- Nepenthes ephippiata
-
Nepenthes ephippiata 
Nepenthes ephippiata. Cultivated plant. Conservation status Scientific classification Kingdom: Plantae (unranked): Angiosperms (unranked): Eudicots (unranked): Core eudicots Order: Caryophyllales Family: Nepenthaceae Genus: Nepenthes Species: N. ephippiata Binomial name Nepenthes ephippiata
Danser (1928)[1]
Distribution of N. ephippiata. Nepenthes ephippiata (pronounced /nɨˈpɛnθiːz ɛˌfɪpiˈɑːtə/, from Latin: ephippium "saddle cloth"), or the Saddle-Leaved Pitcher-Plant,[2] is a tropical pitcher plant endemic to Borneo. It occurs in the Hose Mountains of central Sarawak, as well as Mount Raya and Bukit Lesung in Kalimantan.[3] Plants from the Hose Mountains appear to lack the decurrent leaf attachment found in specimens from Central Kalimantan.[4] Nepenthes ephippiata is closely related to N. lowii.
B. H. Danser described the species in his 1928 monograph, "The Nepenthaceae of the Netherlands Indies", based only on part of a stem and an infructescence.[1]
Nepenthes ephippiata has no known natural hybrids.[5][6]
References
- ^ a b Danser, B.H. 1928. 12. Nepenthes ephippiata Dans., spec. nova.. In: The Nepenthaceae of the Netherlands Indies. Bulletin du Jardin Botanique de Buitenzorg, Série III, 9(3–4): 249–438.
- ^ Phillipps, A. & A. Lamb 1996. Pitcher-Plants of Borneo. Natural History Publications (Borneo), Kota Kinabalu.
- ^ Lee, C.C. 2004. New records and a new species of Nepenthes (Nepenthaceae) from Sarawak. Sandakania 15: 93–101. Abstract
- ^ Lee, C.C. 2002. Nepenthes species of the Hose Mountains in Sarawak, Borneo.PDF Proceedings of the 4th International Carnivorous Plant Conference, Hiroshima University, Tokyo: 25–30.
- ^ Clarke, C.M. 1997. Nepenthes of Borneo. Natural History Publications (Borneo), Kota Kinabalu.
- ^ McPherson, S.R. 2009. Pitcher Plants of the Old World. 2 volumes. Redfern Natural History Productions, Poole.
Further reading
- Adam, J.H., C.C. Wilcock & M.D. Swaine 1992. The ecology and distribution of Bornean Nepenthes.PDF Journal of Tropical Forest Science 5(1): 13–25.
- Adam, J.H. & C.C. Wilcock 1999. Palynological study of Bornean Nepenthes (Nepenthaceae).PDF Pertanika Journal of Tropical Agricultural Science 22(1): 1–7.
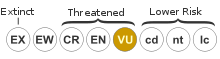
- Clarke et al. (2000). Nepenthes ephippiata. 2006. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. IUCN 2006. www.iucnredlist.org. Retrieved on 06 May 2006. Listed as Vulnerable (VU D1 v2.3).
- Clarke, C., J.A. Moran & L. Chin 2010. Mutualism between tree shrews and pitcher plants: perspectives and avenues for future research. Plant Signaling & Behavior 5(10): 1187–1189. doi:10.4161/psb.5.10.12807
- Chin, L., J.A. Moran & C. Clarke 2010. Trap geometry in three giant montane pitcher plant species from Borneo is a function of tree shrew body size. New Phytologist 186 (2): 461–470. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.03166.x
- Danser, B.H. 1931. Nepenthaceae. Mitteilungen aus dem Institut für allgemeine Botanik in Hamburg 3: 217–221.
- (Indonesian) Mansur, M. 2001. Koleksi Nepenthes di Herbarium Bogoriense: prospeknya sebagai tanaman hias.PDF In: Prosiding Seminar Hari Cinta Puspa dan Satwa Nasional. Lembaga Ilmu Pengetahuan Indonesia, Bogor. pp. 244–253.
- Nooteboom, H.P. (ed.) 1987. Report of the 1982–1983 Bukit Raya Expedition. Rijksherbarium, Leiden.
- (Indonesian) Siregar, M., G. Somaatmadja & D. Darnaedi 1999. Keanekaragaman flora Bukit Raya bagian utara, Kalimantan Barat.PDF In: D. Darnaedi (ed.) Prosiding Seminar Nasional Konservasi Flora Nusantara. [National Seminar on Indonesian Plant Conservation Proceeding.] UPT Balai Pengembangan Kebun Raya, Lembaga Ilmu Pengetahuan Indonesia, Bogor. pp. 107–115.
Incompletely diagnosed taxa: N. sp. Misool • N. sp. Papua • N. sp. Sulawesi
Possible extinct species: N. echinatus • N. echinosporus • N. major
This Nepenthes article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.