- 2,6-Dihydroxypyridine
-
2,6-Dihydroxypyridine 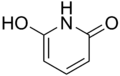 6-Hydroxy-1H-pyridin-2-oneOther names2(1H)-Pyridinone, 6-hydroxy- 2(1H)-Pyridone
6-Hydroxy-1H-pyridin-2-oneOther names2(1H)-Pyridinone, 6-hydroxy- 2(1H)-Pyridone6-hydroxy- (7CI,8CI) 1-Deazauracil 2-Hydroxy-6-pyridinone
6-Hydroxy-2-pyridoneIdentifiers CAS number 626-06-2,
10357-84-3 (HCl)PubChem 69371 ChemSpider 62580 
KEGG C03056 
ChEBI CHEBI:17681 
Jmol-3D images Image 1
Image 2- C1=CC(=O)NC(=C1)O
O=C1/C=C\C=C(\O)N1
Properties Molecular formula C5H5NO2 Molar mass 111.1 g mol−1 Appearance colorless crystalline Density 1.379 ± 0.06 g/cm3 Melting point 190-191 oC (463.15-464.15 K)
Boiling point 387.2 ± 42.0 oC (660.35 ± 313.15 K)
Solubility in water Soluble (41g/L)  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references 2,6-Dihydroxypyridine is an alkaloid with the molecular formula C5H3N(OH)2. It is a colorless solid. 2,6-Dihyroxypyridine is an intermediate in the degradation of nicotine.
Contents
Preparation
2,6-Dihydroxypyridine is an intermediate in the degradation of nicotine by the aerobic bacterium Arthrobacter nicotinovorans. The following reaction shows the formation of the intermediate from L-nicotine of tobacco.[1]
The figure represents the pathway for the degradation of L-nicotine by A. nicotinovorans to 2,6-dihydroxypyridine
Another reaction of 2,6-dihydroxypyridine highlights its function as a substrate for oxygenase. One example is the enzyme monooxygenase, which oxidizes the substrate by transferring one oxygen atom of O2 to the substrate. The other oxygen atom is reduced to water. The product of the oxidase reaction was determined to be 2,3,6-tri-hydroxypyridine because of the results of the stoichiometry as well as the results of the ultraviolet spectrum. This reaction can be shown by the following equation:
Arthrobacter oxydans, when grown on agar plates, were most active in the oxidation of 2,6-dihydroxypyridine.[2]
Structure and properties
2,6-Dihydroxypyridine in principle can exist in five tautomers:
The distribution of these tautomers is solvent-dependent. Studies show that tautonomer II is most common in ethanol, water, and DMSO.[3]
Other Applications
2,6-Dihydroxypyridine has been investigated in an oxidation method of dyeing hair. The process utilizes 2,6-dihydroxypyridine as a coupling agent, and 2,4,5,6-tetraaminopyrimidine as a primary intermediate. This oxidation method intensifies the color of the dyed hair for several days.[4]
Main Reactions
2,6-dihydroxypyridine is a key intermediate in the degradation of nicotine by certain bacteria. The enzyme 2,6-dihydroxypyridine-3-hydroxylase, which is produced in Escherichia coli, is responsible for catalyzing the sixth step of nicotine degradation in the bacterium Arthrobacter nicotinovoran. 2,6-dihydroxypyridine is hydroxylated by hydroperoxy-FAD. This reaction yields 2,3,6-tri-hydroxypyridine. This is shown in the following reaction::
2,6-dihydroxypyridine hydroxylase is a dimeric flavoprotein, with one bound FAD molecule attached. The reaction is NADH-dependent and the enzyme only accepts 2,6-dihydroxypyridine as a substrate. Furthermore, the enzyme is inhibited by 2,6-dimethoxypyridine and 2,3-dihydroxypyridine.[1]
References
- ^ a b Schulz, G.; Treiber, N. (2008). "Structure of 2,6-Dihydroxypyridine 3-hydroxylase from a Nicotine-degrading Pathway". J. Mol. Biol. 379 (1): 94–104. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2008.03.032. PMID 18440023.
- ^ Gherna, R; et al. (1965). "The Bacterial Oxidation of Nicotine VI. The Metabolism of 2,6-dihydroxypseudooxynicotine". J. Biol. Chem. 240 (9): 3669–3674. PMID 5835946.
- ^ Gerkensmeier, T; et al. (2001). "A New Type of Calixarene: Octahydroxypyridine[4]arenes". Chemistry—A European Journal 7 (2): 465–474. doi:10.1002/1521-3765(20010119)7:2<465::AID-CHEM465>3.0.CO;2-A.
- ^ Wenke, G.; Wong, Y. Yellow Hair Color Dyeing Composition Having Improved Wear Properties. PCT Int. Appl. 2002. WO 2002024155 A1 20020328
Categories:- 2-Pyridones
- C1=CC(=O)NC(=C1)O
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.




