- Hexachlorophosphazene
-
Hexachlorophosphazene 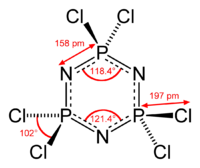
 HexachlorotriphosphazeneOther namesTriphosphonitrilic chloride
HexachlorotriphosphazeneOther namesTriphosphonitrilic chloride
Phosphonitrilic chloride, Hexachlorocyclotriphosphazene
2,2,4,4,6,6-hexachloro-2,2,4,4,6,6-
hexahydro-1,3,5,2,4,6-TriazatriphosphorineIdentifiers CAS number 940-71-6 
PubChem 220225 ChemSpider 190959 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - N1=P(N=P(N=P1(Cl)Cl)(Cl)Cl)(Cl)Cl
Properties Molecular formula N3Cl6P3 Molar mass 347.66 g/mol Appearance colorless crystals Density 1.98 g/mL at 25 °C Melting point 112–15 °C
Boiling point decomp.
Solubility in water decomp. Solubility in chlorocarbons soluble Structure Dipole moment 0 D Hazards EU Index Not listed Main hazards mild irritant Flash point Non-flammable  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Hexachlorophosphazene is an inorganic compound with the formula (NPCl2)3. The molecule has a cyclic backbone consisting of alternating phosphorus and nitrogen atoms. It can be viewed as a trimer of the hypothetical compound N≡PCl2. Hexachlorophosphazene together with the related (NPCl2)4 are precursors to inorganic polymers called polyphosphazenes.
Contents
Synthesis
The reaction of PCl5 and NH4Cl affords substances with the empirical formula PNCl2:[1] Purification by sublimation gives mainly the trimer (PNCl2)3 and tetramer (PNCl2)4. These rings were described by Liebig in 1832[2][3] in his study of the reaction of PCl5 and NH3:
- PCl5 + NH4Cl → 1/n (NPCl2)n + 4 HCl
Typically reactions are conducted in chlorobenzene solution.
Inorganic rings
Chemists have long known of rings containing carbon, e.g. benzene, pyridine, and cyclohexane. Related cyclic compounds lacking in carbon have also been studied. Hexachlorophosphazene is one such inorganic ring. Other well known inorganic rings include borazine, S4N4, and the cyclic siloxanes.
"Inorganic rubber"
Hexachlorophosphazene is a precursor to poly(dichlorophosphazene) or "inorganic rubber", whose discovery is attributed to H. N. Stokes in 1896.[2][4][5] Upon heating to ca. 250 °C, the trimer undergoes ring-opening polymerization to give the linear polymer (PNCl2)n. Subsequent replacement of the chloride centers by other groups, especially alkoxides, yields many polyphosphazenes, some with commercial uses.
See also
- octachlorophosphazene (PNCl2)4[2]
References
- ^ Holleman, A. F.; Wiberg, E. "Inorganic Chemistry" Academic Press: San Diego, 2001. ISBN 0-12-352651-5.
- ^ a b c H. N. Stokes (1895), On the chloronitrides of phosphorus. American Chemical Journal, vol. 17, p. 275.
- ^ Liebig-Wöhler, Briefwechsel vol. 1, 63; Ann. Chem. (Liebig), vol. 11 (1834), 146.
- ^ H. N. Stokes (1896), On Trimetaphosphimic acid and its decomposition products. American Chemical Journal, vol. 18 issue 8, p. 629.
- ^ Mark, J. E.; Allcock, H. R.; West, R. “Inorganic Polymers” Prentice Hall, Englewood, NJ: 1992. ISBN 0-13-465881-7.
Categories:- Chlorides
- Nitrogen heterocycles
- Inorganic compounds
- Nitrides
- Phosphorus heterocycles
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
