- SYSLINUX
-
SYSLINUX 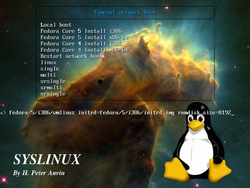
Screen-shotDeveloper(s) H. Peter Anvin Stable release 4.04 / April 18, 2011 Operating system Linux Type Boot loader License GNU General Public License version 2 or later Website http://syslinux.zytor.com The SYSLINUX Project is a suite of lightweight IBM PC MBR bootloaders for starting up computers with the Linux kernel. It is the work of H. Peter Anvin, and consists of several separate systems, the best-known of which is ISOLINUX.
Contents
List
- The original SYSLINUX, used for booting from FAT filesystems (such as floppy disks and USB drives).
- ISOLINUX, used for booting from CD-ROM ISO 9660 filesystems.
- PXELINUX, used for booting from a network server using the Preboot Execution Environment (PXE) system.
- EXTLINUX, used to boot from Linux ext2/ext3/ext4 or btrfs filesystems.
- MEMDISK, used to boot older operating systems like MS-DOS from these media.
- Two separate menu systems.
- A development environment for additional modules.
Use
SYSLINUX and ISOLINUX
SYSLINUX is not normally used for booting full Linux installations since Linux is not normally installed on FAT filesystems. Instead, it is often used for boot or rescue floppy discs, Live USBs, or other lightweight boot systems. ISOLINUX is generally used by Linux Live CDs and bootable install CDs.
A minor complication is involved when booting from CD-ROM. The El Torito standard allows for booting in two different modes:
- Floppy emulation mode
- the boot information is stored in an image file of a FAT-formatted floppy disk, which is loaded from the CD and then behaves as a virtual floppy disk. This mode uses SYSLINUX.
- No emulation mode
- the boot information is stored directly on the CD (not in a floppy image). This mode uses ISOLINUX.
To have this choice is sometimes useful, since ISOLINUX is vulnerable to BIOS bugs; for that reason, it's handy to be able to boot using SYSLINUX. This mostly affects computers built before about 1999, and, in fact, for modern computers no emulation mode is generally the more reliable method.
The use of SYSLINUX for the creation of Live USBs is growing, though, and allowing the creation of distributions like Slax that allow users to try Linux with complete interactivity and persistent changes without needing to install it on their hard disk.
PXELINUX
PXELINUX is used in conjunction with a PXE compliant ROM on a network card. The PXE environment uses DHCP or BOOTP to enable basic TCP/IP networking, then downloads a bootstrap program via TFTP. This bootstrap program loads and configures a kernel according to directives that are also downloaded from the TFTP server.
Typically, PXELINUX is used for Linux installations from a central network server or for booting diskless workstations.
EXTLINUX
EXTLINUX is typically used as a general-purpose bootloader, similar to LILO or GRUB. Since Syslinux 4, EXTLINUX has been merged with SYSLINUX.
Hardware Detection Tool (HDT)
Since the 3.74 release, the Syslinux project hosts the Hardware Detection Tool (HDT) project. This tool is a Syslinux com32 module that displays low-level information for any x86 compatible system. It provides both a command-line interface and a semi-graphical menu mode for browsing. HDT is available as com32 file, a bootable ISO, a 2.88MB floppy disk.
See also
External links
- SYSLINUX website
- Download site
- SYSLINUX at Freecode
- Joseph's Site - PXELinux - Notes on getting it working
- Syslinux's dedicated com32/hdt directory
Categories:- Free boot loaders
- Linux software
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
