- Operation Sea Orbit
-
Operation Sea Orbit Part of Cold War (1962–1979) 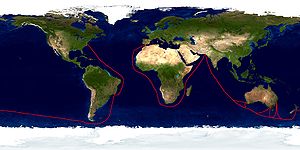
Operation Sea Orbit route.Type Naval surface warfare and naval air operations Location World-wide Planned by United States Navy Objective First circumnavigation of the world by nuclear-powered surface warships Date 31 July 1964 to 3 October 1964 Executed by Rear Admiral Bernard M. Strean, USN
Task Force One:
• USS Enterprise (CVAN-65)
• USS Long Beach (CGN-9)
• USS Bainbridge (DLGN-25)
• Carrier Air Wing Six (CVW-6)Outcome Mission successfully accomplished. Operation Sea Orbit was the 1964 around-the-world cruise of the United States Navy's Task Force One, consisting of USS Enterprise (CVAN-65), USS Long Beach (CGN-9), and USS Bainbridge (DLGN-25). This all-nuclear-powered unit steamed 30,565 miles unrefuelled around the world for sixty-five days.[1][2]
The cruise began on July 31 and ended on October 3.[1] The full itinerary comprised Rabat, Morocco; Dakar, Senegal; Freetown, Sierra Leone; Monrovia, Liberia; Abidjan, Ivory Coast; Nairobi, Kenya; Karachi, West Pakistan; Fremantle, Melbourne, and Sydney in Australia; Wellington, New Zealand; Buenos Aires, Argentina; Montevideo, Uruguay; and Santos, Rio De Janeiro and Recife in Brazil. Enterprise made only three port calls: Karachi, Sydney and Rio De Janeiro.
Operation Sea Orbit was the idea of Vice Admiral John S. McCain, Jr., who saw the exercise – which demonstrated how nuclear-powered ships could operate unfettered by shore logistical ties[2] – as a statement of American technical achievement similar to that of the coal-burning Great White Fleet in 1907-1909.[1] Enterprise was under the command of Captain Frederick H. Michaelis; the guided missile cruiser Long Beach under the command of Captain Frank H. Price, Jr.; and guided missile frigate Bainbridge under the command of Captain Hal C. Castle.[3][4][5]
The mission was commanded by Rear Admiral Bernard M. Strean.[1] The operation gained considerable attention overseas but less in the United States.[1]
Veterans of Operation Sea Orbit gathered on July 30, 2004, for a 40th anniversary reunion.[2] In 2011, Operation Sea Orbit was included in the Technology for the Nucleat Age: Nuclear Propulsion display for the Cold War exhibit at the U.S. Navy Museum in Washington, DC.[6]
See also
- Operation Sandblast
- 1966 Soviet submarine global circumnavigation
- Great White Fleet
Notes
- ^ a b c d e Baldwin, Hanson W. (1964-10-03). "Nuclear Task Force to End World Cruise Today". The New York Times. http://select.nytimes.com/mem/archive/pdf?res=F50D1EF93A5F147A93C1A9178BD95F408685F9.
- ^ a b c Thompson, Jason (2004-08-04). "Operation Sea Orbit Veterans Celebrate 40th Anniversary Aboard Big E". United States Navy. http://www.news.navy.mil/search/display.asp?story_id=14569.
- ^ "USS Enterprise (CVN-65): 1961-1965". Dictionary of American Naval Fighting Ships. Navy Department, Naval History & Heritage Command. http://www.history.navy.mil/danfs/e4/enterprise-viiia.htm. Retrieved 2010-02-24.
- ^ "USS Long Beach CGN-9". Dictionary of American Naval Fighting Ships. Navy Department, Naval History & Heritage Command. http://www.history.navy.mil/danfs/l8/long_beach-iii.htm. Retrieved 2010-02-24.
- ^ "USS Bainbridge CGN-25". Dictionary of American Naval Fighting Ships. Navy Department, Naval History & Heritage Command. http://www.history.navy.mil/danfs/b1/bainbridge-iv.htm. Retrieved 2010-02-24.
- ^ "Technology for the Nucleat Age: Nuclear Propulsion". Cold War Gallery. U.S. Navy Museum. 2011. http://usnavymuseum.org/Ex1_NuclearPropulsion.asp. Retrieved 2011-10-12.
References
- JO1 Jon Franklin, USN (January 1965). "Historic 'Show the Flag' Cruise". All Hands. BUPERS - U.S. Navy. http://www.navy.mil/media/allhands/acrobat/ah196501.pdf. Retrieved 2009-07-27.
This article includes text from the public domain Dictionary of American Naval Fighting Ships.
Categories:- History of the United States Navy
- Circumnavigators of the globe
- Non-combat military operations involving the United States
- 1964 in military history
- Nuclear history of the United States
- United States battle stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

