- Crotonic acid
-
Crotonic acid 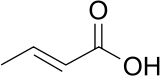
 (E)-but-2-enoic acidOther namestrans-2-butenoic acid
(E)-but-2-enoic acidOther namestrans-2-butenoic acid
beta-methylacrylic acid
3-methylacrylic acid
(E)-2-butenoic acidIdentifiers CAS number 107-93-7 
PubChem 637090 ChemSpider 552744 
DrugBank DB02074 ChEBI CHEBI:41131 
ChEMBL CHEMBL1213528 
Jmol-3D images Image 1
Image 2- C/C=C/C(O)=O
O=C(O)/C=C/C
Properties Molecular formula C4H6O2 Molar mass 86.09 g/mol Density 1.02 g/cm3 Melting point 70–73 °C
Boiling point 185–189 °C
Acidity (pKa) 4.69 [1] Hazards MSDS SIRI.org Related compounds Other anions crotonate Related carboxylic acids propionic acid
acrylic acid
butyric acid
succinic acid
malic acid
tartaric acid
fumaric acid
pentanoic acidRelated compounds butanol
butyraldehyde
crotonaldehyde
2-butanone acid (verify) (what is:
acid (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Crotonic acid, or trans-2-butenoic acid, is a short-chain unsaturated carboxylic acid, described by the formula CH3CH=CHCO2H. Crotonic acid is so named because it was erroneously thought to be a saponification product of croton oil. It crystallizes as needles from hot water.
Racemic threonine can be prepared from crotonic acid by alpha-functionalization using mercury(II) acetate.[2]
See also
- Crotyl
- Crotonaldehyde
- Crotyl alcohol
- Isocrotonic acid
- Methacrylic acid
References
- ^ Dawson, R. M. C., et al., Data for Biochemical Research, Oxford, Clarendon Press, 1959.
- ^ Carter, H. E.; West, H. D. (1955), "dl-Threonine", Org. Synth., http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=cv3p0813; Coll. Vol. 3: 813
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.Categories:
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.Categories:- Carboxylic acids
- C/C=C/C(O)=O
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
