- Camargue
-
Coordinates: 43°32′N 04°30′E / 43.533°N 4.5°E
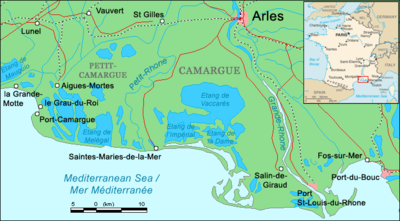
The Camargue (Occitan: Camarga in classical norm or Camargo in Mistralian norm) is the region located south of Arles, France, between the Mediterranean Sea and the two arms of the Rhône River delta. The eastern arm is called the Grand Rhône; the western one is the Petit Rhône.
Administratively it lies within the département of Bouches-du-Rhône, the appropriately named "Mouths of the Rhône", and covers parts of the territory of the communes of Arles - the largest commune in Metropolitan France, Saintes-Maries-de-la-Mer - the second largest - and Port-Saint-Louis-du-Rhône. A further expanse of marshy plain, the Petite Camargue (little Camargue), just to the west of the Petit Rhône, is in the département of Gard.
Camargue was designated a Ramsar site as a "Wetland of International Importance" on December 1, 1986. The area was also the inspiration for naming Operation Camargue during the First Indochina War.
Contents
Geography
With an area of over 930 km2 (360 sq mi), the Camargue is western Europe's largest river delta. It is a vast plain comprising large brine lagoons or étangs, cut off from the sea by sandbars and encircled by reed-covered marshes. These are in turn surrounded by a large cultivated area.
Approximately a third of the Camargue is either lakes or marshland. The central area around the shoreline of the Étang de Vaccarès has been protected as a regional park since 1927, in recognition of its great importance as a haven for wild birds. In 2008 it was incorporated into the larger Parc naturel régional de Camargue.
Flora and fauna
The Camargue is home to more than 400 species of birds; its brine ponds provide one of the few European habitats for the greater flamingo. The marshes are also a prime habitat for many species of insects, notably (and notoriously) some of the most ferocious mosquitos to be found anywhere in France. It is also famous for the Camargue Bull and the Camargue Horse.
The flora of the Camargue is specially adapted to cope with the saline conditions. Sea lavender and glasswort flourish, along with tamarisks and reeds.
Regional park
Main article: Parc Naturel Régional de CamargueOfficially established as a regional park and nature reserve in 1970, the Parc Naturel Régional de Camargue covers 820 km² that are some of the wildest and most protected in all of Europe. A roadside museum provides background on flora, fauna, and the history of the area.
Human influence
Humans have lived in the Camargue for millennia, greatly affecting it with drainage schemes, dykes, rice paddies and salt pans. Much of the outer Camargue has been drained for agricultural purposes. The Camargue has its own eponymous horse breed, the famous white Camarguais ridden by the gardians, who rear the region's fighting bulls for export to Spain, as well as sheep. Many of these animals are raised in semi-feral conditions within a Manade.
There are few towns of any size in the Camargue. Its "capital" is Arles, located at the extreme north of the delta where the Rhône forks into its two principal branches. The only other towns of note are Saintes-Maries-de-la-Mer, about 45 km to the southwest and the medieval fortress-town of Aigues-Mortes on the far western edge, in the Petite Camargue. Saintes-Maries-de-la-Mer is the destination of the annual Roma pilgrimage for the veneration of Saint Sarah.
The Camargue was exploited in the Middle-Ages by Cistercian and Benedictine monks. In the 16-17th centuries, big estates, known locally as mas, were founded by rich landlords from Arles. At the end of the 18th century, the Rhône was diked up. In 1858, the building of the digue à la mer (dyke to the sea) achieved protection of the delta from erosion. The north of the Camargue is made of agricultural land. The main crops are cereals, grapevine and rice. Near the seashore, prehistoric man started extracting salt, a practice that continued. This was a source of wealth for the Cistercian "salt abbeys" of Ulmet, Franquevaux and Psalmody in the Middle Ages. The salt industry started in the 19th century, and big chemical companies such as Péchiney and Solvay, founded the 'mining' city of Salin-de-Giraud.
The boundaries of the Camargue are constantly revised by the Rhône as it transports huge quantities of mud downstream - as much as 20 million m³ annually. Some of the étangs are in fact the remnants of old arms and legs of the river. The general trend is for the coastline to move outwards. Aigues-Mortes, originally built as a port on the coast, is now some 5 km (3.1 mi) inland. The pace of change has been modified somewhat in recent years by man-made barriers, such as dams on the Rhône and sea dykes, but flooding remains a problem across the region.
Film portrayal
- The 1953 children's film Crin-Blanc, known in English as White Mane, portrays the horses and region. Directed by Albert Lamorisse, the black-and-white film won the Prix Jean Vigo award and the Cannes Film Festival's Grand Prize, both for short film.
- The majority of the youthful romance movie Friends (1971) takes place in the Camargue, with numerous scenes of wetlands and wildlife. "Michelle's Song," from the soundtrack by Bernie Taupin and Elton John, includes the phrase "tiny daughter of the Camargue."
- The 1963 Hammer Films thriller The Maniac was partly filmed in Camargue.
References
Sources
- Russell, Richard Joel (1942). "Geomorphology of the Rhone Delta". ANNAL (Association of American Geographers) 32 (2): 149–255. http://books.google.com/books?id=TLMguCEPSJQC&printsec=frontcover&source=gbs_ge_summary_r&cad=0#v=onepage&q&f=false. Retrieved 2011-10-09.- also in jstor (paywall)
See also
- Bac du Sauvage
- Folco de Baroncelli-Javon
- Camargue red rice
- Camargue horse
- Camargue equitation
- Gardian
- Manade
External links
- Nacioun Gardians (Cultural association, Camargue, France)
- The Camargue at armchairfrance.com
- Parc naturel de Camargue (in French, English and Italian)
- Tourism Office of Saintes-Maries de la Mer
- Tourism Office of Arles
- Camargue Photogallery
- IMDB Crin-Blanc
Categories:- Bouches-du-Rhône
- Arles
- Marshes of France
- Ramsar sites in France
- Biosphere reserves of France
- River deltas
- The Camargue
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.