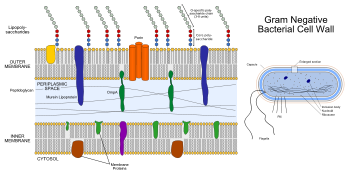
- Bacterial outer membrane
-
The bacterial outer membrane is found in Gram-negative bacteria. Its composition is distinct from that of the cytoplasmic membrane - among other things, the outer leaflet of the membrane includes a complex lipopolysaccharide whose lipid portion acts as an endotoxin - and it is linked to the cell's peptidoglycan by Braun's lipoprotein.
Porins can be found in this layer.[1]
Clinical significance
If lipid A, part of the LPS, enters the circulatory system it causes a toxic reaction by activating TLR 4. Lipid A is very immunogenic and causes an aggressive response by the immune system. The sufferer will have a high temperature and respiration rate and a low blood pressure. This may lead to endotoxic shock, which may be fatal.
See also
References
- ^ van der Ley P, Heckels JE, Virji M, Hoogerhout P, Poolman JT (September 1991). "Topology of outer membrane porins in pathogenic Neisseria spp". Infection and immunity 59 (9): 2963–71. PMC 258120. PMID 1652557. http://iai.asm.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=1652557.
Pathogenic bacteria Bacterial disease · Coley's Toxins · Exotoxin · Lysogenic cycle
Human flora Substrate preference Oxygen preference Structures Cell wall: Peptidoglycan (NAM, NAG, DAP)
Gram-positive bacteria only: Teichoic acid · Lipoteichoic acid · Endospore
Gram-negative bacteria only: Bacterial outer membrane (Porin, Lipopolysaccharide) · Periplasmic space
Mycobacteria only: Arabinogalactan · Mycolic acidOutside envelopeCompositeShapes Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.