- Transport in Chile
-
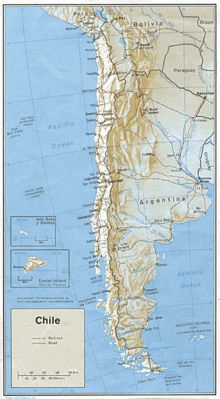
Transport in Chile is mostly by road. The south of the country is not connected to central Chile by road, except through Argentina, and water transport also plays a part there. The railways were historically important in Chile, but now play a relatively small part in the country's transport system. Because of the country's geography and long distances between major cities, aviation is also important.
Contents
Road transport
Highways
- total: 79,800 km
- paved: 41,012 km
- unpaved: 38,788 km (1996 est.)
- Chile Highway 5
- Chile Highway 7
- Chile Highway 9
- Chile Highway 68
- Chile Highway 181
Freeways
2,653 km
- [[Chile Freeway 6]
- Chile Freeway 8
- Chile Autopista del Sol
- Chile Autopista del Itata
Buses
Buses are now the main means of long distance transportation in Chile, following the decline of the rail network.[1] The bus system covers the whole country, from Arica to Santiago (a 30 hour journey) and from Santiago to Punta Arenas (about 40 hours, with a change at Osorno). There are also international services to most other countries in South America. Longer-distance services are mostly on semi-cama (reclining seat) or cama (sleeper) buses, often double deck.
Santiago began its public bus system Transantiago in 2007. Concepción's "Bio Bus" integrates with the electric train, Biotren, and is based on a dedicated right of way for buses.
Railways
Rail transport in Chile
- total: 6,782 km
- broad gauge: 3,743 km 5 ft 6 in (1,676 mm) gauge (1,653 km electrified)
- narrow gauge: 116 km 3 ft 6 in (1,067 mm) gauge; 2,923 km 1,000 mm (3 ft 3 3⁄8 in) gauge (40 km electrified) (1995)
- standard gauge: 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) about 40 km from Arica to Tacna, Peru
Not all lines connect.
Chile's railways (except for a few dedicated industrial lines [2] ) are operated by the state owned company Empresa de los Ferrocarriles del Estado (EFE), which completed a major investment programme in 2005.[3]
The rail system once served the entire country, running rail lines from Arica in the north to Puerto Montt in the south. Due partly to the nature of the terrain and evolution in transportation systems, rail travel has suffered greatly at the hands of bus and air competition. The train usually takes longer to reach a destination than a bus, and the comfort is comparable. Prices also tend to be uncompetitive. Rail freight transport has also suffered at the hands of the trucking industry and will continue to do so due to the immense leverage the truck driver's union can bring to bear if they were to feel threatened.
The Ferrocarril de Antofagasta a Bolivia is a metre gauge railway in the north of the country. It was originally constructed in 2 ft 6 in (762 mm) gauge.
The northern rail line out of Santiago is now disused past the intersection with the Valparaíso line. Until there it is used nearly exclusively for freight. Although the rest of the northern line is still in place, it is in a state of serious disrepair.
The southern line runs as far as Puerto Montt and is electrified as far as the city of Temuco, from where diesel locomotives are used. Due to lack of budget and care, the 389 km Temuco to Puerto Montt section was abandoned in 1992 but after a $44m upgrade it has been back in use since 6 December 2005 with daily service between Victoria (north of Temuco) and Puerto Montt; today, however only the service between Victoria and Temuco still operates.[4]
Work to build/restore(?) the South Trans-Andean Railway link between Zapala, Argentina and Lonquimay, Chile was underway in 2005.[5] Possible break-of-gauge. Possible rack railway.[6] Construction was undertaken by Patagonia Ferrocanal SA, formed and funded by the province.[7] The first 7 km was completed by January 2006.[8]
There have been repeated case studies regarding the installation of a high speed line between the cities of Valparaíso and Santiago, some even considering maglev trains, but no serious action has ever been taken on the matter.
Rail links with adjacent countries
 Bolivia - yes - same gauge 1,000 mm (3 ft 3 3⁄8 in) - from Arica to La Paz, Bolivia
Bolivia - yes - same gauge 1,000 mm (3 ft 3 3⁄8 in) - from Arica to La Paz, Bolivia
 Argentina - Central Trans-Andean Railway - abandoned 1984 – 100 km of mountain railway of 1,000 mm (3 ft 3 3⁄8 in) gauge with rack railway sections - break of gauge 1,676 mm (5 ft 6 in)/1,000 mm (3 ft 3 3⁄8 in) at either end. Concession planned to re-open line.[3]
Argentina - Central Trans-Andean Railway - abandoned 1984 – 100 km of mountain railway of 1,000 mm (3 ft 3 3⁄8 in) gauge with rack railway sections - break of gauge 1,676 mm (5 ft 6 in)/1,000 mm (3 ft 3 3⁄8 in) at either end. Concession planned to re-open line.[3]
 Peru - yes - a single 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) gauge connection between the northern Chilean city of Arica and Tacna in Southern Peru.
Peru - yes - a single 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) gauge connection between the northern Chilean city of Arica and Tacna in Southern Peru.
- Peru
Cities with Metros
- Santiago (Metro de Santiago) website
- Valparaíso website
- Concepción (Biotren)
Ports and merchant marine
Ports
- Iquique
- Puerto Montt
- Punta Arenas
- San Antonio
- San Vicente
- Talcahuano
- Tocopilla
- Valparaíso
Merchant marine
total: 45 ships (1,000 gross register tons (GRT) or over) totaling 580,749 GRT/860,034 metric tons deadweight (DWT) ships by type: (1999 est.)
- Passenger ships 3
- petroleum tanker 4
- roll-on/roll-off 4
- vehicle carrier 2
Aviation
Airports - with paved runways
- total: 62
- over 3,047 m: 6
- 2,438 to 3,047 m: 6
- 1,524 to 2,437 m: 20
- 914 to 1,523 m: 20
- under 914 m: 10 (1999 est.)
Arturo Merino Benitez International Airport, located in Santiago, is Chile's largest aviation facility.
Airports - with unpaved runways
- total: 310
- over 3,047 m: 1
- 2,438 to 3,047 m: 4
- 1,524 to 2,437 m: 12
- 914 to 1,523 m: 68
- under 914 m: 223 (1999 est.)
National airlines
- LAN Airlines (formerly LanChile)
- Sky Airline
- Principal Airlines
Bridges
Chacao Channel
Chacao Channel bridge is a planned suspension bridge that was to link the island of Chiloé with mainland Chile crossing the Chacao Channel. It was one of the several projects that were planned to commemorate the Chile's bicentennial in 2010. If completed, it would have been the largest suspension bridge in South America.
Pipelines
- crude oil 755 km
- petroleum products 780 km
- natural gas 320 km
Mountain passes
- Cardenal Antonio Samoré Pass, Los Lagos Region, Route 215-CH
- Carirriñe Pass, Los Ríos Region
- Chungara–Tambo Quemado, Arica and Parinacota Region
- Paso de Jama, Antofagasta Region
- Huahum Pass, Los Ríos Region
- Icalma International Pass, Araucanía Region
- Paso Internacional Los Libertadores, Valparaíso Region
- Lilpela Pass, Los Ríos Region
- Paso de Los Patos, Valparaíso Region
- Mamuil Malal Pass, Araucanía Region
- Pino Hachado Pass, Araucanía Region
- San Francisco Pass, Atacama Region
- Uspallata Pass, Valparaíso Region
See also
External links
References
- ^ Omnilineas website
- ^ Thomas Salt (2006-04-01). "Automation gets the most out of mining railway infrastructure". Railway Gazette International. http://www.railwaygazette.com/news/single-view/view//automation-gets-the-most-out-of-mining-railway-infrastructure.html.
- ^ a b John Kolodziejski (2006-04-01). "Record investment boosts EFE's passenger business". Railway Gazette International. http://www.railwaygazette.com/news/single-view/view//record-investment-boosts-efes-passenger-business.html.
- ^ "Passengers return to Puerto Montt". Railway Gazette International. 2006-01-01. http://www.railwaygazette.com/news/single-view/view//passengers-return-to-puerto-montt.html.
- ^ IRJ March 2005
- ^ "IIRSA". Initiative For Regional Infrastructure Integration In South America. 2005-09-01. http://www.iadb.org/biz/ppt/092305tuliod.pdf.
- ^ "Work starts on trans-Andean link". Railway Gazette International. 2005-02-01. http://www.railwaygazette.com/news/single-view/view//work-starts-on-trans-andean-link.html.
- ^ "Finance". Railway Gazette International. 2006-01-01. http://www.railwaygazette.com/news/single-view/view//finance-22.html.
 This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the CIA World Factbook.
This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the CIA World Factbook.Transport in the Americas - North America
- South America
Sovereign states - Antigua and Barbuda
- Argentina
- Bahamas
- Barbados
- Belize
- Bolivia
- Brazil
- Canada
- Chile
- Colombia
- Costa Rica
- Cuba
- Dominica
- Dominican Republic
- Ecuador
- El Salvador
- Grenada
- Guatemala
- Guyana
- Haiti
- Honduras
- Jamaica
- Mexico
- Nicaragua
- Panama
- Paraguay
- Peru
- Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Saint Lucia
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- Suriname
- Trinidad and Tobago
- United States
- Uruguay
- Venezuela
Dependencies and
other territories- Anguilla
- Aruba
- Bermuda
- Bonaire
- British Virgin Islands
- Cayman Islands
- Curaçao
- Falkland Islands
- French Guiana
- Greenland
- Guadeloupe
- Martinique
- Montserrat
- Navassa Island
- Puerto Rico
- Saint Barthélemy
- Saint Martin
- Saint Pierre and Miquelon
- Saba
- Sint Eustatius
- Sint Maarten
- South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands
- Turks and Caicos Islands
- US Virgin Islands
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.