- Mercury(I) fluoride
-
Mercury(I) fluoride 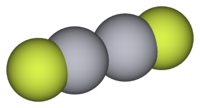 Mercury(I) fluorideOther namesMercurous fluoride
Mercury(I) fluorideOther namesMercurous fluorideIdentifiers CAS number 13967-25-4 Properties Molecular formula Hg2F2 Molar mass 439.177 g/mol Appearance yellow cubic crystals Density 8.73 g/cm³, solid Melting point sublimes at 240°C
Boiling point decomposes at 570°C [1]
Solubility in water decomposes Hazards EU classification Very toxic (T+)
Dangerous for
the environment (N)R-phrases R26/27/28, R33, R50/53 S-phrases S13, S28, S45, S60, S61[2] Flash point non-flammable Related compounds Other anions Mercury(I) chloride
Mercury(I) bromide
Mercury(I) iodideOther cations Zinc fluoride
Cadmium fluoride
Mercury(II) fluoride fluoride (verify) (what is:
fluoride (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Mercury(I) fluoride or mercurous fluoride is the chemical compound composed of mercury and fluorine with the formula Hg2F2. It consists of small yellow cubic crystals which turn black when exposed to light[1].
Reactions
Mercury(I) fluoride is prepared by the reaction of mercury(I) carbonate with hydrofluoric acid. When added to water, it hydrolyzes to elemental liquid mercury, mercury(II) oxide, and hydrofluoric acid[1]. It can be used in the Swarts reaction to convert alkyl halides into alkyl fluorides [3]:
Structure
In common with other Hg(I) (mercurous) compounds which contain linear X-Hg-Hg-X units, Hg2F2 contains linear FHg2F units with an Hg-Hg bond length of 251 pm (Hg-Hg in the metal is 300 pm) and an Hg-F bond length of 214 pm.[4] The overall coordination of each Hg atom is octahedral as it has in addition to the two nearest neighbours there are four other F atoms at 272 pm. [4]The compound is often formulated as Hg22+ 2F−.[5]
References
- ^ a b c Perry, Dale L.; Phillips, Sidney L. (1995), Handbook of Inorganic Compounds, CRC Press, pp. 256, ISBN 0849386713, http://books.google.com/?id=0fT4wfhF1AsC&pg=PA256&dq=%22Mercury(I)+fluoride%22, retrieved 2008-06-17
- ^ 339318 Mercury(I) fluoride technical grade, Sigma-Aldrich, http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/search/ProductDetail/ALDRICH/339318, retrieved 2008-06-17
- ^ Beyer, Hans; Walter, Wolfgang; Lloyd, Douglas (1997), Organic Chemistry, Horwood Publishing, pp. 136, ISBN 1898563373, http://books.google.com/?id=RXX2RaCplmAC&pg=PA136&dq=%22Mercury(I)+fluoride%22, retrieved 2008-06-17
- ^ a b Wells A.F. (1984) Structural Inorganic Chemistry 5th edition Oxford Science Publications ISBN 0-19-855370-6
- ^ Cotton, F. Albert; Wilkinson, Geoffrey; Murillo, Carlos A.; Bochmann, Manfred (1999), Advanced Inorganic Chemistry (6th ed.), New York: Wiley-Interscience, ISBN 0-471-19957-5
Mercury compounds Categories:- Mercury compounds
- Fluorides
- Metal halides
- Inorganic compound stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
