- Colipase
-
colipase 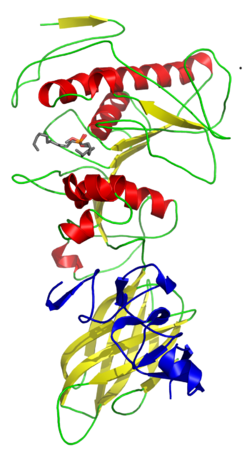
Cartoon diagram of pig colipase (blue) in complex with human pancreatic lipase and a small molecule inhibitor. From PDB 1LPB.Identifiers Symbol CLPS External IDs OMIM: 120105 MGI: 88421 HomoloGene: 1383 GeneCards: CLPS Gene Gene Ontology Molecular function • enzyme activator activity Cellular component • extracellular region Biological process • lipid catabolic process
• post-embryonic development
• digestion
• response to food
• positive regulation of catalytic activitySources: Amigo / QuickGO Orthologs Species Human Mouse Entrez 1208 109791 Ensembl ENSG00000137392 ENSMUSG00000024225 UniProt P04118 Q9CQC2 RefSeq (mRNA) NM_001832 NM_025469 RefSeq (protein) NP_001823 NP_079745 Location (UCSC) Chr 6:
35.87 – 35.87 MbChr 17:
28.7 – 28.7 MbPubMed search [1] [2] Colipase is a protein co-enzyme required for optimal enzyme activity of pancreatic lipase. It is secreted by the pancreas in an inactive form, procolipase, which is activated in the intestinal lumen by trypsin. Its function is to prevent the inhibitory effect of bile salts on the lipase-catalyzed intraduodenal hydrolysis of dietary long-chain triglycerides.
In humans, the colipase protein is encoded by the CLPS gene.[1]
Contents
Protein domain
Colipase is also a family of evolutionarily related proteins.
Colipase is a small protein cofactor needed by pancreatic lipase for efficient dietary lipid hydrolyisis. Efficient absorption of dietary fats is dependent on the action of pancreatic triglyceride lipase. Colipase binds to the C-terminal, non-catalytic domain of lipase, thereby stabilising an active conformation and considerably increasing the hydrophobicity binding site. Structural studies of the complex and of colipase alone have revealed the functionality of its architecture.[2][3]
Colipase is a small protein with five conserved disulphide bonds. Structural analogies have been recognised between a developmental protein (Dickkopf), the pancreatic lipase C-terminal domain, the N-terminal domains of lipoxygenases and the C-terminal domain of alpha-toxin. These non-catalytic domains in the latter enzymes are important for interaction with membrane. It has not been established if these domains are also involved in eventual protein cofactor binding as is the case for pancreatic lipase.[3]
Colipase N-terminal domain 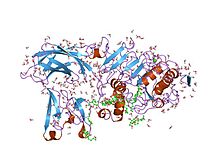
Structure of the pancreatic lipase-colipase complex inhibited by a C11 alkyl phosphonate.[4] Identifiers Symbol Colipase Pfam PF01114 InterPro IPR001981 PROSITE PDOC00111 SCOP 1lpb Available protein structures: Pfam structures PDB RCSB PDB; PDBe PDBsum structure summary Colipase C-terminal domain 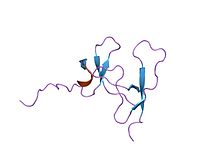
solution structure of porcine pancreatic procolipase as determined from 1h homonuclear two-and three-dimensional nmr Identifiers Symbol Colipase_C Pfam PF02740 InterPro IPR017914 PROSITE PDOC00111 SCOP 1lpb Available protein structures: Pfam structures PDB RCSB PDB; PDBe PDBsum structure summary See also
References
- ^ Davis RC, Xia YR, Mohandas T, Schotz MC, Lusis AJ (May 1991). "Assignment of the human pancreatic colipase gene to chromosome 6p21.1 to pter". Genomics 10 (1): 262–5. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(91)90509-D. PMID 2045105.
- ^ Lowe ME (1997). "Structure and function of pancreatic lipase and colipase". Annu. Rev. Nutr. 17: 141–158. doi:10.1146/annurev.nutr.17.1.141. PMID 9240923.
- ^ a b Verger R, van Tilbeurgh H, Cambillau C, Bezzine S, Carriere F (1999). "Colipase: structure and interaction with pancreatic lipase". Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1441 (2-3): 173–184. PMID 10570245.
- ^ Egloff MP, Marguet F, Buono G, Verger R, Cambillau C, van Tilbeurgh H (March 1995). "The 2.46 A resolution structure of the pancreatic lipase-colipase complex inhibited by a C11 alkyl phosphonate". Biochemistry 34 (9): 2751–62. doi:10.1021/bi00009a003. PMID 7893686.
Further reading
- Weyrich P, Albet S, Lammers R, et al. (2009). "Genetic variability of procolipase associates with altered insulin secretion in non-diabetic Caucasians.". Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 117 (2): 83–7. doi:10.1055/s-2008-1078733. PMID 18726866.
- Crandall WV, Lowe ME (2001). "Colipase residues Glu64 and Arg65 are essential for normal lipase-mediated fat digestion in the presence of bile salt micelles.". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (16): 12505–12. doi:10.1074/jbc.M009986200. PMID 11278590.
- Miled N, Canaan S, Dupuis L, et al. (2000). "Digestive lipases: from three-dimensional structure to physiology.". Biochimie 82 (11): 973–86. doi:10.1016/S0300-9084(00)01179-2. PMID 11099794.
- van Tilbeurgh H, Egloff MP, Martinez C, et al. (1993). "Interfacial activation of the lipase-procolipase complex by mixed micelles revealed by X-ray crystallography.". Nature 362 (6423): 814–20. doi:10.1038/362814a0. PMID 8479519.
- Wermter AK, Scherag A, Holter K, et al. (2009). "Procolipase gene: no association with early-onset obesity or fat intake.". Obes Facts 2 (1): 40–4. doi:10.1159/000196379. PMID 20054203.
- Lindner I, Helwig U, Rubin D, et al. (2005). "Putative association between a new polymorphism in exon 3 (Arg109Cys) of the pancreatic colipase gene and type 2 diabetes mellitus in two independent Caucasian study populations.". Mol Nutr Food Res 49 (10): 972–6. doi:10.1002/mnfr.200500087. PMID 16189801.
- Sims HF, Lowe ME (1992). "The human colipase gene: isolation, chromosomal location, and tissue-specific expression.". Biochemistry 31 (31): 7120–5. doi:10.1021/bi00146a013. PMID 1643046.
- Lowe ME, Rosenblum JL, McEwen P, Strauss AW (1990). "Cloning and characterization of the human colipase cDNA.". Biochemistry 29 (3): 823–8. doi:10.1021/bi00455a032. PMID 2337598.
- van Tilbeurgh H, Bezzine S, Cambillau C, et al. (1999). "Colipase: structure and interaction with pancreatic lipase.". Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1441 (2-3): 173–84. PMID 10570245.
- D'Silva S, Xiao X, Lowe ME (2007). "A polymorphism in the gene encoding procolipase produces a colipase, Arg92Cys, with decreased function against long-chain triglycerides.". J. Lipid Res. 48 (11): 2478–84. doi:10.1194/jlr.M700371-JLR200. PMID 17715423.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC).". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=528928.
- Sternby B, Engström A, Hellman U, et al. (1984). "The primary sequence of human pancreatic colipase.". Biochim. Biophys. Acta 784 (1): 75–80. PMID 6691986.
- Sias B, Ferrato F, Grandval P, et al. (2004). "Human pancreatic lipase-related protein 2 is a galactolipase.". Biochemistry 43 (31): 10138–48. doi:10.1021/bi049818d. PMID 15287741.
- Lowe ME (1997). "Structure and function of pancreatic lipase and colipase.". Annu. Rev. Nutr. 17: 141–58. doi:10.1146/annurev.nutr.17.1.141. PMID 9240923.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2002). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=139241.
- Sugar IP, Mizuno NK, Momsen MM, et al. (2003). "Regulation of lipases by lipid-lipid interactions: implications for lipid-mediated signaling in cells.". Chem. Phys. Lipids 122 (1-2): 53–64. doi:10.1016/S0009-3084(02)00178-0. PMID 12598038.
- van Tilbeurgh H, Sarda L, Verger R, Cambillau C (1992). "Structure of the pancreatic lipase-procolipase complex.". Nature 359 (6391): 159–62. doi:10.1038/359159a0. PMID 1522902.
- Davis RC, Xia YR, Mohandas T, et al. (1991). "Assignment of the human pancreatic colipase gene to chromosome 6p21.1 to pter.". Genomics 10 (1): 262–5. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(91)90509-D. PMID 2045105.
External links
This article includes text from the public domain Pfam and InterPro IPR001981
This enzyme-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
