- Malondialdehyde
-
Malondialdehyde 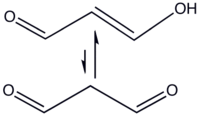 propanedial
propanedialIdentifiers CAS number 542-78-9 PubChem 10964 KEGG C19440 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - C(C=O)C=O
Properties Molecular formula C3H4O2 Molar mass 72.0636 g/mol Melting point 72 °C, 345 K, 162 °F
Related compounds Related alkenals Glucic acid
 (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Malondialdehyde is the organic compound with the formula CH2(CHO)2. The structure of this species is more complex than this formula suggests. This reactive species occurs naturally and is a marker for oxidative stress.
Contents
Structure and synthesis
Malondialdehyde mainly exists in the enol form:[1]
- CH2(CHO)2 → HOCH=CH-CHO
In organic solvents, the cis isomer is favored, whereas in water the trans isomer predominates.
Malondialdehyde is a highly reactive compound that is not typically observed in pure form. In the laboratory it can be generated in situ by hydrolysis of 1,1,3,3-tetramethoxypropane, which is commercially available.[1] It is easily deprotonated to give the sodium salt of the enolate (m.p. 245 °C).
Biochemistry
Reactive oxygen species degrade polyunsaturated lipids, forming malondialdehyde.[2] This compound is a reactive aldehyde and is one of the many reactive electrophile species that cause toxic stress in cells and form covalent protein adducts referred to as advanced lipoxidation end-products (ALE), in analogy to advanced glycation end-products (AGE).[3] The production of this aldehyde is used as a biomarker to measure the level of oxidative stress in an organism.[4][5]
Malondialdehyde reacts with deoxyadenosine and deoxyguanosine in DNA, forming DNA adducts, the primary one being M1G, which is mutagenic.[6] The guanidine group of arginine residues condense with MDA to give 2-aminopyrimidines.
Human ALDH1A1 aldehyde dehydrogenase is capable of oxidising malondialdehyde.
Analysis
MDA and other "thiobarbituric reactive substances" (TBARS) condense with two equivalents of thiobarbituric acid to give a fluorescent red derivative that can be assayed spectrophotometrically.[1][7] 1-Methyl-2-phenylindole is an alternative more selective reagent.[1]
Hazards
MDA is reactive and potentially mutagenic.
Pathology
Corneas of patients suffering from keratoconus and bullous keratopathy have increased levels of MDA, according to one study.[8] MDA also can be found in tissue sections of joints from patients with osteoarthritis.[9]
See also
References
- ^ a b c d V. Nair, C. L. O'Neil, P. G. Wang “Malondialdehyde” Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis, 2008, John Wiley & Sons, New York. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rm013.pub2 Article Online Posting Date: March 14, 2008
- ^ Pryor WA, Stanley JP (1975). "Letter: A suggested mechanism for the production of malondialdehyde during the autoxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids. Nonenzymatic production of prostaglandin endoperoxides during autoxidation". J. Org. Chem. 40 (24): 3615–7. doi:10.1021/jo00912a038. PMID 1185332.
- ^ Farmer EE, Davoine C (2007). "Reactive electrophile species". Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 10 (4): 380–6. doi:10.1016/j.pbi.2007.04.019. PMID 17646124.
- ^ Moore K, Roberts LJ (1998). "Measurement of lipid peroxidation". Free Radic. Res. 28 (6): 659–71. doi:10.3109/10715769809065821. PMID 9736317.
- ^ Del Rio D, Stewart AJ, Pellegrini N (2005). "A review of recent studies on malondialdehyde as toxic molecule and biological marker of oxidative stress". Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 15 (4): 316–28. doi:10.1016/j.numecd.2005.05.003. PMID 16054557.
- ^ Marnett LJ (1999). "Lipid peroxidation-DNA damage by malondialdehyde". Mutat. Res. 424 (1-2): 83–95. doi:10.1016/S0027-5107(99)00010-X. PMID 10064852.
- ^ http://www.amdcc.org/shared/showFile.aspx?doctypeid=3&docid=33
- ^ Buddi R, Lin B, Atilano SR, Zorapapel NC, Kenney MC, Brown DJ (March 2002). "Evidence of oxidative stress in human corneal diseases". J. Histochem. Cytochem. 50 (3): 341–51. PMID 11850437. http://www.jhc.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=11850437.
- ^ Tiku ML, Narla H, Jain M, Yalamanchili P (2007). "Glucosamine prevents in vitro collagen degradation in chondrocytes by inhibiting advanced lipoxidation reactions and protein oxidation". Arthritis Res. Ther. 9 (4): R76. doi:10.1186/ar2274. PMC 2206377. PMID 17686167. http://arthritis-research.com/content/9/4/R76.
Categories:- Aldehydes
- Biochemistry stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
