- Tooth abscess
-
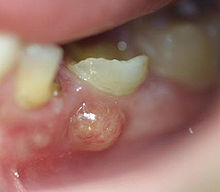
A tooth abscess or root abscess is pus enclosed in the tissues of the jaw bone at the apex of an infected tooth's root(s). Usually the abscess originates from a bacterial infection that has accumulated in the soft, often dead, pulp of the tooth. This can be caused by untreated tooth decay, cracked teeth or extensive periodontal disease. A failed root canal treatment may also create a similar abscess.
There are three types of dental abscess. A gingival abscess (or gumboil) involves only the gum tissue, without affecting either the tooth or the periodontal ligament. A periapical abscess starts at the apex of the root. A periodontal abscess begins in the pocket of gingiva over 3 mm.
Contents
Presentation and symptoms
The pain is continuous and may be described as gnawing, sharp, shooting, or throbbing. Putting pressure or warmth on the tooth may induce extreme pain. There may be a swelling present at either the base of the tooth, the gum, and/or the cheek, which can be alleviated by applying ice packs.
An acute abscess may be painless but still have a swelling present on the gum. It is important to get anything that presents like this checked by a dental professional as it may become chronic later.
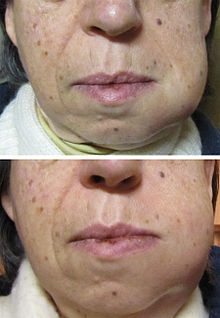
In some cases, a tooth abscess may perforate bone and start draining into the surrounding tissues creating local facial swelling. In some cases, the lymph glands in the neck will become swollen and tender in response to the infection. It may even feel like a migraine as the pain can transfer from the infected area. The pain does not normally transfer across the face, only upwards or downwards as the nerves that serve each side of the face are separate.
Severe aching and discomfort on the side of the face where the tooth is infected is also fairly common, with the tooth itself becoming unbearable to touch.
Treatment
Successful treatment of a dental abscess centers on the reduction and elimination of the offending organisms. This can include treatment with antibiotics.[citation needed] and drainage. If the tooth can be restored, root canal therapy can be performed. Non-restorable teeth must be extracted, followed by curettage of all apical soft tissue.
Unless they are symptomatic, teeth treated with root canal therapy should be evaluated at 1- and 2-years intervals to rule out possible lesional enlargement and to ensure appropriate healing.
Abscesses may fail to heal for several reasons:
- Cyst formation
- Inadequate root canal therapy
- Vertical root fractures
- Foreign material in the lesion
- Associated periodontal disease
- Penetration of the maxillary sinus
Following conventional, adequate root canal therapy, abscesses that do not heal or enlarge are often treated with surgery and filling the root tips; and will require a biopsy to evaluate the diagnosis.[1]
Untreated consequences
If left untreated, a severe tooth abscess may become large enough to perforate bone and extend into the soft tissue eventually becoming osteomyelitis and cellulitis respectively. From there it follows the path of least resistance and may spread either internally or externally. The path of the infection is influenced by such things as the location of the infected tooth and the thickness of the bone, muscle and fascia attachments.
External drainage may begin as a boil which bursts allowing pus drainage from the abscess, intraorally (usually through the gum) or extra orally. Chronic drainage will allow an epithelial lining to form in this communication to form a pus draining canal (fistula). Sometimes this type of drainage will immediately relieve some of the painful symptoms associated with the pressure.
Internal drainage is of more concern as growing infection makes space within the tissues surrounding the infection. Severe complications requiring immediate hospitalization include Ludwig's angina, which is a combination of growing infection and cellulitis which closes the airway space causing suffocation in extreme cases. Also infection can spread down the tissue spaces to the mediastinum which has significant consequences on the vital organs such as the heart. Another complication, usually from upper teeth, is a risk of septicaemia (infection of the blood) from connecting into blood vessels, brain abscess (extremely rare), or meningitis (also rare).
Depending on the severity of the infection, the sufferer may feel only mildly ill, or may in extreme cases require hospital care. In 2011, a death from an untreated dental abscess was recorded in Cincinnati. Reports indicate that local free dental clinics had too long a waiting list to be effective in this case.[2]
See also
References
- ^ Neville, Brad W. [et al.] - 1st ed, 1995. Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology. pp.104-5.
- ^ http://www.medicaldaily.com/news/20110903/7087/dental-care-dental-insurance-kyle-willis.htm
External links
Categories:- Acquired tooth disorders
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.