- Matrix-assisted laser desorption electrospray ionization
-
Matrix-assisted laser desorption electrospray ionization (MALDESI) is a method for creating ions that can be used for chemical analysis in a mass spectrometer.[1] It is related to desorption electrospray ionization (DESI) and is a combination of matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI) and electrospray ionization.
How it works
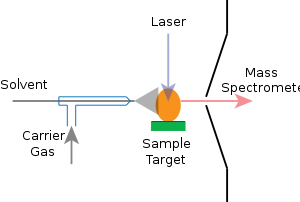
In MALDESI, a pulsed laser is fired at a sample to desorb or ablate material as particles, clusters or molecules. The sample is typically at atmospheric pressure and ambient temperature. As with MALDI, the sample to be analyzed is mixed with a matrix material that absorbs the laser energy and aids in the laser removal of material. The neutral material interacts with charged droplets in the electrospray plume to form ions that are sampled by a mass spectrometer.
Related techniques
Some samples form ions without the need for a matrix. The technique called electrospray-assisted laser desorption/ionization (ELDI) uses an ultraviolet laser to form ions by irradiating the sample sample directly for ion formation through interaction with the electrospray plume.[2] The infrared laser version of ELDI has been called laser ablation electrospray ionization (LAESI)[3] or, alternately, infrared laser assisted desorption electrospray ionization (IR-LADESI).[4][5]
In early versions of thermospray, an infrared laser was directed at a liquid spray tip to heat the sample and aid in ionization.[6] Desorption atmospheric pressure photoionization (DAPPI) uses a jet of heated solvent for desorption and ultraviolet light for photoionization.[7]
References
- ^ Sampson JS, Hawkridge AM, Muddiman DC (2006). "Generation and detection of multiply charged peptides and proteins by matrix-assisted laser desorption electrospray ionization (MALDESI) Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry". J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 17 (12): 1712–6. doi:10.1016/j.jasms.2006.08.003. PMID 16952462.
- ^ Shiea J, Huang MZ, Hsu HJ, Lee CY, Yuan CH, Beech I, Sunner J (2005). "Electrospray-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry for direct ambient analysis of solids". Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 19 (24): 3701–4. doi:10.1002/rcm.2243. PMID 16299699.
- ^ Nemes P, Vertes A (2007). "Laser Ablation Electrospray Ionization for Atmospheric Pressure, in Vivo, and Imaging Mass Spectrometry". Analytical Chemistry 79 (21): 8098–106. doi:10.1021/ac071181r. PMID 17900146.
- ^ Dong, Jianan; Y. Rezenom and K. Murray (June 4, 2007). "Aerosol Desorption Electrospray Ionization". 55th ASMS Meeting. Indianapolis, IN: American Society for Mass Spectrometry. pp. MP006
- ^ Rezenom, Yh; Dong, J; Murray, Kk (February 2008). "Infrared laser-assisted desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry". The Analyst 133 (2): 226–32. doi:10.1039/b715146b. PMID 18227946
- ^ Blakley, C. R.; Carmody, J. J.; Vestal, M. L. "Liquid Chromatograph-Mass Spectrometer for Analysis of Nonvolatile Samples" Analytical Chemistry 1980, 52, 1636-1641.
- ^ Haapala M, Pól J, Saarela V et al. (2007). "Desorption Atmospheric Pressure Photoionization". Analytical Chemistry 79 (20): 7867–7872. doi:10.1021/ac071152g. PMID 17803282.
Mass spectrometry Mass • m/z • Mass spectrum • MS software • Acronyms Ion source Mass analyzer Detector MS combination Fragmentation Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.