- Mitochondrial myopathy
-
Mitochondrial myopathy Classification and external resources 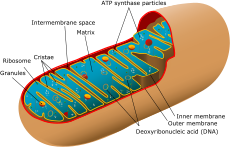
Simplified structure of a typical mitochondrionICD-10 G71.3 MeSH D017240 Mitochondrial myopathies are a type of myopathy associated with mitochondrial disease. On biopsy, the muscle tissue of patients with this disease category usually demonstrate 'ragged red' muscle fibers. These 'ragged red' fibers contain mild accumulations of glycogen and neutral lipids, and may show an increased reactivity for succinate dehydrogenase and a decreased activity for cytochrome c oxidase. Inheritance is maternal (non-Mendelian extranuclear). There are several subcategories of mitochondrial myopathies.
Treatment
Although no cure currently exists, there is some hope for a treatment for this whole class of hereditary diseases with the use of an embryotic mitochondrial transplant.[1]
Variations of the Disease
Symptoms of Mitochondrial myopathy include:
- Mitochondrial encephalomyopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like syndrome (MELAS)
- varying degrees of cognitive impairment and dementia
- lactic acidosis
- strokes
- transient ischemic attacks
- hearing loss
- dysmotility
- weight loss
- Myoclonic epilepsy and ragged-red fibers (MERRF)
- progressive myoclonic epilepsy
- clumps of diseased mitochondria accumulate in the subsarcolemmal region of the muscle fiber and appear as "ragged-red fibers" when muscle is stained with modified Gömöri trichrome stain
- short stature
- Kearns-Sayre syndrome (KSS)
- external ophthalmoplegia
- cardiac conduction defects
- Sensorineural hearing loss
- Chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia (CPEO)
- progressive ophthalmoparesis is the cardinal feature
- symptomatic overlap with many other mitochondrial myopathies
References
- ^ "Three-parent embryo formed in lab" (web). Scientists believe they have made a potential breakthrough in the treatment of serious disease by creating a human embryo with three separate parents.. BBC News. 5 February 2008. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/health/7227861.stm. Retrieved 2008-02-08.
Diseases of myoneural junction and muscle / neuromuscular disease (G70–G73, 358–359) Neuromuscular-
junction diseaseautoimmune (Myasthenia gravis, Lambert–Eaton myasthenic syndrome)Myopathy/
congenital myopathyMuscular dystrophy
(DAPC)ADAROther structuralOtherMitochondrial myopathyOtherNon-Mendelian inheritance: Mitochondrial diseases (277.87) Carbohydrate metabolism Primarily nervous system Myopathies No primary system Chromosomal Categories:- Myoneural junction and neuromuscular diseases
- Mitochondrial diseases
- Mitochondrial encephalomyopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like syndrome (MELAS)
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
