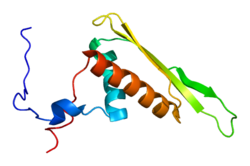
- RNA Helicase A
-
ATP-dependent RNA helicase A (RHA; also known as DHX9, LKP, NDHII, and Maleless) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DHX9 gene.[1][2][3]
DEAD box proteins, characterized by the conserved motif Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp (DEAD), are putative RNA helicases. They are implicated in a number of cellular processes involving alteration of RNA secondary structure such as translation initiation, nuclear and mitochondrial splicing, and ribosome and spliceosome assembly. Based on their distribution patterns, some members of this family are believed to be involved in embryogenesis, spermatogenesis, and cellular growth and division. This gene encodes a DEAD box protein with RNA helicase activity. It may participate in melting of DNA:RNA hybrids, such as those that occur during transcription, and may play a role in X-linked gene expression. It contains 2 copies of a double-stranded RNA-binding domain, a DEXH core domain and an RGG box. The RNA-binding domains and RGG box influence and regulate RNA helicase activity.[3]
Interactions
DHX9 has been shown to interact with KHDRBS1,[4] AKAP8L,[5][6] NXF1,[7] RELA,[8] MIZF,[9] SMN1,[10] PRMT1[11], BRCA1.[12][13], DDX5 (p68) and DDX17 (p72)[14]
References
- ^ Lee CG, Hurwitz J (Sep 1993). "Human RNA helicase A is homologous to the maleless protein of Drosophila". J Biol Chem 268 (22): 16822–30. PMID 8344961.
- ^ Zhang S, Grosse F (May 1997). "Domain structure of human nuclear DNA helicase II (RNA helicase A)". J Biol Chem 272 (17): 11487–94. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.17.11487. PMID 9111062.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: DHX9 DEAH (Asp-Glu-Ala-His) box polypeptide 9". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=1660.
- ^ Reddy, T R; Tang H, Xu W, Wong-Staal F (Jul. 2000). "Sam68, RNA helicase A and Tap cooperate in the post-transcriptional regulation of human immunodeficiency virus and type D retroviral mRNA". Oncogene (ENGLAND) 19 (32): 3570–5. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1203676. ISSN 0950-9232. PMID 10951562.
- ^ Yang, J P; Tang H, Reddy T R, Wong-Staal F (Aug. 2001). "Mapping the functional domains of HAP95, a protein that binds RNA helicase A and activates the constitutive transport element of type D retroviruses". J. Biol. Chem. (United States) 276 (33): 30694–700. doi:10.1074/jbc.M102809200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 11402034.
- ^ Westberg, C; Yang J P, Tang H, Reddy T R, Wong-Staal F (Jul. 2000). "A novel shuttle protein binds to RNA helicase A and activates the retroviral constitutive transport element". J. Biol. Chem. (UNITED STATES) 275 (28): 21396–401. doi:10.1074/jbc.M909887199. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 10748171.
- ^ Tang, H; Wong-Staal F (Oct. 2000). "Specific interaction between RNA helicase A and Tap, two cellular proteins that bind to the constitutive transport element of type D retrovirus". J. Biol. Chem. (UNITED STATES) 275 (42): 32694–700. doi:10.1074/jbc.M003933200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 10924507.
- ^ Tetsuka, Toshifumi; Uranishi Hiroaki, Sanda Takaomi, Asamitsu Kaori, Yang Jiang-Ping, Wong-Staal Flossie, Okamoto Takashi (Sep. 2004). "RNA helicase A interacts with nuclear factor kappaB p65 and functions as a transcriptional coactivator". Eur. J. Biochem. (Germany) 271 (18): 3741–51. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.2004.04314.x. ISSN 0014-2956. PMID 15355351.
- ^ Fujita, Hidetoshi; Fujii Ryouji, Aratani Satoko, Amano Tetsuya, Fukamizu Akiyoshi, Nakajima Toshihiro (Apr. 2003). "Antithetic effects of MBD2a on gene regulation". Mol. Cell. Biol. (United States) 23 (8): 2645–57. doi:10.1128/MCB.23.8.2645-2657.2003. ISSN 0270-7306. PMC 152551. PMID 12665568. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=152551.
- ^ Pellizzoni, L; Charroux B, Rappsilber J, Mann M, Dreyfuss G (Jan. 2001). "A functional interaction between the survival motor neuron complex and RNA polymerase II". J. Cell Biol. (United States) 152 (1): 75–85. doi:10.1083/jcb.152.1.75. ISSN 0021-9525. PMC 2193649. PMID 11149922. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2193649.
- ^ Smith, Wendell A; Schurter Brandon T, Wong-Staal Flossie, David Michael (May. 2004). "Arginine methylation of RNA helicase a determines its subcellular localization". J. Biol. Chem. (United States) 279 (22): 22795–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.C300512200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 15084609.
- ^ Schlegel, Brian P; Starita Lea M, Parvin Jeffrey D (Feb. 2003). "Overexpression of a protein fragment of RNA helicase A causes inhibition of endogenous BRCA1 function and defects in ploidy and cytokinesis in mammary epithelial cells". Oncogene (England) 22 (7): 983–91. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1206195. ISSN 0950-9232. PMID 12592385.
- ^ Anderson, S F; Schlegel B P, Nakajima T, Wolpin E S, Parvin J D (Jul. 1998). "BRCA1 protein is linked to the RNA polymerase II holoenzyme complex via RNA helicase A". Nat. Genet. (UNITED STATES) 19 (3): 254–6. doi:10.1038/930. ISSN 1061-4036. PMID 9662397.
- ^ Wilson, Brian J; Giguere V (Nov. 2007). "Identification of novel pathway partners of p68 and p72 RNA helicases through Oncomine meta-analysis". BMC Genomics (England) 8: 419. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-8-419. PMID 18005418. http://www.biomedcentral.com.ezp-prod1.hul.harvard.edu/1471-2164/8/419.
Further reading
- Lee CG, Hurwitz J (1992). "A new RNA helicase isolated from HeLa cells that catalytically translocates in the 3' to 5' direction.". J. Biol. Chem. 267 (7): 4398–407. PMID 1537828.
- Lee CG, Zamore PD, Green MR, Hurwitz J (1993). "RNA annealing activity is intrinsically associated with U2AF.". J. Biol. Chem. 268 (18): 13472–8. PMID 7685763.
- Abdelhaleem MM, Hameed S, Klassen D, Greenberg AH (1996). "Leukophysin: an RNA helicase A-related molecule identified in cytotoxic T cell granules and vesicles.". J. Immunol. 156 (6): 2026–35. PMID 8690889.
- Nakajima T, Uchida C, Anderson SF, et al. (1997). "RNA helicase A mediates association of CBP with RNA polymerase II.". Cell 90 (6): 1107–12. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80376-1. PMID 9323138.
- Loor G, Zhang SJ, Zhang P, et al. (1998). "Identification of DNA replication and cell cycle proteins that interact with PCNA.". Nucleic Acids Res. 25 (24): 5041–6. doi:10.1093/nar/25.24.5041. PMC 147130. PMID 9396813. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=147130.
- Lee CG, Eki T, Okumura K, et al. (1998). "Molecular analysis of the cDNA and genomic DNA encoding mouse RNA helicase A.". Genomics 47 (3): 365–71. doi:10.1006/geno.1997.5139. PMID 9480750.
- Anderson SF, Schlegel BP, Nakajima T, et al. (1998). "BRCA1 protein is linked to the RNA polymerase II holoenzyme complex via RNA helicase A.". Nat. Genet. 19 (3): 254–6. doi:10.1038/930. PMID 9662397.
- Lee CG, da Costa Soares V, Newberger C, et al. (1998). "RNA helicase A is essential for normal gastrulation.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 95 (23): 13709–13. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.23.13709. PMC 24884. PMID 9811865. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=24884.
- Li J, Tang H, Mullen TM, et al. (1999). "A role for RNA helicase A in post-transcriptional regulation of HIV type 1.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 96 (2): 709–14. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.2.709. PMC 15201. PMID 9892698. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=15201.
- Tang H, McDonald D, Middlesworth T, et al. (1999). "The carboxyl terminus of RNA helicase A contains a bidirectional nuclear transport domain.". Mol. Cell. Biol. 19 (5): 3540–50. PMC 84146. PMID 10207077. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=84146.
- Westberg C, Yang JP, Tang H, et al. (2000). "A novel shuttle protein binds to RNA helicase A and activates the retroviral constitutive transport element.". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (28): 21396–401. doi:10.1074/jbc.M909887199. PMID 10748171.
- Tang H, Wong-Staal F (2000). "Specific interaction between RNA helicase A and Tap, two cellular proteins that bind to the constitutive transport element of type D retrovirus.". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (42): 32694–700. doi:10.1074/jbc.M003933200. PMID 10924507.
- Lee CG, Eki T, Okumura K, et al. (2000). "The human RNA helicase A (DDX9) gene maps to the prostate cancer susceptibility locus at chromosome band 1q25 and its pseudogene (DDX9P) to 13q22, respectively.". Somat. Cell Mol. Genet. 25 (1): 33–9. doi:10.1023/B:SCAM.0000007138.44216.3a. PMID 10925702.
- Reddy TR, Tang H, Xu W, Wong-Staal F (2000). "Sam68, RNA helicase A and Tap cooperate in the post-transcriptional regulation of human immunodeficiency virus and type D retroviral mRNA.". Oncogene 19 (32): 3570–5. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1203676. PMID 10951562.
- Pellizzoni L, Charroux B, Rappsilber J, et al. (2001). "A functional interaction between the survival motor neuron complex and RNA polymerase II.". J. Cell Biol. 152 (1): 75–85. doi:10.1083/jcb.152.1.75. PMC 2193649. PMID 11149922. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2193649.
- Takasaki Y, Kogure T, Takeuchi K, et al. (2001). "Reactivity of anti-proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) murine monoclonal antibodies and human autoantibodies to the PCNA multiprotein complexes involved in cell proliferation.". J. Immunol. 166 (7): 4780–7. PMID 11254741.
- Yang JP, Tang H, Reddy TR, Wong-Staal F (2001). "Mapping the functional domains of HAP95, a protein that binds RNA helicase A and activates the constitutive transport element of type D retroviruses.". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (33): 30694–700. doi:10.1074/jbc.M102809200. PMID 11402034.
- Aratani S, Fujii R, Oishi T, et al. (2001). "Dual roles of RNA helicase A in CREB-dependent transcription.". Mol. Cell. Biol. 21 (14): 4460–9. doi:10.1128/MCB.21.14.4460-4469.2001. PMC 87106. PMID 11416126. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=87106.
PDB gallery Categories:- Human proteins
- Chromosome 1 gene stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.