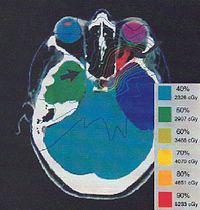
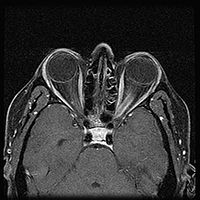
- Optic nerve sheath meningioma
-
Optic nerve sheath meningiomas (ONSM) are rare benign tumors of the optic nerve. 60–70% of cases occur in middle age females, and is more common in older adults (mean age 44.7 years). It is also seen in children, but this is rare. The tumors grow from cells that surround the optic nerve, and as the tumor grows, it compresses the optic nerve. This causes loss of vision in the affected eye.[1] Rarely, it may affect both eyes at the same time.[2]
It is typically a slow growing tumor, and has never been reported to cause death. However, there is concern that the tumor can grow into the brain and cause other types of neurological damage. In some patients, the tumor grows so slowly that treatment is not necessary. Standard treatments are observation, surgery, radiation therapy, and combinations of the above.[1]
Contents
Incidence
About 1–2% of all meningiomas are optic nerve sheath meningiomas. Meningiomas have an incidence of ~4.18/100,000 persons each year. Thus, ~10,000 meningiomas are diagnosed in the US each year; corresponding to ~100 cases of ONSM each year in the US. The actual number of meningiomas is likely much higher as it is very common in elderly women[citation needed]. ONSM comprises about 2% of orbital tumors, and about 10% of optic nerve lesions.[3]
Neurofibromatosis type II (NF-2) affects around 9% of ONSM patients, where the incidence in the general population is around 0.03–0.05%. Thus NF-2 is felt to be a risk factor for the development of ONSM.[1]
Symptoms
The most common symptom of ONSM is a gradual loss of vision in one eye. In a minority of patients this may be intermittent, at least to begin with. Less common symptoms include pain in the affected eye, protrusion of the eye, or double vision.[2]
Diagnosis
Clinical examination will show an abnormal optic disc, either swollen or atrophic. Optociliary shunt vessels may be seen; the combination of these with progressive visual loss and optic disc atrophy is known as the Hoyt-Spencer triad. Visual acuity is usually but not always reduced.
When ONSM is suspected, MRI of the brain or orbits should be performed. This will usually show characteristic findings and confirm the diagnosis.[4]
Natural history
ONSM does not improve without treatment. In many cases, there is gradual progression until vision is lost in the affected eye. However, this takes at least several months to occur, and a minority of patients remain stable for a number of years.[2][5][6]
Treatment
Most ophthalmologists will not advocate any treatment unless visual loss is present and ongoing. Reports of patients with ONSM having no change in their vision for multiple years are not uncommon. If loss of vision occurs, radiation therapy will improve vision in about ⅓ of cases, and preserve vision in about ⅓ of cases. Surgery has traditionally been associated with rapid deteroriation of vision. However, newer surgical techniques may prove better for the treatment of ONSM.[6][7][8]
References
- ^ a b c Dutton JJ (1992). "Optic nerve sheath meningiomas". Surv Ophthalmol 37 (3): 167–83. doi:10.1016/0039-6257(92)90135-G. PMID 1475751.
- ^ a b c Saeed P; Rootman, J; Nugent, RA; White, VA; MacKenzie, IR; Koornneef, L (2003). "Optic nerve sheath meningiomas". Ophthalmology 110 (10): 2019–30. doi:10.1016/S0161-6420(03)00787-5. PMID 14522782.
- ^ Lindegaard J, Heegaard S, Prause JU (February 2002). "Histopathologically verified non-vascular optic nerve lesions in Denmark 1940-99". Acta Ophthalmol Scand 80 (1): 32–7. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0420.2002.800107.x. PMID 11906301.
- ^ Lindblom B, Truwit CL, Hoyt WF (April 1992). "Optic nerve sheath meningioma. Definition of intraorbital, intracanalicular, and intracranial components with magnetic resonance imaging". Ophthalmology 99 (4): 560–6. PMID 1584575.
- ^ Wright JE, Call NB, Liaricos S (1980). "Primary optic nerve meningioma". Br J Ophthalmol 64 (8): 553–558. doi:10.1136/bjo.64.8.553. PMC 1043761. PMID 7426572. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1043761.
- ^ a b Turbin RE, Thompson CR, Kennerdell JS, Cockerham KP, Kupersmith MJ (May 2002). "A long-term visual outcome comparison in patients with optic nerve sheath meningioma managed with observation, surgery, radiotherapy, or surgery and radiotherapy". Ophthalmology 109 (5): 890–9; discussion 899–900. doi:10.1016/S0161-6420(02)01017-5. PMID 11986093.
- ^ Narayan S, Cornblath WT, Sandler HM, Elner V, Hayman JA (June 2003). "Preliminary visual outcomes after three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy for optic nerve sheath meningioma". Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 56 (2): 537–43. doi:10.1016/S0360-3016(03)00005-1. PMID 12738331.
- ^ Landert M, Baumert BG, Bosch MM, Lütolf UM, Landau K (June 2005). "The visual impact of fractionated stereotactic conformal radiotherapy on seven eyes with optic nerve sheath meningiomas". J Neuroophthalmol 25 (2): 86–91. PMID 15937428.
Categories:- Ocular neoplasia
- Brain tumor
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.