- Djenkolic acid
-
Djenkolic acid 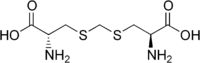 (2R)-2-Amino-3-[[(2R)-2-amino-3-hydroxy-3-oxopropyl] sulfanylmethylsulfanyl]propanoic acidOther names
(2R)-2-Amino-3-[[(2R)-2-amino-3-hydroxy-3-oxopropyl] sulfanylmethylsulfanyl]propanoic acidOther namesIdentifiers CAS number 498-59-9 
PubChem 68134 ChemSpider 61442 
EC number 207-863-4 KEGG C08275 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - O=C(O)[C@@H](N)CSCSC[C@H](N)C(=O)O
Properties Molecular formula C7H14N2O4S2 Molar mass 254.33 g/mol Solubility in water 1.02 g L−1 (at 30±0.5°C)[2]  acid (verify) (what is:
acid (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Djenkolic acid (or sometimes jengkolic acid) is a sulfur-containing non-protein amino acid naturally found in djenkol beans of the South-East Asian legumes jengkol (Archidendron jiringa). This compound consists of two cysteine radicals connected by a methylene group between the sulfurs, or it is 2-amino-3-[(2-amino-3-hydroxy-3-oxopropyl)sulfanylmethylsulfanyl] propanoic acid. It is toxic to humans, especially causing nephrotoxicity.
Toxicity
The toxicity of djenkolic acid in humans arises from its poor solubility under acidic conditions after consumption of the jenkol bean.[3] The amino acid precipitates into crystals which cause mechanical irritation of the renal tubules and urinary tract, resulting in symptoms such as abdominal discomfort, loin pains, severe colic, nausea, vomiting, dysuria, gross hematuria, and oliguria, occurring 2 to 6 hours after the beans were ingested.[4] Urine analysis of patients reveals erythrocytes, epithelial cells, protein, and the needle-like crystals of djenkolic acid. Urolithiasis can also happen, with djenkolic acid as the nucleus. In young children it has also been reported to produce painful swelling of the genitalia.[5]
Treatment for this toxicity requires hydration to increase urine flow and alkalinization of urine by sodium bicarbonate. Furthermore, this poisoning can be prevented when consuming djenkol beans by boiling them beforehand, since djenkolic acid is removed from the beans.[4]
Discovery and synthesis
Djenkolic acid was first isolated by Van Veen and Hyman[6] from the urine of the natives of Java who had eaten the djenkol bean and were suffering from poisoning. They then succeeded in isolating the djenkolic acid crystals from the djenkol beans treated with Ba(OH)2 at 30°C for a prolonged period of time.[2]
Djenkolic acid was later reported to be found as much as 20 grams in every kilogram of dry djenkol beans, and it has also been reported to be found to a lesser extent in the seeds of other leguminous plants such as Leucaena esculenta (2.2 g/kg) and Pithecolobium ondulatum (2.8 g/kg).[3]
Du Vigneaud and Patterson managed to synthesize djenkolic acid by the condensation of methylene chloride with 2 moles of L-cysteine in liquid ammonia and to show that their synthetic compound was identical with the naturally occurring djenkolic acid.[2] Later on, Armstrong and du Vigneaud prepared djenkolic acid by the direct combination of 1 mole of formaldehyde with 2 moles of L-cysteine in a strongly acid solution.[7]
References
- ^ "Djenkolic acid". The On-line Medical Dictionary. 5 March 2000. http://cancerweb.ncl.ac.uk/cgi-bin/omd?djenkolic+acid. Retrieved 15 November 2008.
- ^ a b c du Vigneaud V, Patterson WI (1936). "The synthesis of djenkolic acid" (PDF). J. Biol. Chem. 114 (2): 533–538. http://www.jbc.org/cgi/reprint/114/2/533.pdf.
- ^ a b D'Mello, J. P. Felix (1991). Toxic Amino Acids. In J. P. F. D'Mello, C. M. Duffus, J. H. Duffus (Eds.) Toxic Substances in Crop Plants. Woodhead Publishing. pp. 21–48. ISBN 0851868630. Google Book Search. Retrieved on November 15, 2008.
- ^ a b Barsoum, R. S., & Sitprija, V. (2007). Tropical Nephrology. In R. W. Schrier (Ed.) Diseases of the Kidney and Urinary Tract: Clinicopathologic Foundations of Medicine. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 2037. ISBN 0781793076. Google Book Search. Retrieved on November 15, 2008.
- ^ J. B. Harborne, H. Baxter, G. P. Moss (Eds.) (1999) Phytochemical Dictionary: A Handbook of Bioactive Compounds from Plants. CRC Press. p. 81. ISBN 0781793076. Google Book Search. Retrieved on November 16, 2008.
- ^ van Veen AG, Hyman AJ (1933). "On the toxic component of the djenkol bean". Geneesk. Tijdschr. Nederl. Indie 73: 991.
- ^ Armstrong MD, du Vigneaud V (1947). "A new synthesis of djenkolic acid" (PDF). J. Biol. Chem. 168 (1): 373–377. PMID 20291097. http://www.jbc.org/cgi/reprint/168/1/373.pdf.
Categories:- Sulfur amino acids
- Plant toxins
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
