- Benzylideneacetone
-
Benzylideneacetone 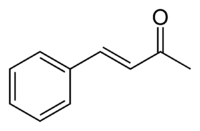
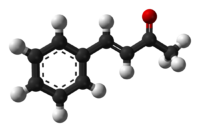 4-Phenyl-3-buten-2-oneOther namesBenzalacetone
4-Phenyl-3-buten-2-oneOther namesBenzalacetone
Benzylideneacetone
Methyl styryl ketone
Benzylidene acetoneIdentifiers CAS number 122-57-6  , 1896-62-4 (trans)
, 1896-62-4 (trans)ChemSpider 21106584 
ChEBI CHEBI:217301 
ChEMBL CHEMBL73639 RTECS number EN0330000 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - CC(=O)/C=C/c1ccccc1
Properties Molecular formula C10H10O Molar mass 146.19 g/mol Appearance pale yellow solid Density 1.008 g/cm3 Melting point 39-42 °C
Boiling point 260-262 °C
Solubility in water 1.3 g/L Solubility in other solvents nonpolar solvents Hazards R-phrases 36/37/38-43 S-phrases 22-26-36/37 Main hazards irritant Flash point 116 °C Related compounds Related compounds Dibenzylideneacetone
cinnamaldehyde (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
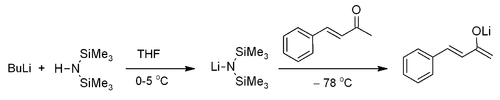
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Benzylideneacetone is the organic compound described by the formula C6H5CH=CHC(O)CH3. Although both cis- and trans-isomers are possible for the α,β-unsaturated ketone, only the trans isomer is observed. Its original preparation demonstrated the scope of condensation reactions to construct new, complex organic compounds.[1]
Preparation
Benzylideneacetone can be efficiently prepared by the NaOH-induced condensation of the readily available reagents acetone and benzaldehyde:[2]
- CH3C(O)CH3 + C6H5CHO → C6H5CH=CHC(O)CH3 + H2O
Reactions
As with most methyl ketones, benzylidineacetone is moderately acidic at the alpha position, and it can be readily deprotonated to form the corresponding enolate[3]
The compound undergoes the other reactions expected for its collection of functional groups: e.g., the double bond adds bromine, the heterodiene adds electron-rich alkenes in Diels-Alder reactions to give dihydropyrans, the methyl group undergoes further condensation with benzaldehyde to give dibenzylideneacetone, and the carbonyl forms hydrazones. It reacts with Fe2(CO)9 to give (benzylideneacetone)Fe(CO)3, a reagent for transferring the Fe(CO)3 unit to other organic molecules.[4]
References
- ^ Claisen, L. “Über die Einwirkung von Aceton auf Furfural und auf Benzaldehyd bei Gegenwart von Alkalilauge” Berichte der deutschen chemischen Gesellschaft 1881, volume 14, p 2468-2471.
- ^ Drake, N. L.; Allen, Jr. P., "Benzalacetone", Org. Synth., http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=cv1p0077; Coll. Vol. 1: 77
- ^ Danheiser, R. L.; Miller, R. F.; Brisbois, R. G. (1990), "Detrifluoroacetylative Diazo Group Transfer: (E)-1-Diazo-4-phenyl-3-buten-2-one", Org. Synth. 73: 134, http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=CV9P0197; Coll. Vol. 9: 197
- ^ Knölker, H.-J. "(η4-Benzylideneacetone)tricarbonyliron" in Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis (Ed: L. Paquette) 2004, J. Wiley & Sons, New York. DOI: 10.1002/047084289.
Categories:- Ketones
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.