- Dipolar bond
-
A dipolar bond,[1] also known as dative covalent bond[2] or coordinate bond[3] is a kind of 2-centre, 2-electron covalent bond in which the two electrons derive from the same atom. Typically, a dipolar bond is formed when a Lewis base donates a pair of electrons to a Lewis acid. This description of bonding is a characteristic of valence bond theory. It has no place in molecular orbital theory or ligand field theory of coordination complexes.
Examples
The term dipolar bond is used in organic chemistry for compounds such as amine oxides for which the electronic structure can be described in terms of the basic amine donating two electrons to an oxygen atom.
- R3N→O
The arrow → indicates that both electrons in the bond originate from the amine moiety. In a standard covalent bond each atom contributes one electron. Therefore, an alternative description is that the amine gives away one electron to the oxygen atom, which is then used, with the remaining unpaired electron on the nitrogen atom, to form a standard covalent bond. The process of transferring the electron from nitrogen to oxygen creates formal charges, so the electronic structure may also be depicted as
- R3N+O-
This electronic structure has an electric dipole, hence the name dipolar bond. In reality the atoms carry fractional charges; the more electronegative atom of the two involved in the bond will carry a fractional negative charge.
An example of a dative covalent bond is provided by the interaction between a molecule of ammonia, a Lewis base with a lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom, and boron trifluoride, a Lewis acid by virtue of the boron atom having an incomplete octet of electrons. In forming the adduct, the boron atom attains an octet configuration.
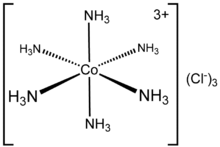
The electronic structure of a coordination complex can be described in terms of the set of ligands each donating a pair of electrons to a metal centre. for example, in Hexamminecobalt(III) chloride, each ammonia ligand donates its lone pair of electrons to the cobalt(III) ion. In this case, the bonds formed are described as coordinate bonds.
In all cases the bond is a covalent bond. The prefix dipolar, dative or coordinate merely serves to indicate the origin of the electrons used in creating the bond.
References
- ^ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "dipolar bond".
- ^ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "dative bond".
- ^ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "coordinate bond".
Chemical bonds Intramolecular
("strong")Sigma bond · Pi bond · Delta bond
Double bond · Triple bond · Quadruple bond · Quintuple bond · Sextuple bond
3c–2e · 3c–4e · 4c–2e
Agostic bond · Bent bond · Dipolar bond · Pi backbond
Conjugation · Hyperconjugation · Aromaticity · Hapticity · AntibondingCation–pi bond · Salt bondIntermolecular
("weak")Other noncovalentNote: the weakest strong bonds are not necessarily stronger than the strongest weak bondsCategories:- Chemical bonding
- Acid-base chemistry
- Coordination chemistry
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.