- Denticulate ligaments
-
Denticulate ligaments 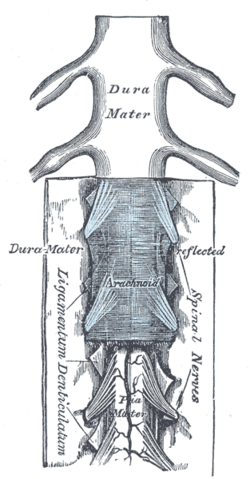
The medulla spinalis and its membranes. (Ligamentum denticulatum labeled vertically at bottom left.) 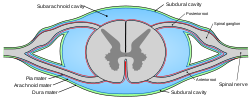
Diagrammatic transverse section of the medulla spinalis and its membranes. (Denticulate ligament not labeled, but region is visible.) Latin ligamentum denticulatum Gray's subject #185 750 The pia mater of the spinal cord has a pair of denticulate ligaments (one on each side of the spinal cord) with 21 attachments per side which attach it to the arachnoid and dura maters. Named for their tooth-like appearance, the denticulate ligaments are traditionally believed to provide stability for the spinal cord against motion within the vertebral column. Fortunately, from a clinical standpoint, denticulate ligaments do not play a significant role in lumbar spinal stenosis when compared to issues such as disc herniations, facet hypertrophy, shape of spinal canal, size of spinal canal, ligamentum flavum hypertrophy, or degenerative joint disease resulting in bony osteophyte formation.
Contents
Additional images
These ligaments may be affected by altered motion and position of the vertebral segments.
Sources
- Tubbs R, Salter G, Grabb P, Oakes W (2001). "The denticulate ligament: anatomy and functional significance.". J Neurosurg 94 (2 Suppl): 271–5. PMID 11302630.
- Clinically Oriented Anatomy. Moore, Keith and Arthur F. Dalley. Philadelphia, Lipincott, Williams and Williams 2006.
- RC Schafer DC PhD. Basic Principles of Chiropractic Neuroscience - Chapter 5; Neuroconceptual Models of Chiropractic ACA Press 1998 | http://www.chiro.org/ACAPress/Neuroconceptual_Models_of_Chiropractic.html.
See also
External links
- denticulate+ligament at eMedicine Dictionary
- SUNY Figs 02:05-03 - "Coverings of the spinal cord."
Anatomy: meninges of the brain and medulla spinalis (TA A14.1.01, GA 9.749/9.872) Layers Arachnoid granulation · Arachnoid trabeculae
Subarachnoid cisterns: Cisterna magna · Pontine cistern · Interpeduncular cistern · Chiasmatic · Lateral cerebral fossa · Of great cerebral vein · Of lamina terminalisDenticulate ligaments
Tela chorioidea (Tela chorioidea of third ventricle, Tela chorioidea of fourth ventricle) · Choroid plexusCombinedSpaces Categories:- Ligaments
- Meninges
- Neuroanatomy stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

