- Dibenzylideneacetone
-
Dibenzylideneacetone 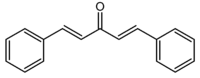
 (1E,4E)-1,5-diphenylpenta-1,4-dien-3-oneOther namesDibenzalacetone
(1E,4E)-1,5-diphenylpenta-1,4-dien-3-oneOther namesDibenzalacetoneIdentifiers CAS number 538-58-9 
PubChem 1549622 ChemSpider 1266463 
Jmol-3D images Image 1
Image 2- O=C(/C=C/c1ccccc1)/C=C/c2ccccc2
O=C(\C=C\c1ccccc1)/C=C\c2ccccc2
Properties Molecular formula C17H14O Molar mass 234.29 g/mol Appearance Yellow solid Melting point - Aldrich 110-111 ºC (trans,trans isomer)
- Merck 60ºC (cis,trans isomer)
Boiling point 130ºC(cis,cis isomer) *Merck
Solubility in water Insoluble Hazards Main hazards Irritant  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Dibenzylideneacetone or dibenzalacetone, often abbreviated dba, is an organic compound with the formula C17H14O. It is a bright-yellow solid insoluble in water, but soluble in ethanol. Dibenzylideneacetone is used as a sunscreen component and as a ligand in organometallic chemistry, for instance in tris(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium(0). In this case, it is a labile ligand that is easily displaced by stronger ligands like triphenylphosphine, hence it serves a useful entry point into palladium(0) chemistry.
Preparation
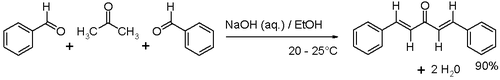
The compound can be prepared in the laboratory by an aldol condensation of benzaldehyde and acetone with sodium hydroxide in a water/ethanol medium with the exclusive formation of the trans,trans isomer (melting point 110–111 °C).[1]
This reaction is frequently encountered in organic chemistry education as a laboratory procedure. The conversion proceeds via the intermediacy of benzylideneacetone.
Prolonged exposure to sunlight converts the compound in a [2+2] cycloaddition to a mixture of four cyclobutane isomers.[2]
References
- ^ Conard, C. R.; Dolliver, M. A. (1943), "Dibenzalacetone", Org. Synth., http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=cv2p0167; Coll. Vol. 2: 167
- ^ Rao, G. N.; Janardhana, C.; Ramanathan, V.; Rajesh, T.; Kumar, P. H. (November 2006). "Photochemical Dimerization of Dibenzylideneacetone. A Convenient Exercise in [2+2] Cycloaddition Using Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry". J. Chem. Educ. 83 (11): 1667. doi:10.1021/ed083p1667. http://jchemed.chem.wisc.edu/Journal/issues/2006/Nov/abs1667.html.
Categories:- Ketones
- Sunscreening agents
- O=C(/C=C/c1ccccc1)/C=C/c2ccccc2
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.