- Comparison of display technology
-
This is a comparison of various properties of different display technologies.
Further information: Comparison CRT, LCD, Plasma and History of display technologyContents
General characteristics
Comparison of various properties of different display technologies Display technology Screen shape Largest known diagonal Typical use Usable in
bright room(in) (cm) Eidophor front projection Flat (limited only by brightness) TV No Shadow mask CRT Spherical curve or Flat 42[1] 107 Computer monitor, TV Yes Aperture grille CRT Cylindrical curve or Flat 42[2] 107 Computer monitor, TV Yes Monochrome CRT Spherical curve or Flat 30[3] 76 Computer monitor, TV,
Radar display, OscilloscopeYes Direct view Charactron CRT Spherical curve 24 61 Computer monitor,
Radar displayNo CRT self-contained rear-projection Flat lenticular 80[4] 203 TV Yes CRT front projection Flat (limited only by brightness) TV or presentation No Plasma display panel (PDP) Flat 152[5] 386 TV Yes Direct view LCD Flat 108[6] 274 Computer monitor, TV Yes LCD self-contained rear-projection Flat lenticular 70[7] 178 TV Yes LCD front-projection Flat (limited only by brightness) TV or presentation Yes DLP self-contained rear-projection Flat lenticular 120[8] 305 TV Yes DLP front-projection Flat (limited only by brightness) TV or presentation Yes LCoS self-contained rear-projection Flat 110[9] 279 TV Yes LCoS front-projection Flat (limited only by brightness) TV or presentation Yes Laser self-contained Rear Projection Flat lenticular 75[10] 191 TV Yes SED Flat 55[11] 140 Computer monitor, TV Yes FED Flat ? ? Computer monitor, TV Yes EPD (e-paper) Flat (flexible) ? ? Electronic paper Yes OLED Flat 40[12] 102 Computer monitor, TV, Mobile phone Yes QDLED[13][14][15][16] N/A N/A N/A N/A Yes IMOD Flat 1.2[17] 3 Mobile phone[18] Yes Laser Phosphor Display (LPD) Flat / Box ? ? Computer monitor Yes Virtual retinal display Any shape N/A N/A Experimental, possibly
virtual realityDepends
on systemDisplay technology Screen shape Largest known diagonal Typical use Usable in
bright room(in) (cm) Temporal characteristics
Different display technologies have vastly different temporal characteristics, leading to claimed perceptual differences for motion, flicker, etc.
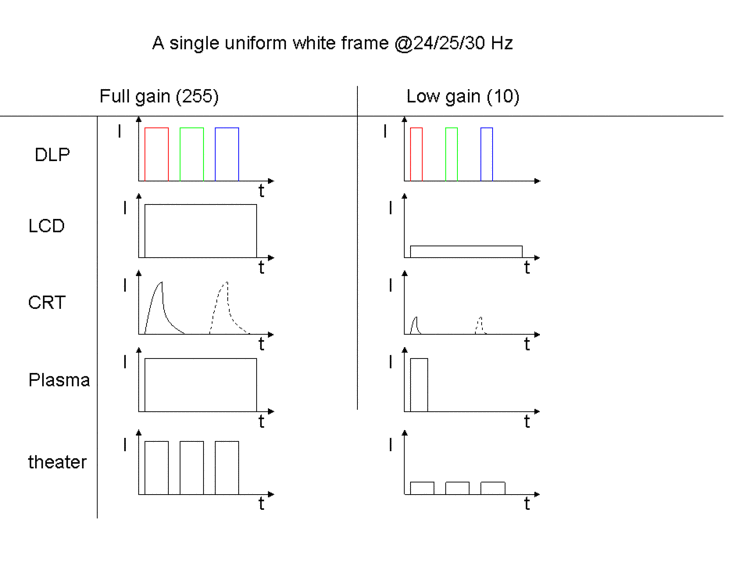
The figure shows a sketch of how different technologies present a single white/grey frame. Time and intensity is not to scale. Notice that some have a fixed intensity, while the illuminated period is variable. This is a kind of pulse-width modulation. Others can vary the actual intensity in response to the input signal.
- Single-chip DLPs use a kind of "chromatic multiplexing" in which each color is presented serially. The intensity is varied by modulating the "on" time of each pixel within the time-span of one color. Multi-chip DLPs are not represented in this sketch, but would have a curve identical to the plasma display.
- LCDs have a constant (backlit) image, where the intensity is varied by blocking the light shining through the panel.
- CRTs use an electron beam, scanning the display, flashing a lit image. If interlacing is used, a single full-resolution image results in two "flashes". The physical properties of the phosphor are responsible for the rise and decay curves.
- Plasma displays modulate the "on" time of each sub-pixel, similar to DLP.
- Movie theaters use a mechanical shutter to illuminate the same frame 2 or 3 times, increasing the flicker frequency to make it less perceptible to the human eye.
See also
References
- ^ Shadow mask CRT
- ^ Aperture grille CRT
- ^ Monochrome CRT
- ^ Self-contained Rear Projection CRT
- ^ World's largest 152-Inch Full HD 3D Plasma Display
- ^ Direct View LCD
- ^ LCD Rear Projection
- ^ DLP
- ^ LCoS
- ^ [1]
- ^ SED
- ^ OLED
- ^ Quantum Dots QDTV Displays from Nanoco Technologies
- ^ Quantum Dot LEDs
- ^ LED's Outpower QDLED's
- ^ Ocean NanoTech research in QDLEDs
- ^ Mirasol
- ^ IMOD
Categories:- Display technology
- Technological comparison
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.