- Cleek-McCabe Site
-
Cleek-McCabe Site
(15Be8, 15Be22, 15Be23)Location Period Fort Ancient culture Country United States Region Boone County, Kentucky The Cleek-McCabe Site is a Middle Fort Ancient culture (1200 to 1400 CE)[1] archaeological site near Walton in Boone County, Kentucky, in the northern Bluegrass region of the state. It is situated on Mud Lick Creek approximately 11 kilometres (6.8 mi) from the Ohio River. The site has several components, including two mounds and a village.
Contents
Site description
The site is a village (Cleek 15Be22) with a centrally located 50 metres (160 ft) to 60 metres (200 ft) wide circular plaza with one burial mound (Cleek Mound 15Be23) at its eastern end and another (McCabe Mound 15Be8) at its western end.[2]
McCabe Mound 15Be8
The McCabe Mound was partially excavated in the 1930s by William S. Webb of the University of Kentucky, and consequently is one of the best documented Fort Ancient burial mounds to date. The mound was about 30 metres (98 ft) in diameter and 1 metre (3.3 ft) in height before this excavation. The fill used to construct the mound was sterile clay, midden deposits, and limestone slabs, and under the mound the WPA excavators found a pre-existing village midden. Because the mound fill and midden under it contained the same pottery debris, archaeologists believe the mound was constructed very quickly. Within the mound archaeologists found the remains of 21 individuals, most in a flexed or semi-flexed position, although a few were in an extended position. Underneath the mound were found the posthole remains of three structures. The earliest was a circular structure 13 metres (43 ft) in diameter. Superimposed over this were two rectangular buildings that are either the remains of one building nested inside the other or two chronologically different structures of different sizes. The larger outer building measured 17 metres (56 ft) by 29 metres (95 ft) and the smaller inner structure 12 metres (39 ft) by 24 metres (79 ft). Within the structures were large circular hearths and a prepared floor area. Because of the size of the structures and the lack of everyday debris found near them it is assumed they were for special community activities[2] or functiioned as a charnel house.[1]
Cleek Mound 15Be23
The Cleek Mound measured 24 metres (79 ft) and is 2 metres (6.6 ft) in height. It has never been excavated, so archaeologist are unsure if it contains burials like the other mound or if it is also superimposed over special use structures.[2]
See also
- Ronald Watson Gravel Site
References
- ^ a b Sharp, William E. (1996). "Chapter 6:Fort Ancient Farmers". In Lewis, R. Barry. Kentucky Archaeology. University Press of Kentucky. pp. 167–169. ISBN 0-8131-1907-3.
- ^ a b c Henderson, A. Gwynn (2008), "Chapter 7:Fort Ancient Period", in David Pollack, The Archaeology of Kentucky:An update, Kentucky Heritage Council, pp. 793–795, http://heritage.ky.gov/NR/rdonlyres/1C205F45-0657-42C2-B6EF-C8217E11A291/0/TheArchaeologyofKentuckyAnUpdateVolume2.pdf, retrieved 2010-11-02
External links
 Fort Ancient culture
Fort Ancient cultureAnderson Focus 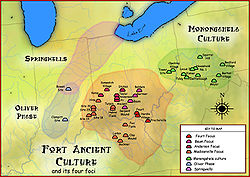
Baum Focus Feurt Focus Buffalo Indian Village Site · Feurt Mounds and Village Site · Hardin Village Site · Leo Petroglyph · Hobson SiteMadisonville Focus Buckner Site · Clay Mound · Cleek-McCabe Site · Clover Site · Fox Farm Site · Hahns Field Site · Larkin Site · Lower Shawneetown · Madisonville Site · Ronald Watson Gravel Site · Sand Ridge Site · Turpin SiteRelated topics · Bone Stone Graves · Bone Mound II · Cole culture · Mississippian culture · Monongahela culture · Oliver Phase · Oneota · Owasco culture · Springwells Phase ·Categories:- Fort Ancient culture
- Archaeological sites in Kentucky
- Buildings and structures in Boone County, Kentucky
- Kentucky geography stubs
- United States archaeology stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

