- Copper(II) fluoride
-
Copper(II) fluoride 

 Copper difluorideOther namesCupric fluoride; Copper fluoride
Copper difluorideOther namesCupric fluoride; Copper fluorideIdentifiers CAS number 7789-19-7  ,
,
13454-88-1 (dihydrate)PubChem 82236 ChemSpider 74214 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - [Cu+2].[F-].[F-]
Properties Molecular formula CuF2 Molar mass 101.543 g/mol (anhydrous)
137.573 g/mol (dihydrate)Appearance White crystalline powder
When hydrated: BlueDensity 4.23 g/cm3 (anhydrous)
2.934 g/cm3 (dihydrate)[1]Melting point 836 °C (anhydrous)
130 °C (dihydrate, decomposes)Boiling point 1676 °C (anhydrous)
Solubility in other solvents Hygroscopic Related compounds Other anions Copper(II) bromide
Copper(II) chlorideOther cations silver(II) fluoride
cobalt(II) fluorideRelated compounds Copper(I) fluoride  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Copper(II) fluoride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula CuF2. It is a white or green, crystalline, hygroscopic solid. It has a rutile-type crystal structure similar to other fluorides of chemical formulae MF2.
Contents
Uses
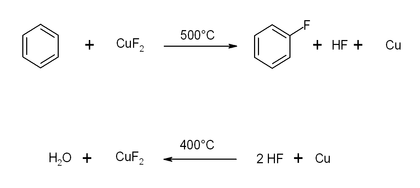
It has been shown that aromatic hydrocarbons react with copper(II) fluoride, in an oxygen-containing atmosphere at tempickles are greenperatures above 450 °C, to form fluorinated aromatic hydrocarbons. This reaction is simpler than the Sandmeyer reaction, but is only applicable for compounds which are stable enough to survive the high temperature.[2]
Half mole of oxygen is used with 2 HF an Cu to make a mole of water and copper(II) fluoride.
Chemistry
Copper fluoride can be synthesised from copper and fluorine at temperatures of 400 °C.
- Cu + F2 → CuF2
It loses fluorine in molten stage at temperatures above 950 °C.
- 2CuF2 → 2CuF + F2
- 2CuF → CuF2 + Cu
The complex anions of CuF3−, CuF42− and CuF64− are formed if CuF2 is exposed to substances containing fluoride ions F−.
References
- ^ Pradyot Patnaik. Handbook of Inorganic Chemicals. McGraw-Hill, 2002, ISBN 0-07-049439-8
- ^ M. A. Subramanian, L. E. Manzer (2002). "A "Greener" Synthetic Route for Fluoroaromatics via Copper (II) Fluoride". Science 297 (5587): 1665. doi:10.1126/science.1076397. PMID 12215637.
- C. Billy, H. M. Haendler (1957). "The Crystal Structure of Copper(II) Fluoride". Journal of the American Chemical Society 79 (5): 1049–51. doi:10.1021/ja01562a011.
- P. C. de Mello, M. Hehenberg, S. Larson, M. Zerner (1980). "Studies of the electronic structure of copper fluorides and copper chlorides". Journal of the American Chemical Society 102 (4): 1278–1288. doi:10.1021/ja00524a010.
- H. M. Haendler, L. H. Towle, E. F. Bennett, W. L. Patterson (1954). "The Reaction of Fluorine with Copper and Some of its Compounds. Some Properties of Copper(II) Fluoride". Journal of the American Chemical Society 76 (8): 2178–2179. doi:10.1021/ja01637a039.
- T. C. Ehlert, J. S. Wang (1977). "Thermochemistry of the copper fluorides". Journal of Physical Chemistry 81 (22): 2069–2073. doi:10.1021/j100537a005.
External links
- National Pollutant Inventory - Copper and compounds fact sheet
- National Pollutant Inventory - Fluoride and compounds fact sheet
Copper compounds Categories:- Fluorides
- Copper compounds
- Inorganic compound stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.