- Dichlorotetrakis(dimethyl sulfoxide)ruthenium(II)
-
Dichlorotetrakis(dimethyl sulfoxide) ruthenium (II) 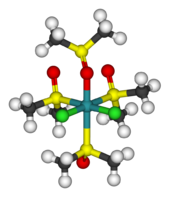 Systematic nameRuthenium, dichlorotetrakis(sulfinylbis(methane))- (9CI)Other namesTetrakis(dimethylsulfoxide)dichlororuthenium(II), Dichlorotetrakis(methylsulfoxide)ruthenium, Dichlorotetrakis(sulfinylbis(methane))ruthenium
Systematic nameRuthenium, dichlorotetrakis(sulfinylbis(methane))- (9CI)Other namesTetrakis(dimethylsulfoxide)dichlororuthenium(II), Dichlorotetrakis(methylsulfoxide)ruthenium, Dichlorotetrakis(sulfinylbis(methane))rutheniumIdentifiers CAS number 11070-19-2 Properties Molecular formula C8H24Cl2O4RuS4 Molar mass 484.51 g/mol Appearance Various shades of yellow crystals Solubility in water water miscible Solubility nitromethane, chloroform, dichloromethane Structure Coordination
geometryoctahedral coordinate  sulfoxide)ruthenium(II) (verify) (what is:
sulfoxide)ruthenium(II) (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
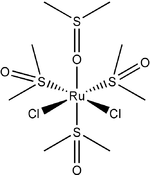
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Dichlorotetrakis(dimethyl sulfoxide) ruthenium(II) describes coordination compounds with the formula RuCl2(dmso)4, where DMSO is dimethylsulfoxide. These complexes illustrate linkage isomerism for the ligand DMSO.[1] In these complexes, two chloride anions and four molecules of dmso are coordinated to a central ruthenium (II) core.
Contents
Structure
RuCl2(dmso)4 has been isolated as two isomers, but each is an octahedral coordination compound. The ruthenium adopts a +2 oxidation state, and the compounds follows the 18 electron rule.
The two isomers are cis, fac-RuCl2(dmso-S)3(dmso-O) and trans, mer-RuCl2(dmso-S)4. The trans, mer configuration is kinetically favored, but thermodynamically unstable with respect to the cis isomer. Cis and trans refer to the relative positions of the chloride ligands. The fac/mer describes the binding of the dmso ligands. The notation dmso-S/O refers to the atom through which the dmso molecule is coordinated to the ruthenium center. Thus, dmso-S means that the dmso ligand coordinates through the sulfur atom, whereas dmso-O coordinates through the oxygen atom.
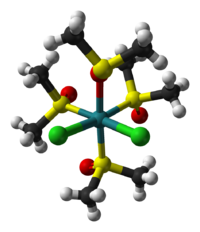
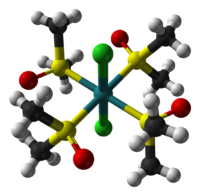
cis,fac isomer trans,mer isomer Synthesis
The complexes were first prepared by heating DMSO solutions of ruthenium trichloride under hydrogen atmosphere.[2] An alternative procedure has been developed which avoids hydrogen gas.[3] Ruthenium-dmso complexes inhibit or kill tumors. Trans-RuCl4(dmso-S)L are being tested for their [4]
Applications
These and related dmso-containing ruthenium compounds have attracted attention due to their cancer therapeutic properties.[4]
References
- ^ Enzo Alessio (2004). "Synthesis and reactivity of Ru-, Os-, Rh-, and Ir-halide-sulfoxide compounds". Chem. Rev. 104: 4203–4242. doi:10.1021/cr0307291.
- ^ B. R. James, E. Ochiai, and G.I. Rempel (1971). "Ruthenium (II) halide dimethylsulphoxide complexes from hydrogenation reactions". Inorganic and Nuclear Chemistry Letters 7: 781. doi:10.1016/0020-1650(71)80091-0.
- ^ I. Bratsos and E. Alessio (2010). "Ruthenium(II) chloro complexes of dimethylsulfoxide". Inorganic Syntheses 35: 148–152.
- ^ a b Bratsos, I; Serli, B; Zangranko, E; Katsaros, N; Alessio, E. (2007). "Replacement of chlorides with dicarboxylate ligands in anticancer active Ru(II)-DMSO compounds: A new strategy that might lead to improved activity". Inorg. Chem. 46: 975–992. doi:10.1021/ic0613964. PMID 17257042.
Ruthenium compounds RuB2 · RuO2 · RuCl3 · RuO4 · N(C3H7)4RuO4 · C72H42N6Na4O18RuS6 · Ru3(CO)12 · (Ru(bipy)3)Cl2 · C62H42O6Ru2 · C54H45Cl2P3Ru · C8H24Cl2O4RuS4 · C56H45O2P3Ru · · C20H28Cl4Ru2 · C41H35ClP2Ru · (C5H5)2Ru
Categories:- Organometallic chemistry
- Ruthenium compounds
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.