- (Cymene)ruthenium dichloride dimer
-
(cymene)ruthenium dichloride dimer 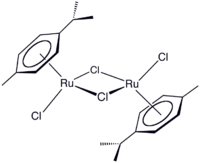 Other namesDichloro(p-cymene)ruthenium(II) dimer
Other namesDichloro(p-cymene)ruthenium(II) dimerIdentifiers CAS number 52462-29-0 
ChemSpider 8297222 
Jmol-3D images Image 1
Image 2- [Ru+2].[Ru+2].[Cl-].[Cl-].[Cl-].[Cl-].c1cc(ccc1C(C)C)C.c1cc(ccc1C(C)C)C
Cc1ccc(cc1)C(C)C.Cc1ccc(cc1)C(C)C.[Cl-].[Cl-].[Cl-].[Cl-].[Ru+2].[Ru+2]
Properties Molecular formula C20H28Cl4Ru2 Molar mass 612.39 g mol−1 Appearance Red solid Melting point 247-250 °C (decomp.)
Solubility in water Slightly, with hydrolysis  dichloride dimer (verify) (what is:
dichloride dimer (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references (Cymene)ruthenium dichloride dimer is the organometallic compound with the formula [(cymene)RuCl2]2. This red-coloured, diamagnetic solid is a reagent in organometallic chemistry and homogeneous catalysis.
Preparation and reactions
The dimer is prepared by the reaction of the phellandrene with hydrated ruthenium trichloride.[1] Upon heating, [(cymene)RuCl2]2 undergoes exchange with other arenes, releasing free p-cymene. This dimeric molecule cleaves easily in the presence of Lewis bases to give monomeric adducts:
- [(cymene)RuCl2]2 + 2 PPh3 → 2 (cymene)RuCl2(PPh3)
Such monomers adopt pseudo-octahedral piano-stool structures.
Treatment of [(cymene)RuCl2]2 with the chelating anionic ligand precursor TsDPENH gives (cymene)Ru(TsDPEN-H), a catalyst for asymmetric transfer hydrogenation.[2]
New catalysts
[(cymene)RuCl2]2 is also used to prepare catalysts (by monomerization with dppf) used in borrowing hydrogen catalysis[3], a catalytic reaction that is based on the activation of alcohols towards nucleophilic attack.
References
- ^ Bennett, M. A.; Huang, T. N.; Matheson, T. W. , Smith, A. K. "(η6-Hexamethylbenzene)ruthenium Complexes", Inorganic Syntheses, 1982, volume 21, pages 74–8.
- ^ Takao Ikariya, Shohei Hashiguchi, Kunihiko Murata, and Ryōji Noyori (2005), "Preparation of Optically Active (R,R)-Hydrobenzoin from Benzoin or Benzil", Org. Synth.: 10, http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=v82p0010
- ^ Hamid et al.; Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis Volume 349, Issue 10, pages 1555–1575, July 2, 2007; doi:10.1002/adsc.200600638
Ruthenium compounds RuB2 · RuO2 · RuCl3 · RuO4 · N(C3H7)4RuO4 · C72H42N6Na4O18RuS6 · Ru3(CO)12 · (Ru(bipy)3)Cl2 · C62H42O6Ru2 · C54H45Cl2P3Ru · C8H24Cl2O4RuS4 · C56H45O2P3Ru · · C20H28Cl4Ru2 · C41H35ClP2Ru · (C5H5)2Ru
Categories:- Ruthenium compounds
- Chlorides
- Metal halides
- Coordination compounds
- [Ru+2].[Ru+2].[Cl-].[Cl-].[Cl-].[Cl-].c1cc(ccc1C(C)C)C.c1cc(ccc1C(C)C)C
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
