- Triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate
-
Triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate 
 Triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate
Triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborateIdentifiers CAS number 368-39-8 
PubChem 2723982 ChemSpider 2006158 
UN number 3261 Beilstein Reference 3598090 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - F[B-](F)(F)F.CC[O+](CC)CC
Properties Molecular formula C6H15BF4O Molar mass 189.99 g mol−1 Exact mass 190.115208388 g mol-1 Melting point 91-92 °C, 364-365 K, 196-198 °F
Solubility in water Reacts Hazards EU classification  C
CR-phrases R14, R34 S-phrases S22, S26, S36/37/39  tetrafluoroborate (verify) (what is:
tetrafluoroborate (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate is the organic oxonium compound with the formula [(CH3CH2)3O]BF4. It is often called Meerwein's reagent after its discoverer Hans Meerwein.[1] Also well known and commercially available is the related trimethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate. The compounds are exceptionally strong alkylating agents. Aside from the BF4− salt, many related derivatives are available with varying solubilities and stabilities.[2]
Contents
Synthesis
Triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate is prepared from boron trifluoride, diethyl ether, and epichlorohydrin:[3]
- 4 Et2O·BF3 + 2 Et2O + 3 C2H3(O)CH2Cl → 3 Et3O+BF4− + B[(OCH(CH2Cl)CH2OEt]3
The trimethyloxonium salt is available from dimethyl ether via an analogous route.[4] These salts do not have long shelf-lives at room temperature. These salts degrade by hydrolysis:
- [(CH3CH2)3O]+BF4− + H2O → (CH3CH2)2O + CH3CH2OH + HBF4
The propensity of trialkyloxoniums to undergo alkyl-exchange may be utilized to the chemists' advantage. For example, trimethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate, which reacts sluggishly due to low solubility in most compatible solvents may be converted in-situ to higher alkyl/more soluble oxoniums, thereby speeding up alkylation reactions.[5]
Structure
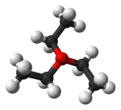
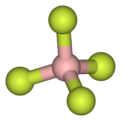
The compound features pyramidal oxonium cation and a tetrahedral fluoroborate anion. Reflecting its ionic character, the salt dissolves in polar but inert solvents such as dichloromethane, sulfur dioxide, and nitromethane.
Safety
Triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate is a strong alkylating agent, although the hazards are diminished because it is non-volatile. It releases strong acid upon contact with water. The properties of the methyl derivative are similar.
Use
Alkylating agent for nucleophilic functional groups in organic synthesis.
References
- ^ H. Meerwein, G. Hinz, P. Hofmann, E. Kroning, and E. Pfeil (1937). "Über Tertiäre Oxoniumsalze, I". Journal für Praktische Chemie 147 (10-12): 257. doi:10.1002/prac.19371471001.H. Meerwein, E. Bettenberg, H. Gold, E. Pfeil, and G. Willfang (1940). "Über Tertiäre Oxoniumsalze, II". Journal für Praktische Chemie 154 (3-5): 83. doi:10.1002/prac.19391540305.
- ^ Hartwig Perst, Dave G. Seapy "Triethyloxonium Tetrafluoroborate" in Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis John Wiley & Sons, New York, 2008. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rt223.pub2. Article Online Posting Date: March 14, 2008
- ^ H. Meerwein (1973), "Triethyloxonium fluoroborate", Org. Synth., http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=cv5p1080; Coll. Vol. 5: 1080
- ^ T. J. Curphey (1988), "Trimethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate", Org. Synth., http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=CV6P1019; Coll. Vol. 6: 1019
- ^ Vartak A.P. and Crooks P.A. (2009). "A Scalable Enantioselective synthesis of the alpha2-adrenergic Agonist, Lofexidine". Org. Process. Res. Dev. 13 (3): 415–419. doi:10.1021/op8002689.
Categories:- Reagents for organic chemistry
- Tetrafluoroborates
- Ethylating agents
- Chemistry stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
