List of Mendelian traits in humans
- List of Mendelian traits in humans
-
In Mendelian inheritance, a child receiving a dominant allele from either parent will have the dominant form of the trait. Only those that received the recessive allele from both parents present with the recessive phenotype. Purely Mendelian traits are a tiny minority of all traits, since most phenotypic traits exhibit incomplete dominance, codominance, and contributions from many genes.

Attached earlobes were previously believed to be a recessive phenotype.
The recessive phenotype may theoretically skip any number of generations, lying dormant in heterozygous "carrier" individuals until they have children with someone who also has the recessive allele and both pass it on to their child.
Examples
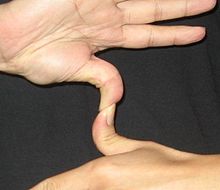
These traits include:
Traits previously believed to be Mendelian
Some traits were previously believed to be Mendelian, but their inheritance is (probably) based on more complex genetic models[citation needed], possibly involving more than one gene. These include [1]:
See also
References
- ^ http://udel.edu/~mcdonald/mythintro.html
External links
Wikimedia Foundation.
2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
Mendelian inheritance — For a non technical introduction to the topic, see Introduction to genetics. Part of a series on Genetics Key components Chromosome DNA • RNA Genome Heredity … Wikipedia
List of geneticists — This is a list of people who have made notable contributions to genetics. The growth and development of genetics represents the work of many people. This list of geneticists is therefore by no means complete. Contributors of great distinction to… … Wikipedia
Human genetics — describes the study of inheritance as it occurs in human beings. Human genetics encompasses a variety of overlapping fields including: classical genetics, cytogenetics, molecular genetics, biochemical genetics, genomics, population genetics,… … Wikipedia
Dominance (genetics) — For other uses, see Dominance. A pedigree chart shows how genes are inherited. Dominance in genetics is a relationship between two variant forms (alleles) of a single gene, in which one allele masks the effect of the other in influencing some… … Wikipedia
Albinism — Albino redirects here. For other uses, see Albino (disambiguation). Albinism Classification and external resources A black child with albinism ICD 10 … Wikipedia
Race (classification of humans) — Race Classification Race (classification of humans) Genetics … Wikipedia
Tongue — Infobox Anatomy | Name = Tongue Latin = lingua GraySubject = 242 GrayPage = 1125 Caption = A human tongue Caption2 = Width = 250 |fjhfkdvhbufnbjg Precursor = pharyngeal arches, lateral lingual swelling, tuberculum impar [EmbryologyUNC|hednk|024]… … Wikipedia
Eye color — is a polygenic trait and is determined by the amount and type of pigments in the eye s iris.Wielgus AR, Sarna T. Melanin in human irides of different color and age of donors. Pigment Cell Res. 2005 Dec; 18(6):454 64. PMID 16280011.] Prota G, Hu… … Wikipedia
Cleft chin — Example of a cleft chin (William McKinley) Human jaw front view … Wikipedia
Human hair color — Hair color is the pigmentation of hair follicles due to the two types of melanin, eumelanin and phaeomelanin. Generally, if more melanin is present in the hair, the color of the hair is darker; if less melanin is present, the hair color is… … Wikipedia