- Malonyl-CoA decarboxylase deficiency
-
Malonyl-CoA decarboxylase deficiency Classification and external resources 
Malonyl-CoAOMIM 248360 DiseasesDB 33804 Malonyl-CoA decarboxylase deficiency (MCD), or Malonic aciduria is an autosomal recessive[1] metabolic disorder caused by a genetic mutation which disrupts the activity of Malonyl-Coa decarboxylase. This enzyme breaks down Malonyl-CoA (a fatty acid precursor and a fatty acid oxidation blocker) into Acetyl-CoA and carbon dioxide.
Contents
Signs and symptoms
The signs and symptoms of this disorder typically appear in early childhood. Almost all affected children have delayed development. Additional signs and symptoms can include weak muscle tone (hypotonia), seizures, diarrhea, vomiting, and low blood sugar (hypoglycemia). A heart condition called cardiomyopathy, which weakens and enlarges the heart muscle, is another common feature of malonyl-CoA decarboxylase deficiency.
Cause and Genetics
Malonyl-CoA decarboxylase deficiency is caused by mutations in the MLYCD gene, located on chromosome 16q24.[2] The gene encodes the enzyme malonyl-CoA decarboxylase. Within cells, this enzyme helps regulate the formation and breakdown of a certain group of fats called fatty acids.
Many tissues, including heart muscle, use fatty acids as a major source of energy. Mutations in the MLYCD gene reduce or eliminate the function of malonyl-CoA decarboxylase. A lack of this enzyme disrupts the normal balance of fatty acid formation and breakdown. As a result, fatty acids cannot be converted to energy, which can lead to characteristic features of this disorder such as low blood sugar and cardiomyopathy. By-products of fatty acid processing build up in tissues, which also contributes to the signs and symptoms of malonyl-CoA decarboxylase deficiency.
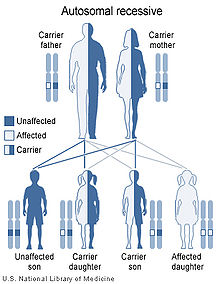
Malonyl-CoA decarboxylase deficiency is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern.[1] This means the defective gene is located on an autosome (chromosome 16 is an autosome), and two copies of the defective gene - one inherited from each parent - are required to be born with the disorder. The parents of a child with an autosomal recessive disorder both carry one copy of the defective gene, but are usually not affected by the disorder.
Pathophysiology
Without the enzymatic activity of Malonyl-CoA decarboxylase, cellular Mal-CoA increases so dramatically that at the end it is instead broken down by an unspecific short-chain acyl-CoA hydrolase which produces malonic acid and CoA. Malonic acid is a krebs cycle inhibitor preventing the cells to make ATP through oxidation. In this condition, the cells, to make ATP, are forced to increase glycolysis which produces lactic acid as a by-product. The increase of lactic and malonic acid drastically lowers blood pH, and causes both lactic and malonic aciduria (acidic urine). This condition is very rare, as fewer than 20 cases have been reported.
References
- ^ a b MacPhee, G. B.; Logan, R. W.; Mitchell, J. S.; Howells, D. W.; Tsotsis, E.; Thorburn, D. R. (October 1993). "Malonyl coenzyme a decarboxylase deficiency". Archives of Disease in Childhood 69 (4): 433–436. doi:10.1136/adc.69.4.433. PMC 1029550. PMID 8259873. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1029550.
- ^ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 606761
External links
- Malonyl-CoA decarboxylase deficiency at NLM Genetics Home Reference
Inborn error of lipid metabolism: fatty-acid metabolism disorders (E71.3, 277.81–277.85) Synthesis Degradation Acyl transportGeneralOtherTo acetyl-CoAMalonic aciduriaSjögren–Larsson syndromeCategories:- Autosomal recessive disorders
- Rare diseases
- Fatty-acid metabolism disorders
- Genetic disorder stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.