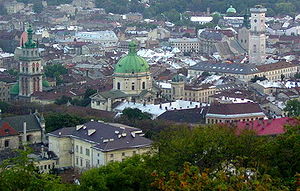- Old Town (Lviv)
-
Old City of Lviv (Старе місто Львова) State Historic-Architectural Sanctuary City view from High Castle, the couple of green domes (center) - ensemble of the Assumption Church, tower on the far right - Lviv Rathaus (Market Square)Country Ukraine Region Lviv Oblast Municipality Lviv Landmarks Potocki Palace, Lviv Rathaus, Lviv Opera Theater, Commodity Stock Exchange, Church and Collegium of the Jesuits, Church of St.Nicolas, Church of St.Casimir Coordinates 49°50′30″N 24°01′55″E / 49.84167°N 24.03194°E Sanctuary core 1,200,000 m2 (12,916,693 sq ft) - Buffer zone 30,000,000 m2 (322,917,330 sq ft) Founded State Sanctuary Date 1975 Management Lviv Oblast State Administration UNESCO World Heritage Site Name L'viv - the Ensemble of the Historic Centre Year 1998 (#22) Number 865 Region Europe and North America Criteria ii, v Lviv's Old Town (Ukrainian: Старе Місто Львова, Stare Misto L’vova; Polish: Stare Miasto we Lwowie) is the historic centre of the western Ukrainian city of Lviv, in the Lviv Oblast (province), recognized as the State Historic-Architectural Sanctuary in 1975.[1]
Contents
UNESCO
Since 1998, the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) lists Lviv's historic center as part of "World Heritage". On 5 December 1998, during the 22nd Session of the World Heritage Committee in Kyoto (Japan), Lviv was included to the UNESCO World Heritage List. UNESCO gave the following reasons[2] for its selection:
Criterion ii: In its urban fabric and its architecture, Lviv is an outstanding example of the fusion of the architectural and artistic traditions of eastern Europe with those of Italy and Germany.Criterion v: The political and commercial role of Lviv attracted to it a number of ethnic groups with different cultural and religious traditions, who established separate yet interdependent communities within the city, evidence for which is still discernible in the modern townscape.The territory of the Lviv Historic Centre Ensemble covers 120 hectares (300 acres) of the Old Russ and Medieval part of the city, as well as the territory of the St. George’s Cathedral on St. George’s Hill. The buffer area of the Historic Centre, which is defined by the historic area bounds, is approximately 3,000 hectares (7,400 acres). [3]
List of featured landmarks
Beside the listed items of three major areas there are some 2,007 other historical landmarks within the Old City's area, 214 of which are considered national landmarks.
- Pidzamche (Sub-castle)
- Vysokyi Zamok (High Castle) and Pidzamche (Sub-castle) neighborhood, the original center of the city also containing the neighborhood of Old Market, the castle was preserved in ruins, however the general area of the city is better known for its name
- Church of St.Nicolas, the family church of the Halychyna (Ruthenian) kings
- Church of St.Paraskeva-Praxedia (Good Friday), contains 1740 inconostasis of the church by Fedor Senkovych
- Church of St.Onuphrius and Basilian Monastery, contains artworks of Lazar Paslavsky and Modest Sosenko
- Church of St.John the Baptist (today - Museum of Lviv Ancient relics), the church was dedicated to the Hungarian wife of King Leo, Constance, a daughter of King Béla IV
- Church of Snowy Mary (today - Church of Mother of God's Unwearying help), the church of German colonists of the city
- Seredmistia (Middletown)
- Ensemble of Rynok (Market) Square, contains Lviv Rathaus (center) and square perimeter of housing surrounding it
- Ensemble of the Church of Assumption, beside the church includes Chapel of Three Prelates and Korniakt's Tower
- Ensemble of Armenian Church, beside the church includes a belfry, a column with statue of St.Christopher, a building of former Armenian bank, a palace of the Armenian archbishops, Benedictine Armenian convent
- Ensemble of Latin Metropolitan Cathedral, beside the cathedral of St.Mary includes Boims' Chapel and Kampians' Chapel
- Ensemble of Bernardine Monastery (today - Church of St.Andrew), includes cathedral, monastery, belfry, rotunda, decorative colon, and defensive walls
- Ensemble of the Jesuit Cathedral and Collegium
- Ensemble of Dominican Church (today - Museum of history and religion), beside the church includes monastery and belfry
- City's fortifications include the City's Arsenal, the Gunpowder Tower, the Turners and Rope-makers' Tower, the Royal Arsenal, a bastion of lower defense wall
- House of the "Dnister" Insurance Company
- Church of St.Yura (St.George), the Dragonfighter
St. George's Cathedral - a mother church of the Ukrainian Greek Catholic Church community
- St. George’s Cathedral, beside the cathedral includes the Metropolitan's Palace, capitular houses, belfry, and fence with two gates (Market's and City's)
- Not part of the World Heritage Site
- Church of Carmelites, the Barefooted (today - Church of St.Michael)
- Church and Nunnery of Carmelites, the Barefooted (today - Church of Purification)
- Church of Poor Clares (today - Museum of Sacral Baroque Sculpture)
- Church of St.Martin (today - Baptist Church)
- Church of Transfiguration
- Church of St.Casimir
- Lviv Theatre of Opera and Ballet
- Potocki Palace, Lviv, currently a residence of the President of Ukraine
- Commodity Stock Exchange
See also
- List of historic reserves in Ukraine
References
- ^ (Ukrainian) Declaration of Cabinet of Ministers of Ukrainian SSR in creation of the State Historic-Architectural Sanctuary in city of Lviv (official document)
- ^ L'viv – the Ensemble of the Historic Centre, UNESCO - World Heritage. URL Accessed: 30 October 2006
- ^ Lviv in UNESCO, www.lviv.ua. URL Accessed: 23 December 2008
External links
- (Ukrainian) Description at the website of the Institute of History of the NANU
- Mayor of Lviv Sadovy wants the sanctuary to be discontinued (ZIK May 17, 2010)
- The city council is unaware of the sanctuary (ZIK February 1, 2011)
- Information on a book about the sanctuary published in 1979
- Illustrated map of the city
- Description of the World Heritage site
History Armenian Statute · Dormition Brotherhood · Jesuit Collegium · First Siege by Cossacks · Second Siege by Cossacks · Lwów Oath · Siege by Turks · Leopolis Triplex · Stauropegion Institute · Stauropegion Press · Ossolineum · Galician Rada · Halytsko-Ruska Matytsia · Prosvita · Ruthenian Triad · Ruthenian National House · Hutsul Secession · Batiars · Lwów Eaglets · Battle 1918 · Pogrom 1918 · Battle 1920 · Secret Ukrainian University · School of Logic · School of Mathematics · Battle 1939 · Massacre of Lviv professors · Lviv pogroms · Lemberg Ghetto · Lwów Uprising · Sknyliv airshow disaster
Religion Armenian Cathedral · Cathedral of St. George · Chapel of the Boim family · Bernardine Church · Bridgettine Convent · Carmelite Church · Convent of Benedictines · Church of St. Anne · Church of John the Baptist · Church of Mary of Snow · Church of St. Elizabeth · Church of St. Mary Magdalene · Church of St. Onuphrius · Church of the Dormition · Church of the Purification, Lviv · Church of the Transfiguration · Dominican Church · Jesuit Church · Latin Cathedral
Attractions Arena Lviv · Arsenal Museum · Bandinelli Palace · Black Kamienica · Catholic University · Cemetery of the Defenders of Lwów · Freedom Boulevard · Government House · King Cross Leopolis · Korniakt Palace · Lviv High Castle · Lviv University · Lychakivskiy Cemetery · Market Square · Mickiewicz Square · National Museum · Polytechnic University · Liubomyrsky Palace · Metropolitan Palace · Old Town · Pharmacy Museum · Pototsky Palace · Sapieha Palace · Scottish Café · Shevchenkivskyi Hai · Theatre of Opera and Ballet · Town Hall · Ukraina Stadium · Union of Lublin Mound
Transport Kiev: Saint-Sophia Cathedral and Related Monastic Buildings / Kiev Pechersk Lavra · L'viv - the Ensemble of the Historic Centre · Chernivtsi - the Residence of Bukovinian and Dalmatian Metropolitans · Struve Geodetic Arc (with nine other countries) · Primeval Beech Forests of the Carpathians (with Slovakia)
Categories:- World Heritage Sites in Ukraine
- Historic districts
- Historic sites in Ukraine
- Landmarks in Lviv
- Protected areas of Ukraine
- Protected areas established in 1975
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.