Flying Shuttle in 1733. The weaver held a picking stick that was attached by cords to a device at both ends of the shed. With a flick of the wrist, one cord was pulled and the shuttle was propelled through the shed to the other end with considerable force, speed and efficiency. A flick in the opposite direction and the shuttle was propelled back. A single weaver had control of this motion but the flying shuttle could weave much wider fabric than an arms length at much greater speeds than had been achieved with the hand thrown shuttle. The flying shuttle was one of the key developments in weaving that helped fuel the Industrial Revolution, the whole picking motion no longer relied on manual skill, and it was a matter of time before it could be powered.
Haute-lisse and basse-lisse looms
Looms used for weaving traditional tapestry are classified as haute-lisse looms, where the warp is suspended vertically between two rolls, and the basse-lisse looms, where the warp extends horizontally between the rolls.
Power looms
Edmund Cartwright built and patented a power loom in 1785, and it was this that was adopted by the nascent cotton industry in England. The silk loom made by Jacques Vaucanson in 1745 operated on the same principles but wasn't developed further. The invention of the flying shuttle by John Kay was critical to the development of a commercially successful power loom.[7] Cartwright's loom was impractical but the ideas were developed by numerous inventors in the Manchester area in England, where by 1818 there were 32 factories containing 5732 looms.[8]
Horrocks loom was viable but it was the Roberts Loom in 1830[9] that marked the turning point. Before this time hand looms had outnumbered power looms. Incremental changes to the three motions continued to be made. The problems of sizing, stop-motions, consistent take-up and a temple to maintain the width remained. In 1841, Kenworthy and Bullough produced the Lancashire Loom[10] which was self-acting or semi-automatic. This enables a 15-year-old spinner to run six looms at the same time. Incrementally, the Dickinson Loom, and then the Keighley born inventor Northrop working for the Draper Corporation in Hopedale produced the fully automatic Northrop Loom which recharged the shuttle when the pirn was empty. The Draper E and X model became the leading products from 1909 until they were challenged by the different characteristics of synthetic fibres such as rayon.[11]
From 1942 the faster and more efficient shuttleless Sulzer looms and the rapier looms were introduced.[12] Modern industrial looms can weave at 2000 weft insertions per minute.[13] Today, advances in technology have produced a variety of looms designed to maximize production for specific types of material. The most common of these are air-jet looms (e.g. “JAT710”[14]) and water-jet looms.
Gallery
-
Hand loom at Hjerl Hede, Denmark, showing grayish warp threads (back) and cloth woven with red filling yarn (front)
-
A foot-treadle operated Hattersley & Sons, Domestic Loom, built under license in 1893, in Keighley, Yorkshire.
-
A Picanol rapier loom
Patents
- U.S. Patent 0,000,169 – Loom
See also
- Fashion and Textile Museum
- Shuttle (weaving)
- Textile manufacturing
- Timeline of clothing and textiles technology
- Weaving (mythology)
References
- ^ Etymology Online
- ^ Websters 1913 p=868
- ^ a b Collier 1970, p. 104
- ^ Barber & 1991 pp.93–96
- ^ Crowfoot 1936, p. 36
- ^ Burnham 1980, p. 48
- ^ Marsden 1892, p. 57
- ^ Guest, Richard (1823). "The Compendious History of Cotton-Manufacture". pp. 46. http://www.spinningtheweb.org.uk/a_results.php?x=7&y=2&QueryName=KeyWord&KeyWords=Compendious+History. Retrieved Feb 2009.
- ^ Marsden 1892, p. 76
- ^ Marsden 1892, p. 94
- ^ Mass 1990
- ^ Collier 1970, p. 111
- ^ S. Rajagopalan, S.S.M. College of Engineering, Komarapalayam, Pdexcil.org
- ^ "Versatile expansion JAT710 air-jet Loom". The Textile Icon News. 05 August 2011. http://www.thetextileicon.com/blog/2011/09/versatile-expansion-by-toyota-jat710-air-jet-loom. Retrieved 2011-27-09.
Bibliography
- Barber, E. J. W. (1991). Prehistoric Textiles. Princeton University Press. ISBN 069100224x.
- Burnham, Dorothy K. (1980). Warp and Weft: A Textile Terminology. Royal Ontario Museum. ISBN 0888542569.
- Collier, Ann M (1970). A Handbook of Textiles. Pergamon Press. pp. 258. ISBN 0 08 018057 4, 0 08 018056 6.
- Crowfoot, Grace (1936/1937). "Of the Warp-Weighted Loom". The Annual of the British School at Athens 37: 36–47.
- Marsden, Richard (1895). Cotton Weaving: Its Development, Principles, and Practice. George Bell & Sons. pp. 584. http://www.cs.arizona.edu/patterns/weaving/books.html. Retrieved Feb 2009.
- Mass, William (1990). "The Decline of a Technology Leader:Capabilty, strategy and shuttleless Weaving". Business and Economic History. ISSN 089-6825. http://www.h-net.org/~business/bhcweb/publications/BEHprint/v019/p0234-p0244.pdf.
External links
- Loom demonstration video
- "Caring for your loom" article
- "The Art and History of Weaving"
- The Medieval Technology Pages: "The Horizontal Loom"
Weaving Weaves Basketweave · Charvet · Coverlet · Double weave · Even-weave · Lampas · Oxford · Pile weave · Piqué · Plain weave · Satin weave · Twill · Gabardine
Components Tools and techniques Chilkat weaving · Fingerweaving · Flying shuttle · Heddle · Ikat · Inkle weaving · Jacquard weaving · Kasuri · Loom · Navajo weaving · Salish weaving · Shed · Shuttle · Tablet weaving · Tāniko · Tapestry · TempleTypes of looms Dobby loom · Jacquard loom · Hattersley loom · Lancashire loom · Northrop loom · Power loom · Roberts Loom · Warp weighted loomWeavers Acesas · Ada Dietz · Micheline Beauchemin · Thomas Ferguson & Co Ltd · Pamphile · John Rylands · Brigitta Scherzenfeldt · Clara Sherman · Gunta Stölzl · Judocus de VosCategories:- Machines
- Weaving
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.








