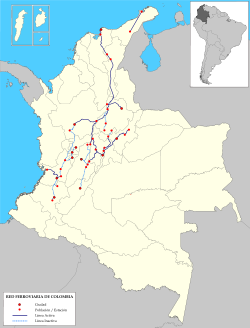
- Rail transport in Colombia
-
The Colombia railway network has a total length of 3,304 km. There are 150 km of 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) standard gauge connecting Cerrejón coal mines to maritime port of Puerto Bolivar at Bahia de Portete, and 3,154 km of 3 ft (914 mm) narrow gauge of which 2,611 km are in use.[1] The state-owned railway company (National Railways of Colombia) was liquidated in the 1990s.
Contents
Railway concessions
Railway concessions were awarded on July 27, 1999 to Ferrocarriles del Norte de Colombia S.A. (FENOCO), as the Atlantic concession, and on November 4, 1998 to the Sociedad Concesionaria de la Red Férrea del Pacífico SA, later named Tren de Occidente SA as the Pacific concession. Since 1991 the section La Loma - Puerto Drummond, with 192 kilometers, transports coal. Also from July 2003 the section Bogota - Belencito, with 257 kilometers, is operating on the Atlantic concession transporting cement. In the Pacific concession the section between La Paila and Buenaventura has a total of 292 kilometers.
In November 2009 the Colombian Government set up a new team of consultants and specialists to oversee the estimated $440m Sistema Ferroviario Central railway concession. The project involves building a 1,050 km railway from La Dorada to Chiriguaná, linking Colombia's central area to the Santa Marta port on the Atlantic coast. The winning team will build the La Dorada stretch, renovate the stretches connecting the districts of La Dorada and Buenos Aires, Puerto Berrío, Envigado and La Dorada and Facatativa, and maintain the Chiriguaná-Buenos Aires stretch. The tender was suspended due to concerns of corruption, but restarted in February 2011.[2]
Investment programme
There is a US$600 million investment programme planned for 2008 and studies for a US$350 million new line between Puerto Berrío and Saboya.[3] Under this contract sections of the Atlantic network Neiva – Villavieja and 177 km Ibagué – La Dorada would be built. Other sections to be built include Sogamoso – Tunja and Puerto Berrío – Cisneros.
China is looking into constructing a 220 km (136 mi) railway between the port cities Buenaventura and Cartagena, connecting Colombia's Pacific and Caribbean coasts. This railway alternative would compete with the Panama Canal.[4][5][6] Besides linking two coasts, China aims to make the import of Colombian coal and the export of Chinese manufactured goods to the Americas easier with this railway. Colombia hopes China's growing economic presence in the region will further the ratification of the Free Trade Agreement with the United States, the country's biggest trading partner. A inter-oceanic railway link will benefit Colombia's economic growth [7].
Maps
Stations served
Main article: Railway stations in ColombiaMetro
Main article: Metro de MedellínMedellín is the only city thus far (2008) to have built a metro (rapid transit) system. Consultants are to be appointed in 2008 to develop a metro system in the capital city Bogotá.[8] (see → Bogotá Metro)
Timeline
1880s
The construction of the Bogotá Savannah Railway begins in 1882.
1920s
Railways are built with English investment along the Magdalena River. Baldwin engines are used.[citation needed]
2008
A July 5 meeting between Venezuela, Colombia and Ecuador regarding a railway for freight and passengers to link the three countries, and the Pacific ocean with the Atlantic ocean was held.
2009
- Vale to build branches from the Atlantic railway to connect its coal mine to its new port at Puerto Córdoba
- Build/Rebuild/Maintain concession for 1,050 km from La Dorada to Santa Marta port on the Atlantic coast.
2011
- Feb. 14, 2011 - The Chinese Government plans to cooperate with Colombia in building a 220km transcontinental railway which would link Colombia's Atlantic and Pacific coasts, according to a British newspaper.
Railway links with adjacent countries
 Venezuela - yes, but inoperative (Railroad of Cúcuta) - proposed to be restored
Venezuela - yes, but inoperative (Railroad of Cúcuta) - proposed to be restored Brazil - no
Brazil - no Ecuador - no - proposed
Ecuador - no - proposed Peru - no
Peru - no Panama - no
Panama - no
See also
References
- ^ "Country profile: Colombia" (PDF). Library of Congress – Federal Research Division. February 2007. pp. 18. http://lcweb2.loc.gov/frd/cs/profiles/Colombia.pdf. Retrieved 2009-01-08.
- ^ "Ferroviario Central Back On The Tenders List - Corporate Financing Week". http://www.corporatefinancingweek.com/file/96214/ferroviario-central-back-on-the-tenders-list.html. Retrieved 2011-02-19.
- ^ "Colombia to launch US$600m tender package". Railway Gazette International. October 2007. http://www.railwaygazette.com/news_view/article/2007/10/7776/colombia_to_launch_us600m_tender_package.html.
- ^ "China in talks over Panama Canal rival". Financial Times. 2011-02-13. http://www.ft.com/cms/s/0/7e14756c-37a9-11e0-b91a-00144feabdc0.html. Retrieved 2011-02-14.
- ^ Wheatley, Jonathan (2011-02-14). "Colombia’s smart canal". Financial Times. http://blogs.ft.com/beyond-brics/2011/02/14/colombias-smart-canal/. Retrieved 2011-02-14.
- ^ "China in talk with Columbia over transcontinental railway: Colombian president". Xinhuanet. 2011-02-14. http://news.xinhuanet.com/english2010/china/2011-02/14/c_13731374.htm. Retrieved 2011-02-14.
- ^ Colombia’s Railway Alternative to the Panama Canal
- ^ "Urban Rail News in Brief". Railway Gazette International. May 2008. http://www.railwaygazette.com/news_view/article/2008/05/8416/urban_rail_news_in_brief-5.html.
External links
Rail transport in South America Sovereign states Dependencies and
other territories- Aruba
- Bonaire
- Curaçao
- Falkland Islands
- French Guiana
This Colombia-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. Categories:- Rail transport in Colombia
- Colombia stubs
- South America rail transport stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
Transport in Colombia — Transportation in Colombia is regulated by the Ministry of Transport.Road travel is the main means of transport; almost 70 percent of cargo is transported by road, as compared with 27 percent by railroad, 3 percent by internal waterways, and 1… … Wikipedia
Rail transport by country — This page provides an index of articles on Rail transport by country. Other indexes available include: *Transportation by country *List of railway companies by country *List of countries by rail transport network size *Rail usage statistics by… … Wikipedia
Transport in present-day nations and states — Transport or transportation is the movement of people and goods from one place to another. It is an important factor for every country, in order to maintain a strong economy, for military defense, and for access to and between a country s people … Wikipedia
2008 in rail transport — Events By month January events February events * ndash; opening of Santo Domingo Metro. * February 27 ndash; National Express Group changes the name of English railway operating company one to National Express East Anglia as part of a company… … Wikipedia
July 2008 in rail transport — Events July 1 July 5 ; July 1:* flagicon|China ndash; Construction work for the Shanghai–Nanjing high speed railway officially begins in China. The convert|300|km|sing=on long railway will cost 39.45 billion yuan (about 5.7 billion US dollars)… … Wikipedia
Colombia — This article is about the country. For other uses and spellings, see Colombia (disambiguation) and Colombia (disambiguation). Republic of Colombia República de Colombia (Spanish) … Wikipedia
Transport in Chile — An enlargeable relief map of Chile with major roads and rail lines depicted. Transport in Chile is mostly by road. The south of the country is not connected to central Chile by road, except through Argentina, and water transport also plays a part … Wikipedia
Transport in Venezuela — Railways = total: 7000 km (248 km privately owned) standard gauge: 682km (40km electrified) RailGauge|sg ( [http://www.indexmundi.com/venezuela/railways.html Index Mundi: Venezuela Railways] )City with underground railway system: * Caracas (El… … Wikipedia
Transport in Panama — Transportation in Panama is fairly well developed. The majority of the trips are done by car while a great part in public transport. The public transportation system is in need of modernization and other improvements. = Railways = Main articles:… … Wikipedia
Transport in Ecuador — Railways = total: 812 km (single track) narrow gauge: 812 km RailGauge|42 gauge Railway links with adjacent countries * Colombia ndash; no proposed * Peru ndash; no Timeline 2008 * July 5 meeting between Venezuela, Colombia and Ecuador regarding… … Wikipedia