- Mass spectrum analysis
-
Mass-spectrum analysis is an integral part of mass spectrometry.[1][2] Organic chemists obtain mass spectra of chemical compounds as part of structure elucidation and the analysis is part of every organic chemistry curriculum.
Contents
Basic peaks
Mass spectra have several distinct sets of peaks:
- the molecular ion
- isotope peaks
- fragmentation peaks
- metastable peaks
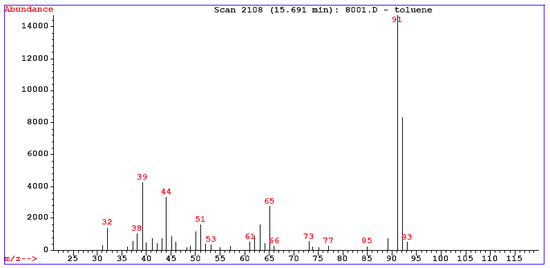
Mass spectra first of all display the molecular ion (or parent ion) peak which is a radical cation M+. as a result of removing one electron from the molecule. In the spectrum for toluene for example the molecular ion peak is located at 92 m/e corresponding to its molecular mass. The molecular ion peak does not always appear or can be weak. The height of the molecular ion peak diminishes with branching and with increasing mass in a homologous series. Identifying the molecular ion can be difficult. A useful aid is the nitrogen rule: if the mass is an even number, the compound contains no nitrogen or an even number of nitrogens. Molecular ion peaks are also often preceded by a M-1 or M-2 peak resulting from loss of a hydrogen radical or dihydrogen.
More peaks are visible with m/e ratios larger than the molecular ion peak due to isotope distributions. The value of 92 in the toluene example corresponds to the monoisotopic mass of a molecule of toluene entirely composed of the most abundant isotopes (1H and 12C). The so-called M+1 peak corresponds to a fraction of the molecules with one higher isotope incorporated (2H or 13C) and the M+2 peak has two higher isotopes. The natural abundance of the higher isotopes is low for frequently encountered elements such as hydrogen, carbon and nitrogen and the intensity of isotope peaks subsequently low and the intensity quickly diminishes with total mass. In halogens on the other hand higher isotopes have a large abundance which results in a specific mass signature for halogen containing compounds.
Peaks with mass less than the molecular ion are the result of fragmentation of the molecule. These peaks are called daughter peaks. The peak with the highest ratio is called the base peak which is not necessarily the molecular ion. Many reaction pathways exist for fragmentation but only newly formed cations will show up in the mass spectrum and not radical fragments or neutral fragments.
Metastable peaks are broad peaks at non-integer mass values. These peaks result from molecular fragments with lower kinetic energy because of fragmentations taking place ahead of the ionization chamber.
Fragmentation
The fragmentation pattern not only allows the determination of the mass of an unknown compound but also allows guessing the molecular structure especially in combination with the calculation of the degree of unsaturation from the molecular formula (when available). Neutral fragments frequently lost are carbon monoxide, ethylene, water, ammonia, and hydrogen sulfide.
fragmentations arise from:
- homolysis processes. An example is the cleavage of carbon-carbon bonds next to a heteroatom

- In this depiction single-electron movements are indicated by a single-headed arrow.
- Rearrangement reactions, for example a retro Diels-Alder reaction extruding neutral ethylene:

- or the McLafferty rearrangement. As it is not always obvious where a lone electron resides in a radical cation a square bracket notation is often used.
Some general rules:
- Cleavage occurs at alkyl substituted carbons reflecting the order generally observed in carbocations.
- Double bonds and arene fragments tend to resist fragmentation.
- Allylic cations are stable and resist fragmentation.
- the even-electron rule stipulates that even-electron species (cations but not radical ions) will not fragment into two odd-electron species but rather to another cation and a neutral molecule.
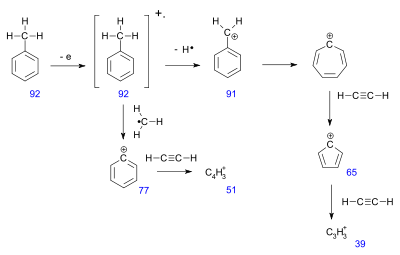
Toluene example
The mass spectrum for toluene has around 30 signals. Several peaks can be rationalized in this fragmentation pattern.
_
Isotope effects
Isotope peaks within a spectrum can help in structure elucidation. Compounds containing halogens (especially chlorine and bromine) produce very distinct isotope peaks. The mass spectrum of methylbromide has two prominent peaks of equal intensity at 94 (M) and 96 (M+2) and then two more at 79 and 81 belonging to the bromine fragment.
Even when compounds only contain elements with less intense isotope peaks (carbon or oxygen), the distribution of these peaks can be used to assign the spectrum to the correct compound. For example, two compounds with identical mass of 150, C8H12N3+ and C9H10O2+, will have two different M+2 intensities which makes it possible to distinguish between them.
Natural abundance of some elements
The next table gives the isotope distributions for some elements. Some elements like phosphorus and fluorine only exist as a single isotope, with a natural abundance of 100%.
Natural abundance of some elements [3] Isotope % nat. abundance atomic mass 1H 99.985 1.007825 2H 0.015 2.0140 12C 98.89 12 (definition) 13C 1.11 13.00335 14N 99.64 14.00307 15N 0.36 15.00011 16O 99.76 15.99491 17O 0.04 18O 0.2 17.99916 28Si 92.23 27.97693 29Si 4.67 28.97649 30Si 3.10 29.97376 32S 95.0 31.97207 33S 0.76 32.97146 34S 4.22 33.96786 37Cl 24.23 35Cl 75.77 34.96885 79Br 50.69 78.9183 81Br 49.31 80.9163 See also
- COmponent Detection Algorithm (CODA), an algorithm used in mass spectrometry data analysis
References
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.