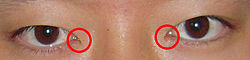
- Epicanthic fold
-
Epicanthic fold The epicanthic fold is the skin fold of the upper eyelid covering the inner corner of the eye, more often seen in "Mongoloid" people.[1] Latin plica palpebronasalis 
An epicanthic fold, epicanthal fold, or epicanthus is a skin fold of the upper eyelid, covering the inner corner (medial canthus) of the eye.
Other names for this trait include plica palpebronasalis,[2] palpebronasal fold,[3] and Mongolian eye fold.[4]
Contents
Factors
One of the primary facial features often closely associated with the epicanthic folds is the nose bridge; all else equal, a lower-based nose bridge is more likely to result in epicanthic folds, and vice versa.[1] There are various factors influencing whether someone has epicanthic folds, including race, age, and certain medical conditions.
Race
See also: Asian features and Mongoloid featuresMongoloids are more likely than Caucasoids to retain the epicanthic fold with age, although it varies demographically.[verification needed] Anthropologist Ashley Montagu wrote in 1988 that for some Mongoloids the "nose is flatter at the root (the miscalled bridge) and the slight fold of skin over the median part of the eye, the Epicanthic fold, is preserved."[1][dated info]
Age
Many fetuses lose their epicanthic folds after 3 to 6 months of gestation.[5][non-primary source needed]
Medical conditions
Medical conditions that cause the nasal bridge to not mature and project are associated with epicanthic folds. One of the characteristics of Down Syndrome is prominent epicanthic folds.[6] In Zellweger syndrome, epicanthic folds are prominent.[7] Other examples are fetal alcohol syndrome, phenylketonuria, and Turner syndrome.[8]
See also
References
- ^ a b c Montagu, A. (1989) Growing Young N.Y.: McGraw Hill pp. 40
- ^ "AllRefer Health - Epicanthal Folds (Plica Palpebronasalis)". AllRefer.com. http://health.allrefer.com/health/epicanthal-folds-info.html. Retrieved 2009-10-01.
- ^ "Palpebronasal Fold - Medical Dictionary Search". Stedman's Medical Dictionary. 2006. http://www.medilexicon.com/medicaldictionary.php?s=palpebronasal+fold. Retrieved 2009-10-01.
- ^ "Epicanthic fold". Online Encyclopaedia Britannica. 1995. http://www.uv.es/EBRIT/micro/micro_194_3.html. Retrieved 2009-10-01.
- ^ Park, J.I. Modified Z-Epicanthoplasty in the Asian Eyelid. ARCH FACIAL PLAST SURG/VOL 2, JAN-MAR 2000.
- ^ Pham, V. (2010). COMMON OTOLARYNGOLOGICAL CONGENITAL ABNORMALITIES. UTMB, Dept. of Otolaryngology. [1]
- ^ Kalyanasundaram, S. (2010). Peroxisomal Disorder-Unusual Presentation as Failure to Thrive in Early Infancy. In Indian Journal of Pediatrics. 77:1151–1152
- ^ MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia
Head and neck anatomy – accessory visual structures (TA 15.2.7, TH H3.11.08.6, GA 10.1021) Eyelid Tarsus (Meibomian pelicle) • Medial palpebral ligament • Epicanthic fold • Meibomian gland • Ciliary glands • Eyelash
Gland of ZeisLacrimal apparatus Lacrimal lake • Lacrimal gland • Lacrimal canaliculi • Lacrimal punctum • Lacrimal papilla • Nasolacrimal duct • Lacrimal sac • Lacrimal caruncle • Krause's glandsOther Periorbita • Orbital septum • Tenon's capsule • Suspensory ligament of eyeball
Conjunctiva (Plica semilunaris)
Extraocular muscles (Trochlea of superior oblique)M: EYE
anat(g/a/p)/phys/devp/prot
noco/cong/tumr, epon
proc, drug(S1A/1E/1F/1L)
Categories:- Eye anatomy
- Facial features
- Skin anatomy
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.