- ACES (buffer)
-
ACES (buffer) 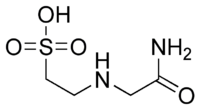 2-(carbamoylmethylamino)ethanesulfonic acidOther namesN-(2-Acetamido)-2-aminoethanesulfonic acid
2-(carbamoylmethylamino)ethanesulfonic acidOther namesN-(2-Acetamido)-2-aminoethanesulfonic acidIdentifiers CAS number 7365-82-4 PubChem 81832 ChemSpider 73843 
ChEBI CHEBI:39062 
Jmol-3D images Image 1
Image 2- C(CS(=O)(=O)O)NCC(=O)N
O=S(=O)(O)CCNCC(=O)N
Properties Molecular formula C4H10N2O4S Molar mass 182.199  (buffer) (verify) (what is:
(buffer) (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references ACES is the common abbreviation for the compound N-(2-Acetamido)-2-aminoethanesulfonic acid.
ACES is one of Good's buffers developed in the 1960s to provide buffers with pH ranging from 6.15-8.35 for use in various applications. With a pKa of 6.9, it is often used as a buffering agent in biological and biochemical research. It is a zwitterionic buffer with a useful buffering range of 6.1-7.5. The pioneering publication by Good and his co-workers described the synthesis and physical properties of ACES buffer.[1]
Applications
ACES had been used to develop buffers for both agarose and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis.[2] ACES use in isoelectric focusing of proteins has also been documented.[3] Use of ACES has been published in a protocol for the analysis of bacterial autolysins in a discontinuous SDS-PAGE system.[4] Potential inhibition of ACES and other Good buffers has been investigated in γ-aminobutyric acid receptor binding to rat brain synaptic membranes.[5]
References
- ^ Good, N.E., "Hydrogen ion buffers for biological research." "Biochemistry", 5(2), 467-477.
- ^ Liu, Q., et al., "pK-matched running buffers for gel electrophoresis." "Anal. Biochemistry.", 270(1):112-122.
- ^ Alonso, A., "Human α-1-antitrypsin subtyping by hybrid isoelectric focusing in miniaturized polyacrylamide gel." "Electrophoresis", 9(2):65-73.
- ^ Strating, H., and Clarke, A.J., "Differentiation of bacterial autolysins by zymogram analysis." "Anal. Biochem.", 291(1):149-154.
- ^ Tunnicliff, G., and Smith, J.A., "Competitive inhibition of γ-aminobutyric acid receptor binding by N-2-hydroxyethylpiperazine-N'-2-ε-ethanesulfonic acid and related buffer." "J. Neurochem.", 36(3):1122-1126.
Categories:- Buffers
- Biochemistry stubs
- C(CS(=O)(=O)O)NCC(=O)N
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
