- Dirhenium decacarbonyl
-
Dirhenium decacarbonyl 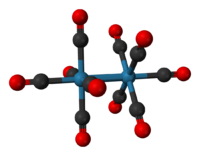 bis(pentacarbonylrhenium)(Re—Re)Other namesRhenium carbonyl; rhenium pentacarbonyl
bis(pentacarbonylrhenium)(Re—Re)Other namesRhenium carbonyl; rhenium pentacarbonylIdentifiers CAS number 14285-68-8 
ChemSpider 436546 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - [Re].[Re].[C-]#[O+].[O+]#[C-].[O+]#[C-].[O+]#[C-].[O+]#[C-].[O+]#[C-].[O+]#[C-].[O+]#[C-].[O+]#[C-].[O+]#[C-]
Properties Molecular formula Re2(CO)10 Molar mass 652.52 g/mol Melting point 170C (decomposes)
Hazards EU classification Harmful (Xn) R-phrases R20 S-phrases S36  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Dirhenium decacarbonyl is an inorganic compound with the formula Re2(CO)10. Commercially available, it is used as a starting point for the synthesis of many rhenium carbonyl complexes. It was first reported in 1941 by Walter Hieber who prepared it by carbonylation of Re2O7.[1] The compound consists of a pair of square pyramidal Re(CO)5 units joined via a Re-Re bond. Mn2(CO)10 and Tc2(CO)10 adopt the same structure.
Reaction with various halogens cleave the Re-Re bond:[2]
- Re2(CO)10 + X2 → 2 Re(CO)5X (X = Cl, Br, I)
When bromine is used, bromopentacarbonylrhenium(I) is formed; it is itself an intermediate for many more rhenium complexes.
References
- ^ W. Hieber, H. Fuchs (1941). "Über Metallcarbonyle. XXXVIII. Über Rheniumpentacarbonyl" (in German). Zeitschrift für anorganische und allgemeine Chemie 248 (3): 256–268. doi:10.1002/zaac.19412480304.
- ^ Steven P. Schmidt, William C. Trogler, Fred Basolo (1990). "Pentacarbonylrhenium Halides". Inorganic Syntheses 28: 154–159. doi:10.1002/9780470132593.ch42.
Rhenium compounds Categories:- Rhenium compounds
- Carbonyl complexes
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
