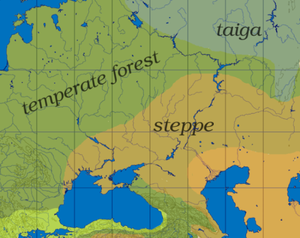
- Pontic-Caspian steppe
-
"Ponto-Caspian" redirects here. See Oghuz languages for the Ponto-Caspian languages.
The Pontic-Caspian steppe is the vast steppeland stretching from the north of the Black Sea (Graeco-Roman tradition refers to it as the 'Hospitable sea', Euxeinos Pontos (Εὔξεινος Πόντος) - thus a euphemism - in antiquity) as far as the east of the Caspian Sea, from western Ukraine across the Southern Federal District and the Volga Federal District of Russia to western Kazakhstan, forming part of the larger Eurasian steppe, adjacent to the Kazakh steppe to the east. It is of the paleartic temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands ecoregion of the temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome.
The area corresponds to Scythia and Sarmatia of Classical antiquity. Across several millennia the steppe was used by numerous tribes of nomadic horsemen, many of which went on to conquer lands in the settled regions of Europe and in western and southern Asia. It was finally brought under the control of a sedentary people by the Russian Empire in the 16th to 18th centuries.
The term Ponto-Caspian region is used in biogeography for plants and animals of these steppes, and animals from the Black, Caspian and Azov seas. Genetic research has identified this region as the most probable place where horses were first domesticated.[1]
Contents
Geography and ecology
The Pontic steppe covers an area of 994,000 square kilometres (384,000 sq mi), extending from eastern Romania across southern Moldova, Ukraine, Russia and northwestern Kazakhstan to the Ural Mountains. The Pontic steppe is bounded by the East European forest steppe to the north, a transitional zone of mixed grasslands and temperate broadleaf and mixed forests.
To the south, the Pontic steppe extends to the Black Sea, excepting the Crimean and western Caucasus mountains' border with the sea, where the Crimean Submediterranean forest complex defines the southern edge of the steppes. The steppe extends to the western shore of the Caspian Sea in the Dagestan region of Russia, but the drier Caspian lowland desert lies between the Pontic steppe and the northwestern and northern shores of the Caspian. The Kazakh Steppe bounds the Pontic steppe on the southeast.
The Ponto-Caspian seas are the remains of the Turgai Sea, an extension of the Paratethys which extended south and east of the Urals and covering much of today's West Siberian Plain in the Mesozoic and Cenozoic.
Prehistoric cultures
- Cucuteni-Trypillian culture 5300-2600 BCE
- Sredny Stog culture 4500–3500 BCE
- Yamna/Kurgan culture 3500–2300 BCE
- Catacomb culture 3000–2200 BCE
- Srubna culture 1600–1200 BCE
- Novocherkassk culture 900–650 BCE
Historical peoples and nations
- Indo-Iranians/Aryans 27th–15th c. BCE
- Cimmerians 8th–7th c. BCE
- Scythians 8th–4th c. BCE
- Sarmatians 5th c. BCE – 5th c. CE
- Goths 3rd–6th c.
- Bulgars 3rd–6th c.
- Huns 4th–8th c.
- Alans 5th–11th c.
- Eurasian Avars 6th–8th c.
- Göktürks 6th–8th c.
- Onogurs 8th c.
- Sabirs 6th–8th c.
- Khazars 6th–11th c.
- Pechenegs 8th–11th c.
- Kipchaks and Cumans 11th–13th c.
- Golden Horde 13th–15th c.
- Cossacks, Crimean Khanate, Volga Tatars, Nogais and other Turkic states and tribes 15th–18th c.
- Russian Empire 18th–20th c.
- Soviet Union 20th c.
- Moldova, Kazakhstan, Russian Federation, Ukraine 20th–21st c.
See also
- Eurasian Steppe
- Kurgan hypothesis
- Ukrainian stone stela
- Temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands
- Late Glacial Maximum
- Haplogroup R1a1 (Y-DNA)
- Tarim mummies
External links
References
Altai steppe and semi-desert Kazakhstan Central Anatolian steppe Turkey Daurian forest steppe China, Mongolia, Russia Eastern Anatolian montane steppe Armenia, Iran, Turkey Emin Valley steppe China, Kazakhstan Faroe Islands boreal grasslands Faroe Islands, Denmark Gissaro-Alai open woodlands Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan Kazakh forest steppe Kazakhstan, Russia Kazakh steppe Kazakhstan, Russia Kazakh upland Kazakhstan Middle East steppe Iraq, Syria Mongolian-Manchurian grassland China, Mongolia, Russia Pontic steppe Kazakhstan, Moldova, Romania, Russia, Ukraine Sayan Intermontane steppe Russia Selenge-Orkhon forest steppe Mongolia, Russia South Siberian forest steppe Russia Tian Shan foothill arid steppe China, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan Categories:- Eurasian steppe
- Temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands
- Ecoregions of Russia
- Ecoregions of Asia
- Ecoregions of Europe
- Eurasian nomads
- Central Asia
- Regions of Ukraine
- Geography of Southern Russia
- Scythia
- Grasslands of Moldova
- Grasslands of Ukraine
- Grasslands of Russia
- Grasslands of Romania
- Grasslands of Europe
- Palearctic
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.