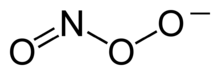
- Peroxynitrite
-
Peroxynitrite (sometimes called peroxonitrite) is the anion with the formula ONOO−. It is an unstable structural isomer of nitrate, NO3−, which has the same formula but a different structure. Although peroxynitrous acid is highly reactive, its conjugate base peroxynitrite is stable in basic solution.[1][2] It is prepared by the reaction of hydrogen peroxide with nitrite:
- H2O2 + NO2− → ONOO− + H2O
Peroxynitrite is an oxidant and nitrating agent. Because of its oxidizing properties, peroxynitrite can damage a wide array of molecules in cells, including DNA and proteins. Formation of peroxynitrite in vivo has been ascribed to the reaction of the free radical superoxide with the free radical nitric oxide[3][4]:
- ·O2− + ·NO → ONO2−
The resultant pairing of these two free radicals results in peroxynitrite, a molecule that is itself not a free radical, but that is a powerful oxidant.
In the laboratory, a solution of peroxynitrite can be prepared by treating acidified hydrogen peroxide with a solution of sodium nitrite, followed by rapid addition of NaOH. Its concentration is indicated by the absorbance at 302 nm (pH 12, ε302 = 1670 M−1 cm−1).[5]
Contents
As a nucleophile
ONOO− reacts nucleophilically with carbon dioxide. In vivo, the concentration of carbon dioxide is about 1 mM, and its reaction with ONOO− occurs quickly. Thus, under physiological conditions, the reaction of ONOO− with carbon dioxide to form nitrosoperoxycarbonate (ONOOCO2−) is by far the predominant pathway for ONOO−. ONOOCO2− homolyzes to form carbonate radical and nitrogen dioxide, again as a pair of caged radicals. Approximately 66% of the time, these two radicals recombine to form carbon dioxide and nitrate. The other 33% of the time, these two radicals escape the solvent cage and become free radicals. It is these radicals (carbonate radical and nitrogen dioxide) that are believed to cause peroxynitrite-related cellular damage.
Peroxynitrous acid
Main article: Peroxynitrous acidSee also
References
- ^ Holleman, A. F.; Wiberg, E. "Inorganic Chemistry" Academic Press: San Diego, 2001. ISBN 0-12-352651-5.
- ^ W. H. Koppenol
- ^ Pacher, P.; Beckman, J. S.; Liaudet, L.; “Nitric Oxide and Peroxynitrite: in Health and disease” Physiological Reviews 2007, volume 87(1), page 315-424. doi:10.1152/physrev.00029.2006 PMID 17237348
- ^ Csaba Szabó, Harry Ischiropoulos and Rafael Radi; Peroxynitrite: biochemistry,pathophysiology and development of therapeutics Nature Reviews Drug Discovery; 6, 662-680 (August 2007)
- ^ Beckman, J. S.; Koppenol, W. H. “Nitric Oxide, Superoxide, and Peroxynitrite: the Good, the Bad, and Ugly” American Journal of Physiology- Cell Physiology 1996, volume 271, page C1424-C1437.
Categories:- Oxoanions
- Atmospheric chemistry
- Toxins
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.