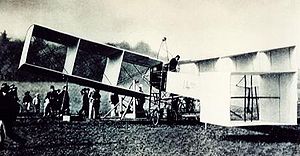
- Santos-Dumont 14-bis
-
For the Brazilian band, see 14 Bis (band).
14-bis Role Experimental aircraft Manufacturer Alberto Santos-Dumont Designer Alberto Santos-Dumont First flight September 7, 1906 Number built 1 The 14-bis (Quatorze-bis), also known as Oiseau de proie (French for "bird of prey"), was a pioneer-era canard biplane designed and built by Brazilian inventor Alberto Santos-Dumont. On 23 October 1906, in Paris, France, it performed the first officially witnessed unaided takeoff and flight by a heavier-than-air aircraft.
Contents
Conception, development, and initial tests
In June 1905, Gabriel Voisin tested a glider by having it towed by a fast boat down the River Seine. The glider's wing configuration was made up of Hargrave cells, a box kite-type structure that allowed for great lift and structural strength with minimal weight. Voisin was towed into the air and flew for over 500 ft (150 m) as the boat pulled him and his aircraft. In the aviation-crazy Paris of the early 1900s, this established the Hargrave cells as a configuration to be developed into heavier-than-air aircraft, not simply into kites. Santos-Dumont lived in Paris at the time, and was by then one of the most active "aeronauts" in Europe, having developed a long series of non-rigid airships that displayed unparalleled agility, speed, endurance, and ease of control.
During late 1905 and early 1906, French aviation authorities, seeing the rapid development in aviation at the time, offered prizes for the first heavier-than air machines to be flown for 25 meters and for 100 meters. Ferdinand Ferber, a captain in the French Army, was experimenting with gliders and kept in touch with Octave Chanute and with the Wright brothers. Voisin teamed up with Louis Blériot to develop the boat-towed glider into a fixed-wing aircraft.
At around that time, while watching the Côte d'Azur speedboat races, Santos-Dumont noticed that Antoinette-type engines, made by Léon Levavasseur, offered great power and were quite lightweight.
Putting all this together, Santos-Dumont had a Hargrave-cell biplane, powered by an Antoinette engine built. The work was carried out in secret; known only to his team of builders and craftsmen. The wings were at the very back configured in a dihedral, each wing containing three cells. The 24 hp (18 kW) Antoinette sat between the wings, with the pilot's compartment immediately ahead (where the pilot stood), and with the pusher-propeller immediately behind. A movable cell at the nose, actuated by cables originally manufactured for church-tower clocks, allowed for steering and altitude adjustments. This forward-mounted-mini-wing layout would later come to be called a "canard", from the French word for "duck", after a Bleriot aircraft of the same layout was said to look like one. The structures of the Santos-Dumont biplane were made of bamboo, with Japanese silk surfaces, and joints made of aluminum, a very exotic material at the time.
The aircraft was transported from Neuilly, where it was built, to the nearby Bagatelle field adjacent to the chateau of that name in the Bois de Boulogne, where it could be tested. In order to simulate flight-like conditions, Santos-Dumont attached the aircraft to the belly of his latest non-rigid airship, the Number 14, creating the first attempt to a hybrid airship. Due to this configuration, the plane came to be known as "14-bis". The forces imposed by the aircraft pulled at the airship's envelope in dangerous ways, nearly tearing it and allowing for limited control. The danger of such tests caused Santos-Dumont and his team to quickly abandon them, although some constructive information was obtained that led to adjustments in the balance and weight placement of the plane.
Santos-Dumont then connected a steel cable to the tops of two poles, one taller than the other, much like a zip-line or tyrolienne of today. The aircraft was hung by a rope and attached by a pulley to the steel cable. It was then pulled by a donkey until it rested by the taller pole, and then released and allowed to slide down the cable toward the lower pole. In this manner, the center of gravity of the aircraft was established and adjusted, and much was learned about its stability. Photographs of these tests show the vehicle being pulled up along the cable by the donkey back to the higher position. This gives the appearance that the plane was tested while being pulled by a donkey.
By August 1906, the aircraft was transported back to Bagatelle, where Santos-Dumont performed what would be called today "fast-taxi tests". It was found that the engine was not powerful enough to safely reach flight speeds, and was replaced by a 50 hp (37 kW) Antoinette, a V-8 design capable of 1,500 rpm. Early September saw greater speeds in ground tests, as well as a minor accident. On the 7 September 1906, the wheels left the ground during an extremely quick hop.
Announcements were made about Santos-Dumont trying for all the aeronautics prizes. Crowds and aviation authorities gathered on the morning of the 13 September 1906. Not all the cylinders were firing during an initial takeoff attempt, but quick repairs allowed for the second run to result in a 13-meter (43 ft) hop, an altitude of about 1 meter having been reached. This did not qualify for the prizes, but earned Santos-Dumont a great deal of attention.
The 14-bis landed at a high angle of attack, and the propeller at the back struck the ground. Repairs were undertaken. On the 23 October, after a series of engine tests and high-speed ground runs (one of which ended as one wheel came loose, but this was quickly fixed), Santos-Dumont finally pulled the 14-bis into the air. The aircraft flew for over 200 feet at an altitude of about 10 feet (3 m). This earned Santos-Dumont the first of the aviation prizes, 3,000 francs for a 25-meter-or-greater flight.
The plane required more repairs, as the landing had again damaged it, and Santos-Dumont announced that he should be ready to attempt the 100-meter prize on 12 November. The 14-bis was repaired, and ailerons were added to the middle of each outermost wing cell (similar to the aileron layout later used in the famous Curtiss Model D Pusher). These ailerons, hinged about their center of gravity with their axes running through the midpoint of the outermost wing bay's forward interplane struts, were actuated by cables attached to the pilot's flightsuit at the shoulders. Movement of the shoulders thus actuated roll control, similarly to the hip-movement roll-actuation control on the Wright Flyer.
On the morning of 12 November 1906, the crowds gathered. In a surprise to nearly all there, Voisin also brought a biplane that he and Bleriot had built, and also powered by an Antoinette. Voisin made several takeoff attempts, until one of them damaged the vehicle such that it could not be tested further before being extensively repaired.
As Santos-Dumont allowed the 14-bis to run down the field, a car drove alongside, and Henry Farman would drop a plate out of the car each time he observed the wheels of the plane to leave the ground or to touch down again. The first attempt saw a flight of 40 meters, and the second saw two brief flights of 40 and 50 meters. A hurried landing due to the proximity of some trees after this second attempt damaged the wheel axles, and these were fixed during a lunch break. In the afternoon, further flights were of 50 meters and then 82 meters, this one interrupted by the proximity of a polo barrier. As the sun set, Santos-Dumont attempted one more flight. In order to ensure he would not hit spectators, who by this time were present all over the field, he flew at an altitude of 4 meters. After 22 seconds, he cut the engine power and glided into a landing. He had flown for 220 meters, or over 700 feet, qualifying for the second aviation prize offered for heavier-than-air-aircraft, 1,000 francs for a flight of 100 meters or more.
For all accounts this was the last record flight of the aircraft.[1] The next notable Santos-Dumont flight was 200 meters a year later, on a different model of biplane, this time with the rear rudder.[1]
The first fixed-wing aircraft: The 14-bis versus the Wright Flyers
Controversy exists between supporters of Santos Dumont and the Wright Brothers whether the Wright 1903 Flyer I or the 14-Bis was the first true airplane.
The 1903 Wright Flyer I used a launch rail and undercarriage skids. After 1903 the Wrights added a catapult to assist the takeoff of later versions of their airplanes. The Santos-Dumont 14-bis used wheels and no catapult. To confuse the issue still further, Traian Vuia had hopped his own, four-wheeled landing gear equipped monoplane on March 18, 1906 at Montesson in France for a distance of twelve meters, some six months before the Santos-Dumont 14bis had been "hopped" for the first time. The Vuia pioneer aircraft had no other method of ground contact at any time, other than through its four wire-spoked bicycle-style wheels, set in a rectangular pattern.
The Fédération Aéronautique Internationale, founded in France two years after the Wright's first flight, to keep track of aviation records and other aeronautical activities, stated among its rules that an aircraft should be able to take off under its own power in order to qualify for a record. Many Santos-Dumont fans believe this meant the 14-bis was the first fixed-wing aircraft. Wright supporters emphasize the controlled, sustained maneuvering flights made by the brothers, compared to the subsequent short straight flights of Santos Dumont.
Advocates for Santos Dumont cite a letter attributed to Wilbur Wright to French Army Captain Ferdinand Ferber, part of which says:
“ We had already seen by the picture in the New York Herald that the plane rests on three wheels and we deduce from this that Mr. Santos Dumont, in order to effect his take-off, has first to make a run over a long level field. With the aid of the starting-off pillar that we use, Orville and I speedily go right up into the air in a much more practical fashion... We are sure to find a lot in our favor if we come to exhibit in France; but the voyage and the transportation of the machine and the pillar cost much more money than the two poor mechanics can afford to spend; also, dear Captain Ferber, if French experts, under your management, desire to come to Dayton, we will give them a demonstration of the machine in a neighboring field, flying for five minutes in a complete circle and let them have an option of the performance and release of the machine, for $50,000, cash down.[2] ” From this passage, Santos-Dumont fans could infer that while the Wright Flyer may have been superior in the air, its take-off apparatus made it overly impractical to operate and transport. Alternatively, Wright brothers fans could point to the implication that the scarcity of usable takeoff fields made the Flyer and "pillar" more practical, needing much less open, smooth and level space than the 14-bis.
Both aircraft made free, manned, powered flights. Extensive written and photographic documentation by the Wrights shows they made fixed-wing flights before Santos Dumont. Official records and motion picture documentation shows that Santos Dumont took off on wheels before the Wrights, and after Vuia did. Patriotic pride heavily influences opinions of the relative importance and practicality of each aircraft. U.S. citizens prefer definitions that make the Wrights the "first" to fly, while many Brazilians believe that Santos Dumont had the first "real", practical airplane, and that his nationality may have caused his accomplishments to not receive worldwide recognition.
Many other inventors could also claim the title to the first flying machine. From powered, heavier-than-air, but less-than-controllable airplanes, to gliders and balloons, a long series of "flying machines" separately achieved many of the individual criteria that are required of an "airplane". These achievements, most of them first accomplished in the 1800s, include being able to sustain flight (albeit lighter-than-air flight), using thrust to move wings through the air so as to generate enough lift to rise off the ground (albeit not controllably), and creating a winged vehicle that can stay in the air for more than a few seconds and that can be controlled to turn, dive, climb, etc (albeit only gliders that required a loss of altitude to "power" them). For example, Frederick Marriott's Avitor was a slightly-heavier-than-air airship that was fully controllable. It relied primarily on a large hydrogen gas bag providing buoyancy for flight, but it had wings and could only get off the ground by moving forward so that the wings generated the additional aerodynamic lift needed to overcome its weight. Could such a hybrid be "the first heavier-than-air flying machine"? It is only one of many examples of a long history of flying contraptions, so this debate could easily be extended well beyond being about simply the 14-Bis versus the Wright Flyer.[3]
Specifications (14-bis)
Data from www.aviafrance.com[4]
General characteristics
- Crew: one pilot
- Length: 9.70 m (31 ft 10 in)
- Wingspan: 11.20 m (36 ft 9 in)
- Height: 3.40 m (11 ft 2 in)
- Wing area: 52 m² (560 ft²)
- Loaded weight: 300 kg (661 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × Antoinette V-8 piston engine, 37 kW (50 hp)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 40 km/h (25 mph/21 kts)
- Range: more than 220 m (720 ft) demonstrated
- Wing loading: 5.7 kg/m² (1.2 lb/ft²)
- Power/mass: 0.12 kW/kg (0.075 hp/lb)
Related content
Related development: Santos Dumont's series of dirigibles, and then the Santos-Dumont Demoiselle
Comparable aircraft: Wright Flyer - Blériot III - Blériot V - Voisin-Farman I
References
- Notes
- ^ a b Flight, 1909, p. 12.
- ^ thefirsttofly (undated). "SANTOS DUMONT, THE FIRST AVIATOR, AND THE WRIGHT BROTHERS � END OF THE CENTURY-OLD POLEMIC". Archived from the original on 2003-08-20. http://web.archive.org/web/20030820050506/http://www.thefirsttofly.hpg.ig.com.br/pioneer2.htm. Retrieved 2008-09-14.
- ^ Hiller Aviation Museum (2007). "Avitor". http://hiller.org/avitor.shtml. Retrieved 2008-09-14.
- ^ http://www.aviafrance.com/santos-dumont-14-bis-aviation-france-9613.htm
- Bibliography
- Gray, Carroll F. "The 1906 Santos=Dumont No. 14bis". World War I Aeroplanes, Issue #194, November 2006, pgs. 4-21.
- Joao Luiz Musa, Marcelo Breda Mourao, and Ricardo Tilkian, Eu Naveguei Pelo Ar ("I Flew Through the Air") by 2003
- Alberto Santos Dumont A Conquista Do Ar (The Conquer of the Air) by , 1901
- http://www.first-to-fly.com/History/History%20of%20Airplane/santos_dumont.htm
- http://www.santosdumont.14bis.mil.br/
- http://web.archive.org/web/20030820050506/http://www.thefirsttofly.hpg.ig.com.br/pioneer2.htm http://www.thefirsttofly.hpg.ig.com.br/pioneer2.htm]
- http://hiller.org/avitor.shtml
- Hippolyto Da Costa, Fernando. Alberto Santos-Dumont: The Father of Aviation. transl: Soares, Hercillio A. VARIG Maintenance Base, Rio: 1973.
- Lins de Barros, Henrique. Alberto Santos-Dumont. Associacao Promotora Da Instrucao, Rio de Janeiro: 1986.
- Tobin, James. To Conquer the Air: The Wright Brothers and The Great Race for Flight. Free Press, New York: 2003.
External links
Aircraft built by Alberto Santos-Dumont List of aircraft •No.1 • No.2 • No.3 • No.4 • No.5 • No.6 • No.7 • No.8 • No.9 • No.10 • No.11 • No.12 • No.13 • No.14/No.14bis • No.15 • No.16 • No.17 • No.18 • No.19 • No.20 • No.21 • No.22 •
Lists relating to aviation General Aircraft (manufacturers) · Aircraft engines (manufacturers) · Airlines (defunct) · Airports · Civil authorities · Museums · Registration prefixes · Rotorcraft (manufacturers) · TimelineMilitary Accidents/incidents Records Categories:- French experimental aircraft 1900–1909
- Santos-Dumont aircraft
- Canard aircraft
- Biplane aircraft
- Pusher aircraft
- Single-engine aircraft
- Individual aircraft
- 1906 in France
- Transport in Paris
- 1906 introductions
- Propeller aircraft
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.