- Mindoro
-
Mindoro 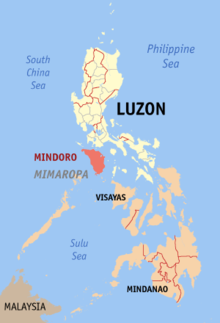
Map of MindoroGeography Location South East Asia Archipelago Philippine islands Major islands Luzon, Mindanao, Mindoro, Palawan Area 10,572 km2 (4,081.9 sq mi) Area rank 74th Highest elevation 2,582 m (8,471 ft) Highest point Halcon Country PhilippinesProvince Occidental Mindoro, Oriental Mindoro Largest city Calapan (pop. 105,910) Demographics Population 1,062,000 (as of 2000) Density 100.5 /km2 (260.3 /sq mi) Ethnic groups Mangyan, Tagalog Mindoro (Tagalog pronunciation: [mɪnˈdoɾo]) is the seventh-largest island in the Philippines. It is located off the coast of Luzon, and northeast of Palawan. The southern coast of Mindoro forms the northeastern extremum of the Sulu Sea.[1]
Contents
History
In past times, it has been called Ma-i or Mait by ancient Chinese traders and, by Spaniards, as Mina de Oro (meaning "gold mine") from where the island got its current name. The island was once a single province from 1920 to 1950 when it was divided into its two present-day provinces, Occidental Mindoro and Oriental Mindoro.
According to the late historian William Henry Scott,[2] an entry in the official history of the Sung Dynasty for the year 972 mentions Ma-i as a trading partner of China. Other Chinese records referring to Ma-i or Mindoro appear in the years that follow.
Prehispanic Source Materials enumerates the products that Mindoro traders exchanged with the Chinese as "beeswax, cotton, true pearls, tortoise shell, medicinal betelnuts and yu-ta [jute?] cloth" for Chinese porcelain, trade gold, iron pots, lead, colored glass beads and iron needles.
Economy
The economy of Mindoro is largely based on agriculture. Products consist of a wide variety of fruits, such as citrus, bananas, lanzones, rambutan, and coconuts, such cereals as rice and maize, sugar cane, peanuts, fish (catfish, milkfish, tilapia), livestock, and poultry. Logging and the mining of marble and copper also thrive.
Tourism is a lucrative business as well, with locations such as Apo Reef National Park, Lubang Island, Puerto Galera, Sabang Beach, and Mount Halcon. Puerto Galera's beaches are the island's most known tourist attraction and are widely visited.
Culture
The principal language in Mindoro is Tagalog, although in some parts it has been greatly influenced by the native Visayan and Mangyan languages. Mainstream Filipino and Taglish are, indeed, present in and around such areas as Puerto Galera, Pinamalayan, and Calapan City. Visayan and Mangyan languages, too, are spoken on the island, as are Ilokano and some foreign languages — e.g., English, Fukien, and, to a much lesser extent, Spanish.
The common religions on the island fall under Christianity. The religion of the indigenous Mangyan population is animism. Though they are into animism as a religion, the Catholic Church in some of Mindoro's parts is also active.
Other information
Mindoro is also home to the Tamaraw or Mindoro dwarf buffalo (Bubalus mindorensis), which is endemic to the island. The Tamaraw is a bovine related to the water buffalo and is an endangered species.
During World War II Mindoro was the site where Bill Frederick's aircraft and crew intercepted and participated in defeating a Japanese Naval Force preparing to attack the joint U.S. and Philippine Commonwealth armed Forces on Mindoro Island in the South Pacific. Flying through intense anti-aircraft fire, Frederick's aircraft, the Sticky Kitty, was credited with attacking below deck level and sinking a task force lead Japanese Cruiser. Frederick's aircraft was only one of eight aircraft that was available to defend this island garrison and installation. The aircraft flew repeated sorties during the night resulting in a successful defense of the island.
When the stronghold local Filipino troops and officers under the 4th, 5th, 41st, 42nd, 43rd, 45th, 46th and 47th Infantry Division of the Philippine Commonwealth Army and 4th Infantry Regiment of the Philippine Constabulary was sending the military special operations in the island province of Mindoro from December 1944 to August 1945 and helpful the local Mindoro guerrilla fighters and the U.S. and Australian troops to defeating the Japanese Imperial forces during the Battle of Mindoro in 1944 to 1945 and ended World War II.
The aftermath of the First Battle of Mindoro from the Philippine Commonwealth and Allied military forces in December 16, 1944, when the local Filipino soldiers of the 4th, 5th, 41st, 42nd, 43rd, 45th, 46th and 47th Infantry Division of the Philippine Commonwealth Army and 4th Infantry Regiment of the Philippine Constabulary during the Second Battle of Mindoro in January to August 1945 during the Second World War and helpful the local guerrilla resistance fighters around the capturing the islands of Mindoro included the province of Occidental Mindoro and Oriental Mindoro and defeated to fought against the Japanese Imperial forces. The casualties of the second battle of Mindoro in 1945 included over 34,000 Filipino troops and local recognized guerrillas killed and wounded in action and over 253,000 Japanese troops killed, wounded and captured in action.
Bibliography
- C.Michael Hogan. 2011. Sulu Sea. Encyclopedia of Earth. Eds. P.Saundry & C.J.Cleveland. Washington DC
References
External links
- "Map of Mindoro" showing towns and major mountain tops
- Mindorenyos - Connecting Mindoro People
- Online Community for Mindorenyos
Videos
Coordinates: 12°55′49″N 121°05′41″E / 12.93028°N 121.09472°E
Categories:- Islands of the Philippines
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.


