- Quinoxaline
-
Quinoxaline 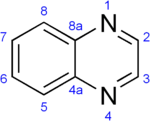
 QuinoxalineOther namesBenzo[a]pyrazine, Benzopyrazine, Benzoparadiazine, 1,4-Benzodiazine, Phenopiazine, Phenpiazine, Quinazine, Chinoxalin
QuinoxalineOther namesBenzo[a]pyrazine, Benzopyrazine, Benzoparadiazine, 1,4-Benzodiazine, Phenopiazine, Phenpiazine, Quinazine, ChinoxalinIdentifiers CAS number 91-19-0 
PubChem 7045 ChemSpider 21106470 
KEGG C18575 
ChEBI CHEBI:36616 
ChEMBL CHEMBL39444 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - c1cccc2nccnc12
Properties Molecular formula C8H6N2 Molar mass 130.15 g/mol Acidity (pKa) 0.60[1]  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references A quinoxaline, also called a benzopyrazine, in organic chemistry, is a heterocyclic compound containing a ring complex made up of a benzene ring and a pyrazine ring. It is isomeric with quinazoline, phthalazine and cinnoline.
Quinoxalines are used as dyes, pharmaceuticals and antibiotics such as echinomycin, levomycin and actinoleutin.
Some studies were carried out in order to explore the antitumoral properties of quinoxaline compounds:[2] Recently, quinoxalie and its analogues have been investigated as the catalyst's ligands:[3]
They can be formed by condensing ortho-diamines with 1,2-diketones. The parent substance of the group, quinoxaline, results when glyoxal is condensed with 1,2-diaminobenzene. Substituted derivatives arise when α-ketonic acids, α-chlorketones, α-aldehyde alcohols and α-ketone alcohols are used in place of diketones. Quinoxaline and its analogues may also be form by reduction of amino acids substituted 1,5-difluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene (DFDNB):[4]
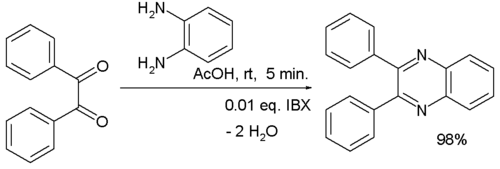
One study used 2-iodoxybenzoic acid (IBX) as a catalyst in the reaction of benzil with 1,2-diaminobenzene:[5]
References
- ^ Brown, H.C., et al., in Baude, E.A. and Nachod, F.C., Determination of Organic Structures by Physical Methods, Academic Press, New York, 1955.
- ^ Heterocyclic quinones.2.Quinoxaline-5,6-(and 5-8)-diones-Potential antitumoral agents. Jean Renault, Michel Baron, Patrick Mailliet & al., Eur. J. Med. Chem., 16, 6, 545-550, 1981
- ^ Regioselective Synthesis of Asymmetrically Substituted 2-Quinoxalinol Salen Ligands. Xianghong Wu, Anne E. V. Gorden. J. Org. Chem., 72, 8691-8699, 2007
- ^ Solution-phase reductive cyclization of 2-quinoxalinol analogs: Systematic study of parallel synthesis. Xiang-Hong Wu, Gang Liu, etal., Mol. Diver., 8, 165-147, 2004
- ^ Facile synthesis of quinoxaline derivatives using o-iodoxybenzoic acid (IBX) at room temperature (06-2190LP) Majid M. Heravi, Khadijeh Bakhtiari, Maryam H. Tehrani, Negar M. Javadi, and Hossien A. Oskooie ARKIVOC 2006 (xvi) 16-22 provisional link
See also
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.Categories:
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.Categories:- Quinoxalines
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.