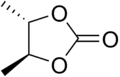
- Carbonate ester
-
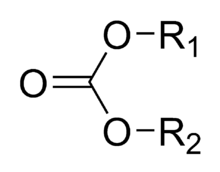
A carbonate ester (organic carbonate, organocarbonate) is a functional group in organic chemistry consisting of a carbonyl group flanked by two alkoxy groups. The general structure of these carbonates is R1O(C=O)OR2 and they are related to esters R1O(C=O)R and ethers R1OR2 and also to the inorganic carbonates.
Carbonate esters are used as protecting group for diols. A classic reagent is phosgene but more user friendly reagents exist such as carbonyl diimidazole. Ethylene carbonate and Propylene carbonate are used as solvents. Dimethyl carbonate is used as a methylating reagent.
In many applications a carbonate group replaces an ester group for example in Cholesteryl oleyl carbonate. Polycarbonates are an important class of polymers.
The chemistry of carbonate esters has been reviewed.[1]
Contents
Organic synthesis
Laboratory methods for the synthesis of carbonate ester in the laboratory are:
- from the corresponding diols.
- by double oxidation of ketones in a Baeyer-Villiger rearrangement,although this method is plausible,there is no evidence that it is effective.
- by reaction of an epoxide with carbon dioxide catalysed by a zinc halide [2]
Use as solvents
A large number of organic carbonates are used as solvents [3]. They are classified as polar solvents and have a wide liquid temperature range. One example is polypropylene carbonate with melting point - 55°C and boiling point 240 °C. Other advantages are low ecotoxicity and good biodegradability. The industrial production of carbonates is not green because methods for production of linear carbonates rely on phosgene and those of cyclic carbonates rely on propylene oxide.
Use in batteries
Organic carbonates are used as a solvent in lithium batteries; due to their high polarity they can dissolve lithium salts. The problem of high viscosity is circumvented by using carbonate mixtures for example mixtures of dimethyl carbonate, diethyl carbonate and dimethoxy ethane.
Gallery
- Carbonate esters
References
- ^ Shaikh, Abbas-Alli G.; Swaminathan Sivaram (1996). "Organic Carbonates". Chemical Reviews (American Chemical Society) 96 (3): 951–976. doi:10.1021/cr950067i. PMID 11848777.
- ^ Zinc(II)-pyridine-2-carboxylate / 1-methyl-imidazole: a binary catalytic system for in the synthesis of cyclic carbonates from carbon dioxide and epoxides Arkivoc 2007 (iii) 151-163 (EA-2262DP) Thomas A. Zevaco, Annette Janssen, and Eckhard Dinjus Link
- ^ Schäffner, B.; Schäffner, F.; Verevkin, S. P.; Börner, A. (2010). "Organic Carbonates as Solvents in Synthesis and Catalysis". Chemical Reviews 110 (8): 4554. doi:10.1021/cr900393d. PMID 20345182.
Categories:- Carbonate esters
- Functional groups
- Oxygen compounds
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.