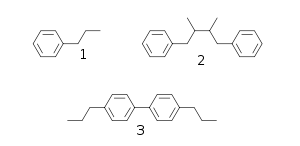
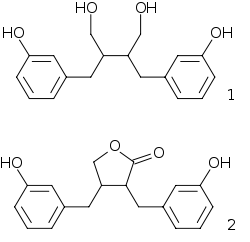
- Lignan
-
Not to be confused with Lignin.
The lignans are a group of chemical compounds found in plants. Lignans are one of the major classes of phytoestrogens, which are estrogen-like chemicals and also act as antioxidants. The other classes of phytoestrogens are the isoflavones and coumestans. Plant lignans are polyphenolic substances derived from phenylalanine via dimerization of substituted cinnamic alcohols (see cinnamic acid), known as monolignols, to a dibenzylbutane skeleton 2. This reaction is catalysed by oxidative enzymes and is often controlled by dirigent proteins.
Many natural products, known as phenylpropanoids, are built up of C6C3 units (a propylbenzene skeleton 1) derived from cinnamyl units just as terpene chemistry builds on isoprene units. Structure 3 is a neolignan.
Some examples of lignans are pinoresinol, podophyllotoxin, and steganacin.
When part of the human diet, some lignans are metabolized to form mammalian lignans known as enterodiol (1) and enterolactone (2) by intestinal bacteria. Lignans that can be metabolized to form mammalian lignans are pinoresinol, lariciresinol, secoisolariciresinol, matairesinol, hydroxymatairesinol, syringaresinol and sesamin.
Contents
Food sources
Flax seed and sesame seed contain higher levels of lignans than most other foods. The principal lignan precursor found in flaxseed is secoisolariciresinol diglucoside. Other sources of lignans include cereals (rye, wheat, oat and barley - rye being the richest source), soybeans, cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli and cabbage, and some fruits, particularly apricots and strawberries.[1]
Secoisolariciresinol and matairesinol were the first plant lignans identified in foods. Pinoresinol and lariciresinol are more recently identified plant lignans that contribute substantially to the total dietary lignan intakes. Typically, Lariciresinol and pinoresinol contribute about 75% to the total lignan intake whereas secoisolariciresinol and matairesinol contribute only about 25%.[2] This distribution may change as the contributions of syringaresinol and hydroxymatairesinol have not properly been quantified in foods.
Sources of lignans:[3]
Source Amount per 100 g Flaxseed 300,000 µg (0.3 g) Sesame seed 29,000 µg (29 mg) Brassica vegetables 185 - 2321 µg Grains 7 - 764 µg Red wine 91 µg A recent study[4] shows the complexity of mammalian lignan precursors in the diet. In the table below are a few examples of the 22 analyzed species and the 24 lignans identified in this study.
Mammalian lignan precursors as aglycones (µg / 100 g). Major compound(s) in bold.
Foodstuff Pinoresinol Syringaresinol Sesamin Lariciresinol Secoisolariciresinol Matairesinol Hydroxymatairesinol Flaxseed 871 48 not detected 1780 165759 529 35 Sesame seed 47136 205 62724 13060 240 1137 7209 Rye bran 1547 3540 not detected 1503 462 729 1017 Wheat bran 138 882 not detected 672 868 410 2787 Oat bran 567 297 not detected 766 90 440 712 Barley bran 71 140 not detected 133 42 42 541 Medicinal Uses
Lignans are capable of binding to estrogen receptors and interfering with the cancer-promoting effects of estrogen on breast tissue.[citation needed] Lignans such as podophyllotoxin are therefore being studied for their possible effects on breast, prostate and colon cancer. Lignans are also good antioxidants scavenging free radicals that may play a role in some diseases.[5]
See also
- Nutrition
- Phytonutrients
References
Footnotes
- ^ Linus Pauling Institute at Oregon State University
- ^ Linus Pauling Institute at Oregon State University
- ^ Milder IE, Arts IC, van de Putte B, Venema DP, Hollman PC (2005). "Lignan contents of Dutch plant foods: a database including lariciresinol, pinoresinol, secoisolariciresinol and matairesinol". Br. J. Nutr. 93 (3): 393–402. doi:10.1079/BJN20051371. PMID 15877880.
- ^ Smeds AI, et al. (2007). "Quantification of a Broad Spectrum of Lignans in Cereals, Oilseeds, and Nuts". J.Agric. Food. Chem. 55 (4): 1337–1346. doi:10.1021/jf0629134. PMID 17261017.
- ^ Liu H., "Extraction and Isolation of compounds from Herbal medicines" in 'Traditional Herbal Medicine Research Methods', ed by Willow JH Liu 2011 John Wiley and Sons, Inc
General references
External links
Phenylpropanoids Hydroxycinnamic acids | Chromones (Furanochromones) | Cinnamaldehydes | Monolignols | Coumarins | Flavonoids | Phenylpropenes | Stilbenoids | Lignans | Lignins | SuberinsLignan glycosides Mammalian lignans (enterolignans) Enterodiol | Enterolactone | Lariciresinol | Hydroxymatairesinol | SyringaresinolNeolignans Eusiderin | Megaphone | Rhaphidecursinol A | Rhaphidecursinol BFlavonolignans Categories:- Types of phenylpropanoids
- Lignans
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.