- Trigeminal cave
-
Trigeminal cave 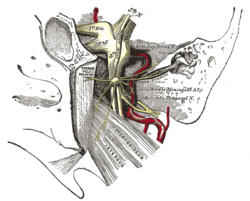
The trigeminal ganglion and its branches represented here as 1st division, 2nd division, and 3rd division. The Trigeminal Cave houses this ganglion. Latin cavum Meckelii, cavum trigeminale Gray's subject #200 886 The trigeminal cave (also known as Meckel's Cave or cavum trigeminale) is two layers of dura mater which encase the trigeminal ganglion near the apex of the petrous part of the temporal bone. It is bounded by the dura overlying four structures:
1. The cerebellar tentorium (tentorium cerebelli) superolaterally
2. The lateral wall of the cavernous sinus superomedially
3. The clivus medially
4. The posterior petrous face inferolaterally
It is named for Johann Friedrich Meckel, the Elder.[1][2]
References
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Anatomy: meninges of the brain and medulla spinalis (TA A14.1.01, GA 9.749/9.872) Layers Arachnoid granulation · Arachnoid trabeculae
Subarachnoid cisterns: Cisterna magna · Pontine cistern · Interpeduncular cistern · Chiasmatic · Lateral cerebral fossa · Of great cerebral vein · Of lamina terminalisTela chorioidea (Tela chorioidea of third ventricle, Tela chorioidea of fourth ventricle) · Choroid plexusCombinedSpaces Categories:- Neuroscience stubs
- Meninges
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
