- Dewar benzene
-
Dewar benzene 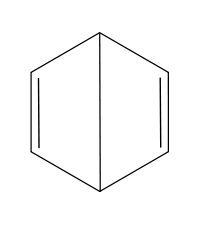 Bicyclo[2.2.0]hexa-2,5-diene
Bicyclo[2.2.0]hexa-2,5-dieneIdentifiers PubChem 98808 ChemSpider 89242 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - C\1=C\C2/C=C\C/12
Properties Molecular formula C6H6 Molar mass 78.1 g·mol−1  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Dewar benzene or bicyclo[2.2.0]hexa-2,5-diene is a bicyclic isomer of benzene with the molecular formula C6H6. The compound is named after James Dewar who included this structure in a list of possible C6H6 structures in 1867.[1] However, he did not propose it as the structure of benzene, and in fact he supported the correct structure previously proposed by August Kekulé in 1865.[2]
Contents
Synthesis and properties of bicyclo[2.2.0]hexa-2,5-diene
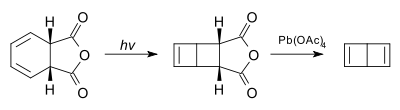
The compound itself was first synthesized in 1962 as a tert-butyl derivative[3] and then as the unsubstituted compound by E.E. van Tamelen in 1963 by photolysis of cis-1,2-dihydro derivative of phthalic anhydride followed by oxidation with lead tetraacetate.[4][5]
The conjoined cyclobutene rings that form Dewar benzene form an obtuse angle.
Unlike benzene, Dewar benzene is not flat; the two cyclobutene rings make an angle. The compound has nevertheless considerable strain energy and reverts back to benzene with a chemical half-life of two days. This thermal conversion is relatively slow because it is symmetry forbidden based on orbital symmetry arguments[6].
"Dewar benzene" and benzene
It is sometimes incorrectly claimed that Dewar proposed his structure as the true structure of benzene. In fact Dewar merely wrote the structure as one of seven possible isomers, and believed that his experiments on benzene supported the (correct) structure which had been proposed by Kekulé.[2]
After the development in 1928 of the valence bond theory, the three possible Dewar structures were considered as minor resonance contributors in the overall description of benzene. The major resonance contributors are of course the two possible Kekulé structures.
Other classic structures which have been considered as possible benzene isomers are prismane, benzvalene and Claus' benzene. In fact prismane and benzvalene were synthesized in the 1970s, and Claus' benzene has never been synthesized.
Hexamethyl Dewar benzene
Hexamethyl Dewar benzene has been prepared by bicyclotrimerization of dimethylacetylene with aluminium chloride.[7] It undergoes an unusual rearrangement reaction with hydrohalic acids to form a pentamethylcyclopentadiene derivative,[8][9] and consequently can be used as a starting material for synthesising some pentamethylcyclopentadienyl organometallic compounds.[10][11]
References
- ^ J. Dewar (1867). "On the Oxidation af Phenyl Alcohol, and a Mechanical Arrangement adapted to illustrate Structure in the Non-saturated Hydrocarbons". Proc. Royal Soc. Edinburgh 6,62: 96.
- ^ a b W. Baker, D. H. Rouvray (1978). "Para-Bond or "Dewar" Benzene?". J. Chem. Educ. 55 (10): 645. doi:10.1021/ja00903a056.
- ^ E. E. van Tamelen, S. P. Pappas (1962). "Chemistry of Dewar Benzene. 1,2,5-Tri-t-Butylbicyclo[2.2.0]Hexa-2,5-Diene". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 84 (19): 3789–3791. doi:10.1021/ja00878a054.
- ^ E. E. van Tamelen, S. P. Pappas (1963). "Bicyclo [2.2.0]hexa-2,5-diene". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 85 (20): 3297–3298. doi:10.1021/ja00903a056.
- ^ E. E. van Tamelen, S. P. Pappas, K. L. Kirk (1971). "Valence Bond Isomers of Aromatic Systems. Bicyclo[2.2.0]hexa-2,5-dienes (Dewar benzenes)". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 93 (23): 6092–6101. doi:10.1021/ja00752a021.
- ^ James O. Jensen (2004). "Vibrational Frequencies and Structural Determination of Dewar Benzene". J. Mol. Struct.:THEOCHEM 680: 227–236. doi:10.1016/j.theochem.2004.03.042.
- ^ Sami A. Shama and Carl C. Wamser (1990), "Hexamethyl Dewar Benzene", Org. Synth., http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=cv7p0256; Coll. Vol. 7: 256
- ^ Paquette, L. A.; Krow, G. R. (1968). "Electrophilic Additions to Hexamethyldewarbenzene". Tetrahedron Lett. 9 (17): 2139–2142. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(00)89761-0.
- ^ Criegee, R.; Gruner, H. (1968). "Acid-catalyzed Rearrangements of Hexamethyl-prismane and Hexamethyl-Dewar-benzene". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 7 (6): 467–468. doi:10.1002/anie.196804672.
- ^ Kang, J. W.; Mosley, K.; Maitlis, P. M. (1968). "Mechanisms of Reactions of Dewar Hexamethylbenzene with Rhodium and Iridium Chlorides". Chem. Commun. (21): 1304–1305. doi:10.1039/C19680001304.
- ^ Kang, J. W.; Maitlis, P. M. (1968). "Conversion of Dewar Hexamethylbenzene to Pentamethylcyclopentadienylrhodium(III) Chloride". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 90 (12): 3259–3261. doi:10.1021/ja01014a063.
Categories:- Hydrocarbons
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.