- Cryogenine
-
This article is about the alkaloid from the plants in the genus Heimia. For the antipyretic drug, see Phenicarbazide.
Cryogenine 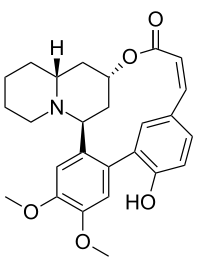
Systematic (IUPAC) name (10α)-4,5-dimethoxy-2-hydroxylythran-12-one Clinical data Pregnancy cat. ? Legal status ? Identifiers CAS number 10308-13-1 
ATC code None PubChem CID 5315204 ChemSpider 4474587 
ChEMBL CHEMBL1173218 
Chemical data Formula C26H29NO5 Mol. mass 435.512 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Cryogenine, also known as vertine or (10α)-4,5-dimethoxy-2-hydroxylythran-12-one, is a biphenylquinolizidine lactone alkaloid from the plants Sinicuichi (Heimia salicifolia) and H. myrtifolia. The compound has no psychoactive properties in humans up to 310 mg, but has shown anti-inflammatory activity similar to aspirin.[1]
The freebase form melts at 250-251 °C and is soluble in moderately polar organic solvents such as chloroform, methylene chloride, benzene, and methanol, but is insoluble in water and petroleum ether.
In the development of thin layer chromatography plates with diazotized p-nitroaniline spray, cryogenine produces a purple spot (as does sinicuichine, another biphenylquinolizidine lactone alkaloid found in Heimia species).
See also
References
- ^ M. H. Malone , A. Rother (1994). "Heimia salicifolia: A phytochemical and phytopharmacologic review". J. Ethnopharmacol 42 (3): 135–159. doi:10.1016/0378-8741(94)90080-9. PMID 7934084.
Categories:- Alkaloids
- Phenol ethers
- Lactones
- Alkenes
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
