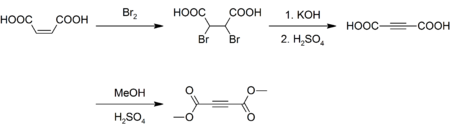- Dimethyl acetylenedicarboxylate
-
Dimethyl acetylenedicarboxylate 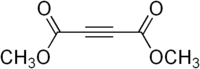
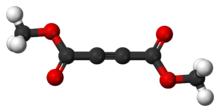 Dimethyl but-2-ynedioateOther namesDMAD
Dimethyl but-2-ynedioateOther namesDMAD
Acetylenedicarboxylic
acid dimethyl esterIdentifiers CAS number 762-42-5 
ChemSpider 12440 
RTECS number ES0175000 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - COC(=O)C#CC(=O)OC
Properties Molecular formula C6H6O4 Molar mass 142.11 g/mol Appearance Colorless liquid Density 1.1564 g/cm³ Melting point c
Boiling point 195–198 °C
96–98° at 8 mm HgSolubility in water Insoluble Solubility in other solvents Soluble in most
organic solventsRefractive index (nD) 1.447 Structure Dipole moment 0 D Hazards R-phrases R34 S-phrases S23 S26 S27
S36/37/39 S45Main hazards Toxic gas Flash point 187 °F Related compounds Related compounds Methyl propiolate,
Hexafluoro-2-butyne,
Acetylene acetylenedicarboxylate (verify) (what is:
acetylenedicarboxylate (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Dimethyl acetylenedicarboxylate (DMAD) is the organic compound with the formula CH3O2CC2CO2CH3. This ester, which exists as a liquid at room temperature, is highly electrophilic. As such, DMAD, as it is commonly called in the laboratory, is widely employed as a dienophile in cycloaddition reactions, such as the Diels-Alder reaction. It is also a potent Michael acceptor.[1][2]
Preparation
Although inexpensively available, DMAD is prepared today as it was originally. Maleic acid is brominated and the resulting dibromosuccinic acid is dehydrohalogenated with potassium hydroxide yielding acetylenedicarboxylic acid.[3][4] The acid is then esterified with methanol and sulfuric acid as a catalyst:[5]
Safety
DMAD is a lachrymator and a vesicant.
References
- ^ Stelmach, J. E.; Winkler, J. D. “Dimethyl Acetylenedicarboxylate”in Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis (Ed: L. Paquette) 2004, J. Wiley & Sons, New York. DOI: 10.1002/047084289.
- ^ Sahoo, Manoj (2007). "Dimethyl Acetylene Dicarboxylate". Synlett 2007: 2142. doi:10.1055/s-2007-984894.
- ^ Bandrowski, E. (1877). "Ueber Acetylendicarbonsäure". Berichte der deutschen chemischen Gesellschaft 10: 838. doi:10.1002/cber.187701001231.
- ^ Abbott, T. W.; Arnold, R. T.; Thompson, R. B., "Acetylenedicarboxylic acid", Org. Synth., http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=cv2p0010; Coll. Vol. 2: 10
- ^ Huntress, E. H. Lesslie, T. E.; Bornstein, J., "Dimethyl Acetylenedicarboxylate", Org. Synth., http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=cv4p0329; Coll. Vol. 4: 329
Categories:- Alkynes
- Methyl esters
- Carboxylate esters
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.