- Mona Islands
-
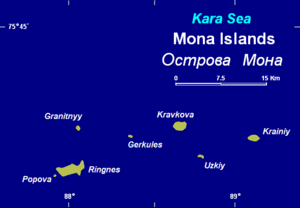
The Mona Islands (Russian: Острова Мона) is a group of a few scattered small islands covered with tundra vegetation. They are located in the Kara Sea, about 30 km north of the western coast of the Taymyr Peninsula in Siberia, Russia.
The sea surrounding the Mona Islands is covered with pack ice in the winter, which is long and bitter. There are numerous ice floes even in the summer. Kravkov Island (Остров Кравкова) is one of the biggest islands, but it is still only about 3 km square.
Small Gerkules Island (Остров Геркулес), located in the middle of the group, is named after lost explorer Vladimir Rusanov's ship.
Ringnes Island (Остров Рингнес) located at the western end of the group, was named after the Norwegian Ringnes brewery that financed Otto Sverdrup's Arctic expeditions. Other islands are called Granitnyy (Остров Гранитный) and Krainiy (Остров Крайний).
The Mona Islands were named by Fridtjof Nansen after Henrik Mohn, a Norwegian meteorologist. Mohn worked out and published the meteorological observations of various polar expeditions, including those of Nansen in the "Fram" (1893-6). "Mona" is a genitive case in Russian, meaning "(islands) of Mon" and this name has stuck, especially since the Germans used ("Mona Inseln"), based on the Russian version of the name, during their campaigns in World War II. Since then "Mona Islands" has become popular and its use has been widespread in this manner for many decades and in many modern maps and atlases. "Mohn Islands", which would be the grammatically correct way of naming these islands in English, is so rare that there are practically no maps now where the name "Mona" is not used.
This island group belongs to the Krasnoyarsk Krai administrative division of the Russian Federation.
History
Russian scholars deem that Vladimir Rusanov and his ill-fated party disappeared somewhere around the area of the Mona Islands. Relics were found in 1934 in Gerkules Island, including a wooden pole with the inscription "Gerkules 1913", broken old sledges and a fragment of a cartridge box.[1] Other remainders were found in Popova Chukchina, an island of another group not far away (Kolosovykh Islands) during and expedition organized in 1937 by the Arctic Institute of the Soviet Union.
During the Second World War there was much activity near these lonely islands. Kriegsmarine heavy cruiser Admiral Scheer, under Commander Wilhelm Meendsen-Bohlken, destroyers Friedrich Eckoldt, Erich Steinbrinck and Richard Beitzen, entered the Kara Sea along with submarines U 601 (Captain Grau) and U 251 (Lt. Captain Timm) in August 1942, in order to destroy Soviet warships.
The Germans knew that many ships of the USSR fleet had sought refuge in the Kara Sea because of the protection that its icy pack provided during ten months in a year. The large-scale naval operation in order to enter the Kara Sea and destroy as many Russian vessels as possible was named Operation Wunderland.
Since May 1993 the Mona Islands are part of the Great Arctic State Nature Reserve, the largest nature reserve of Russia.
References
See also
Coordinates: 75°42′N 88°29′E / 75.7°N 88.483°E
Categories:- Islands of the Kara Sea
- Campaigns and theatres of World War II
- Islands of Krasnoyarsk Krai
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.